Patterns in Mathematics Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Mathematics? |

|
| Patterns in Numbers |

|
| Visualising Number Sequences |

|
| Relations among Number Sequences |

|
| Patterns in Shapes |

|
| Relation to Number Sequences |

|
| Let's Practice! |

|
| Summary |

|
What is Mathematics?
Mathematics is largely about identifying patterns and understanding the reasons behind them. These patterns are not just limited to textbooks; they can be found all around us—in the natural world, in everyday activities like cooking or playing sports, and even in the way the planets move in the sky.
For example, the week follows a pattern: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday. After Sunday, the pattern starts again with Monday.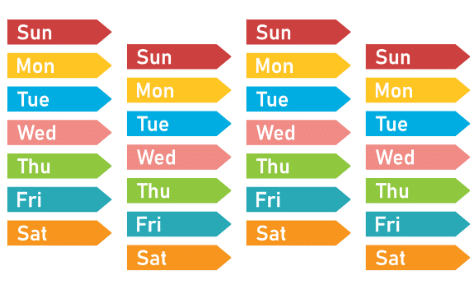 Days of Week making Pattern
Days of Week making Pattern
Mathematicians often describe mathematics as both an art and a science because discovering and explaining these patterns requires creativity as well as logical thinking.
It's important to remember that mathematics doesn't just focus on identifying patterns; it also seeks to explain them. These explanations can often be applied in various ways beyond the situation in which they were first discovered, contributing to advancements that benefit society as a whole.
Patterns in Numbers
Number patterns are one of the simplest and most interesting parts of math. Imagine counting: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4… This is a basic pattern of whole numbers. The study of these number patterns is called number theory.
Some common number sequences include:
Each of these sequences has a specific pattern or rule that determines the next number. For example, in the sequence of odd numbers, you add 2 to get the next number (1 + 2 = 3, 3 + 2 = 5, and so on).
Mathematicians love exploring these patterns, especially in number sequences, which are just ordered lists of numbers that follow a rule. These sequences are some of the coolest patterns you’ll find in math!
Visualising Number Sequences
Number sequences can often be easier to understand when we use pictures. By visualizing them, we can see patterns more clearly. For example:
- Square Numbers: These can be visualized as dots arranged in a perfect square. For example, 4 can be seen as a 2x2 square of dots
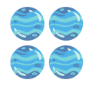 , and 9 as a 3x3 square of dots.
, and 9 as a 3x3 square of dots.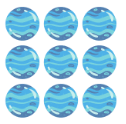
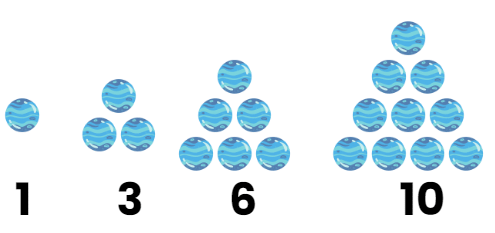
- Triangular Numbers: These can be represented as dots forming a triangle. The first few triangular numbers are 1, 3, 6, 10, and 15, corresponding to dots forming triangles with 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 rows.
- Cube Numbers: These are represented as cubes coming together to form cubes, The first few numbers are 1,8,27,etc.
