Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Notes - Political Parties
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Why do We Need Political Parties? |

|
| How many parties should we have? |

|
| National Parties |

|
| State Parties |

|
| Challenges to Political Parties |

|
| How can Parties be Reformed? |

|
Introduction
Political parties are organized groups of individuals who come together with a shared set of beliefs, values, and goals, aiming to influence or control government policy and decision-making.
 Political parties are fundamental to the operation of modern democracies. They are instrumental in shaping political structures, influencing government policies, and representing various social interests.
Political parties are fundamental to the operation of modern democracies. They are instrumental in shaping political structures, influencing government policies, and representing various social interests.
In this chapter, we will:
- Explore the Role of Political Parties: Understand why political parties are crucial in a democratic system.
- Examine the Ideal Number of Parties: Discuss how many parties are beneficial for a democracy.
- Analyze Political Parties in India: Look at the national and regional parties, their functions, and their impact on the political landscape.
- Address Challenges: Identify issues faced by political parties and consider potential reforms for improvement.
Why do We Need Political Parties?
- Political parties are highly visible in democracies and are often synonymous with democracy for many citizens.
- In remote and less educated areas, people may not be familiar with the Constitution or government structure but are likely to recognize political parties.
- Despite their visibility, political parties often face criticism and are blamed for issues within democracy and political life.
- They are frequently associated with social and political divisions.
The Role of Political Parties
- Representation: Political parties represent diverse social groups and interests within a democracy.
- Policy Formation: They develop and propose policies that address public issues and reflect their ideologies.
- Leadership and Elections: Parties select and support candidates for public office, influencing the formation of governments.
- Governance: Once in power, they implement policies and manage government functions.
- Choice for Voters: They provide voters with options, allowing them to support the party that aligns with their views.
Historical Context: About a hundred years ago, political parties were less common globally. Today, the majority of democracies around the world feature political parties, indicating their growing importance and omnipresence.
 Symbols of Different Political Parties in India
Symbols of Different Political Parties in India
Meaning
A Political Party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
- They come together with a shared vision to promote the collective good through agreed-upon policies and programs.
- Policy Promotion: Parties advocate for policies they believe will benefit society as a whole.
- Electoral Success: They aim to win elections to implement their policies and gain popular support.
- Diverse Views: Different parties represent varying perspectives on what is beneficial for society, reflecting fundamental political divisions.
- Partisanship: Parties are associated with particular parts of society, based on their policies and the interests they represent.
Components of a Political Party:
1. Leaders: Individuals who guide the party's direction and make strategic decisions.
2. Active Members: Party members who are actively involved in the party’s activities and operations.
Functions
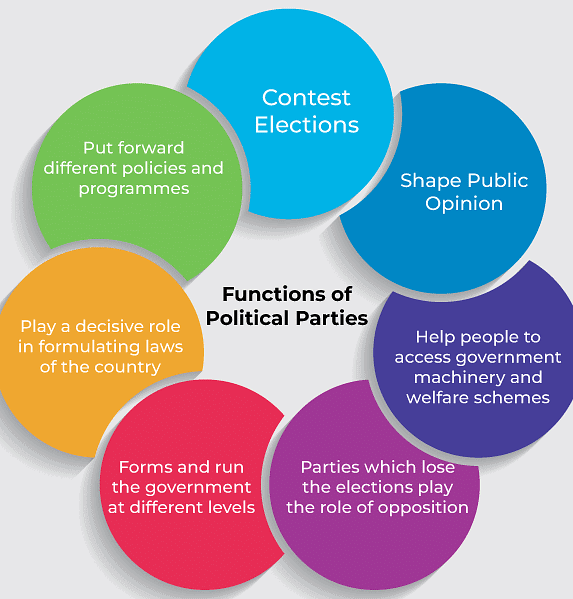
1. Parties contest elections:
- Political parties select and put forward candidates for elections.
- This allows voters to have a choice between different parties and their candidates.
- Parties select and field candidates for elections. Candidate selection methods differ: in some places, members choose candidates (e.g., USA), while in others, party leaders make the selection (e.g., India).
2. Parties present policies and programmes:
- Parties present policies and programs, consolidating diverse views into coherent platforms.
- This helps to provide a direction for the formulation of government policies.
- Parties consolidate a wide range of opinions into a few basic positions that they support.
- Voters can then choose which party's policies align with their own views.
3. Parties play a role in lawmaking:
- While laws are formally debated and passed in the legislature, most members of the legislature belong to political parties.
- Therefore, party direction and leadership often influence the voting decisions of individual lawmakers, regardless of their personal opinions.
4. Parties form and run governments:
- Political parties are responsible for forming and running governments.
- The political executive, which makes big policy decisions, is typically composed of members from political parties.
- Parties recruit and train leaders, who are then appointed as ministers to run the government according to the party's agenda and policies.
5. Parties act as the opposition:
- Parties that do not win elections often take on the role of the opposition.
- They voice different views and criticize the government for its failures or wrong policies.
- Opposition parties serve as a check on the ruling party, mobilize opposition to the government, and offer alternative perspectives to policies and governance.
6. Parties shape public opinion:
- Political parties raise and highlight important issues in society.
- They have a large membership and network of activists, which allows them to mobilize support and launch movements for resolving societal problems.
- Opinions in society often align with the positions taken by political parties, as parties influence public discourse and shape public opinion.
7. Parties provide access to government machinery and welfare schemes:
- Parties serve as a link between the general public and the government machinery.
- Ordinary citizens find it easier to approach a local party leader for assistance or information about government programs and welfare schemes, rather than directly approaching government officials.
Necessity
Political parties are essential for the functioning of modern democracies for several reasons:

1. Coordination and Promise:
- Without parties, elections would be contested by independent candidates with no unified policy platform.
- Parties offer a structured way to make and commit to promises about major policy changes, ensuring that the government has a clear direction and accountability.
2. Government Formation and Accountability:
- In the absence of parties, forming a stable government would be challenging, and its effectiveness could be uncertain.
- Elected representatives would be accountable only for local issues, with no organized approach to national governance.
3. Representation and Organization:
- Even in non-party-based elections (e.g., panchayats), factions or panels often form, mimicking party dynamics.
- This shows that even in informal settings, people organize themselves into groups with common agendas, reflecting the role of parties.
4. Handling Complex Societies:
- As societies grow larger and more complex, they need mechanisms to aggregate and present diverse views.
- Parties help in gathering various perspectives, forming a representative government, and ensuring effective policy-making.
5. Support and Restraint:
- Parties support or restrain the government, influencing policy decisions and providing checks and balances.
- They are crucial for ensuring that different viewpoints are considered in governance.
Ruling Party: Political party that runs government.
How many parties should we have?
- In a democracy, any group of citizens is free to form a political party, leading to a plethora of political parties in each country.
- India, for instance, boasts over 750 registered parties, though only a handful are significant contenders during elections.
- The effectiveness of parties in winning elections and forming a government raises the question of the ideal number of major parties for a democracy.
One-Party Systems:
- Some countries operate under one-party systems where only one party controls and governs, as seen in China with the Communist Party.
 One Party System resembles Dictatorship
One Party System resembles Dictatorship
- Despite the theoretical freedom to establish parties, the lack of free competition renders such systems undemocratic.
Two-Party Systems:
- In certain nations like the United States and the United Kingdom, power typically alternates between two main parties, with other parties contesting for seats.
- This structure allows the two main parties a substantial chance of securing a majority to form a government.