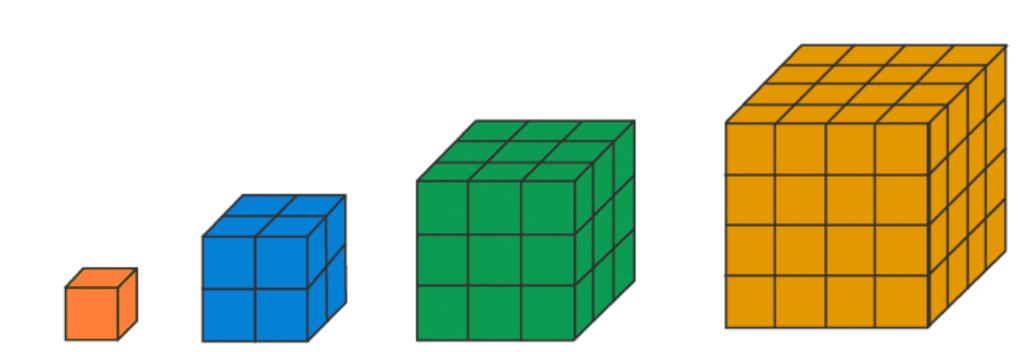
- Some of the few more sequences are:
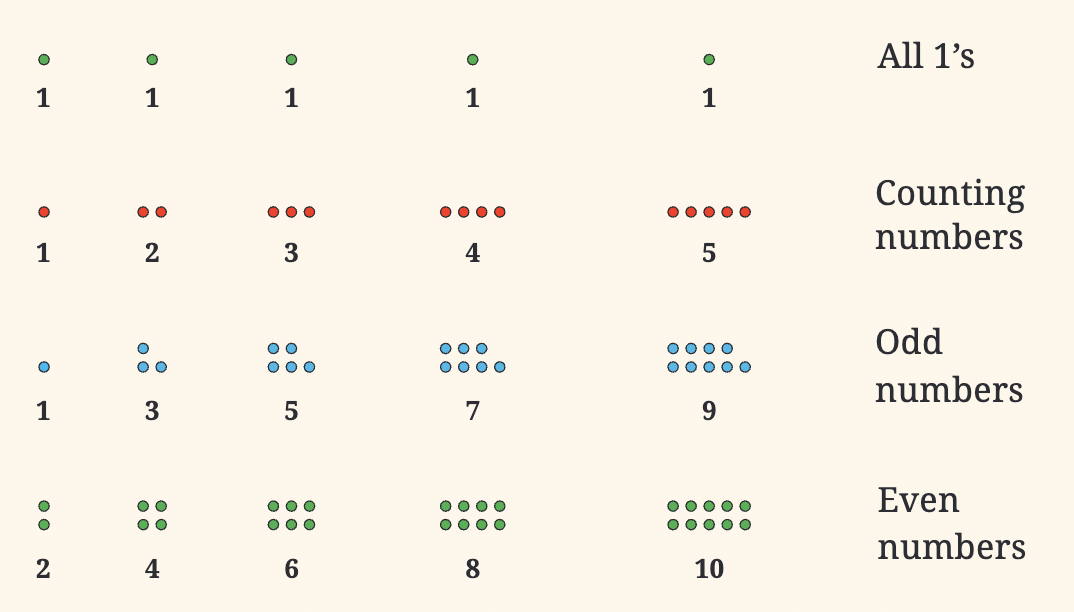
Visualizing these sequences allows us to see the relationship between the numbers more clearly. For example, 36 is a special number because it can be both a square (6x6) and a triangular number.
Relations among Number Sequences
Sometimes, different number sequences are related to each other in surprising ways. When you start adding odd numbers in sequence, like 1, 1+3, 1+3+5, and so on, something interesting happens: the result is always a square number. For example:
- 1 = 1
- 1 + 3 = 4
- 1 + 3 + 5 = 9
- 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 16
This pattern happens every time, and it’s no coincidence. The reason behind this is visualized in the image you provided. The image shows how the sum of odd numbers builds up into a square shape.
- Starting Point (1): The first dot represents the number 1.
- Adding 3: Then, by adding 3 dots, you can form a 2x2 square.
- Adding 5: Adding 5 more dots creates a 3x3 square.
- Adding 7: Add 7 dots to form a 4x4 square.
- Adding 9: Finally, adding 9 dots forms a 5x5 square.
Each time you add the next odd number, it forms a layer around the previous square, making a larger square. This is why the sum of the first few odd numbers always results in a square number. You can visually image it like following: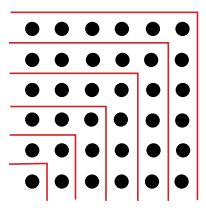
Sum of First 10 or 100 Odd Numbers
Using this method, you can easily visualize that the sum of the first 10 odd numbers will form a 10x10 square, and the sum of the first 100 odd numbers will form a 100x100 square.
- First 10 odd numbers sum:
- First 100 odd numbers sum:
This method of visualization makes it easier to understand and calculate the sum of odd numbers, and it shows how these sequences are related to square numbers.
Patterns in Shapes
In mathematics, just like with numbers, there are patterns that occur with shapes. These patterns can be found in shapes that exist in one, two, or even three dimensions, and they are studied in a branch of mathematics called geometry.
Shape Sequences
One of the key concepts in geometry is the idea of shape sequences. These are ordered lists of shapes that follow a certain pattern or rule. Let’s look at some examples from the image you provided:
Regular Polygons:
- This sequence shows polygons that have equal sides and angles. The sequence starts with a triangle (3 sides) and moves to a quadrilateral (4 sides), then to a pentagon (5 sides), and so on. Each step in the sequence adds one more side to the shape.
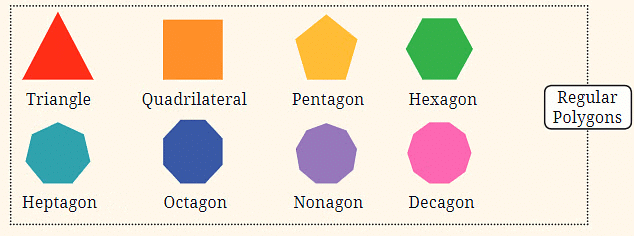
- This sequence shows polygons that have equal sides and angles. The sequence starts with a triangle (3 sides) and moves to a quadrilateral (4 sides), then to a pentagon (5 sides), and so on. Each step in the sequence adds one more side to the shape.
Complete Graphs:
- These are sequences of graphs (a collection of points connected by lines) where each point is connected to every other point. The sequence starts with two points connected by a line, then three points forming a triangle, four points forming a square with diagonals, and so on. The number of connections increases as the sequence progresses.
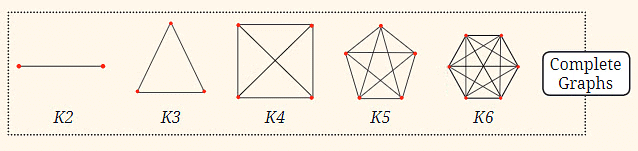
- These are sequences of graphs (a collection of points connected by lines) where each point is connected to every other point. The sequence starts with two points connected by a line, then three points forming a triangle, four points forming a square with diagonals, and so on. The number of connections increases as the sequence progresses.
Stacked Squares:
- This sequence shows squares stacked on top of each other, starting from a single square and growing into a larger square made up of smaller squares. As you move along the sequence, the total number of squares increases in a grid pattern.
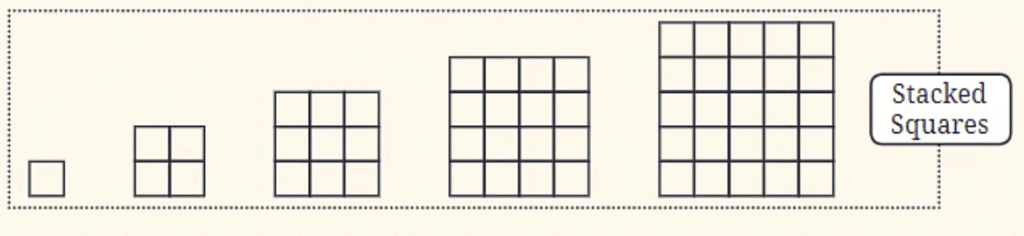
- This sequence shows squares stacked on top of each other, starting from a single square and growing into a larger square made up of smaller squares. As you move along the sequence, the total number of squares increases in a grid pattern.
Stacked Triangles:
- Similar to the stacked squares, this sequence involves triangles stacked to form larger triangles. The sequence starts with a single triangle and grows by adding more rows of smaller triangles, forming a larger triangle.
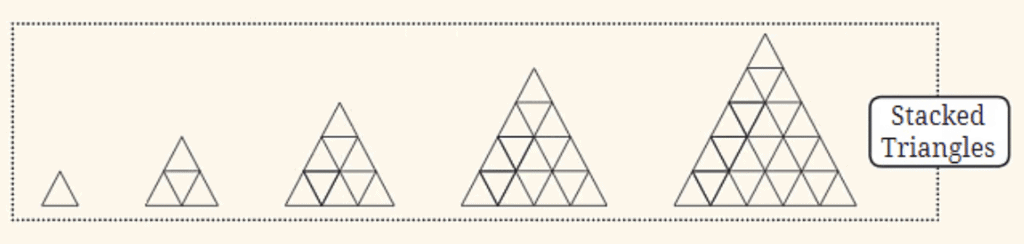
- Similar to the stacked squares, this sequence involves triangles stacked to form larger triangles. The sequence starts with a single triangle and grows by adding more rows of smaller triangles, forming a larger triangle.
Koch Snowflake:
- This is a famous fractal shape that starts with a simple triangle. At each step in the sequence, smaller triangles are added to each side, creating a more complex pattern that resembles a snowflake.
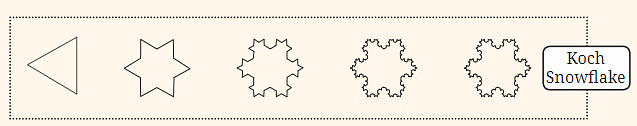
- This is a famous fractal shape that starts with a simple triangle. At each step in the sequence, smaller triangles are added to each side, creating a more complex pattern that resembles a snowflake.
These shape sequences are examples of how patterns can be found not just in numbers but also in the geometry of shapes.
Which of the following shows a pattern made with shapes (shape sequence)?
Relation to Number Sequences
Shape sequences and number sequences are often connected in interesting ways. Understanding these relationships can make it easier to study both types of sequences.
Example: Regular Polygons and Counting Numbers
Let's start with the shape sequence of Regular Polygons. In this sequence, each shape is defined by the number of sides it has. The sequence begins with:
- A triangle (3 sides)
- A quadrilateral (4 sides)
- A pentagon (5 sides)
- And so on...

The number of sides follows the counting numbers starting from 3: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, etc. That’s why these shapes are named accordingly, like triangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), and so on. The term "regular" indicates that all sides are of equal length and all angles are equal, meaning the shape is perfectly symmetrical.
Relationships in Other Shape Sequences
Other shape sequences also have fascinating connections to number sequences. For example:
- Stacked Squares can be related to square numbers (1, 4, 9, 16, ...), where each step in the sequence adds another row and column of squares.
- Complete Graphs relate to the number of connections or edges, which increases in a pattern similar to triangular numbers.
Let's Practice!
Question: What would you call the following sequence of numbers?
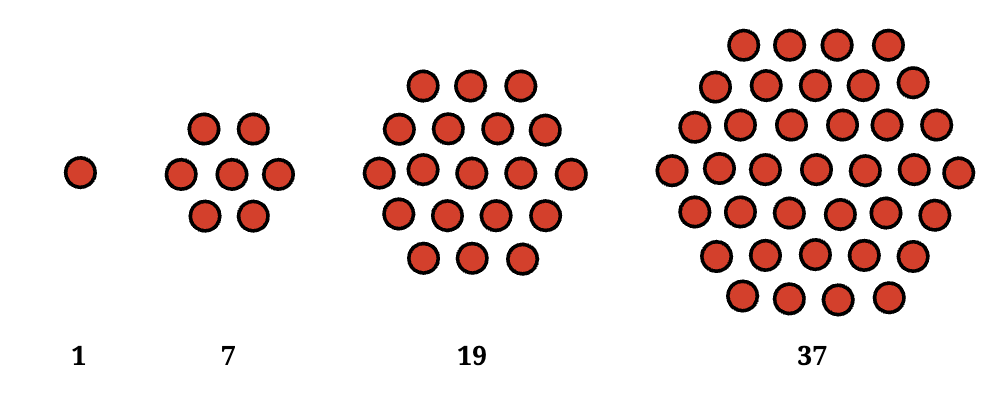
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: They are called hexagonal numbers!
Hexagonal numbers are special numbers that represent dots arranged in the shape of a hexagon. The pattern begins with a single central dot, and each new layer adds a ring of dots around it, forming a larger hexagon. The number of dots in each layer increases by 6, creating a sequence like 1, 7, 19, 37, and so on.
Question: Can you recognize the pattern in this sequence?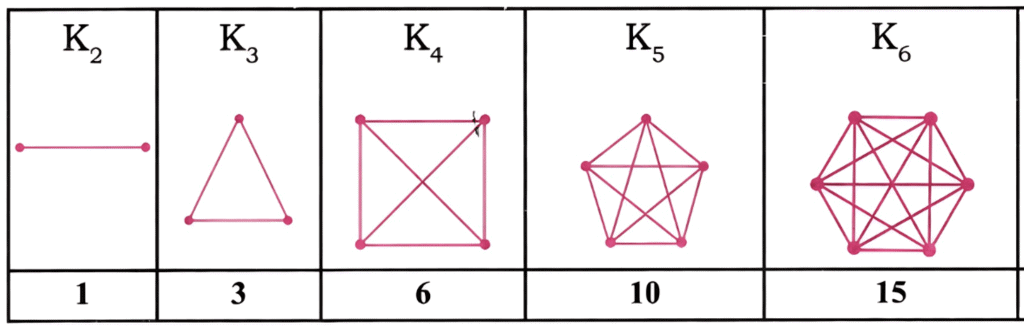
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
Here number of lines is as follows:
K2 = 1
K3 = 3
K4 = 6
K5 = 10
K6 = 15
The series formed is 1, 3, 6, 10, 15,…….
Hence it is a triangular number sequence.
Summary
- Mathematics can be seen as the study of patterns and the reasoning behind their existence.
- One of the fundamental patterns in mathematics is number sequences.
- Key examples of number sequences include counting numbers, odd and even numbers, square numbers, triangular numbers, cube numbers, Virahanka numbers, and powers of 2.
- Number sequences often have fascinating connections. For instance, summing the sequence of odd numbers starting from 1 results in square numbers.
- Using visual representations can aid in understanding number sequences and their interconnections.
- Another fundamental mathematical pattern is shape sequences.
- Notable examples of shape sequences include regular polygons, complete graphs, stacked triangles and squares, and iterations of the Koch snowflake.
Shape sequences often exhibit intriguing relationships with number sequences.
By recognizing these connections between shapes and numbers, you can gain a deeper understanding of both the patterns in geometry and in arithmetic. Understanding these patterns and relationships is a big part of what makes mathematics both challenging and beautiful!
FAQs on Patterns in Mathematics Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the basic concepts of patterns in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How can number sequences be visualized effectively? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between number sequences and patterns in shapes? |  |
| 4. How can students practice identifying patterns in mathematics? |  |
| 5. Why are patterns important in the study of mathematics? |  |
















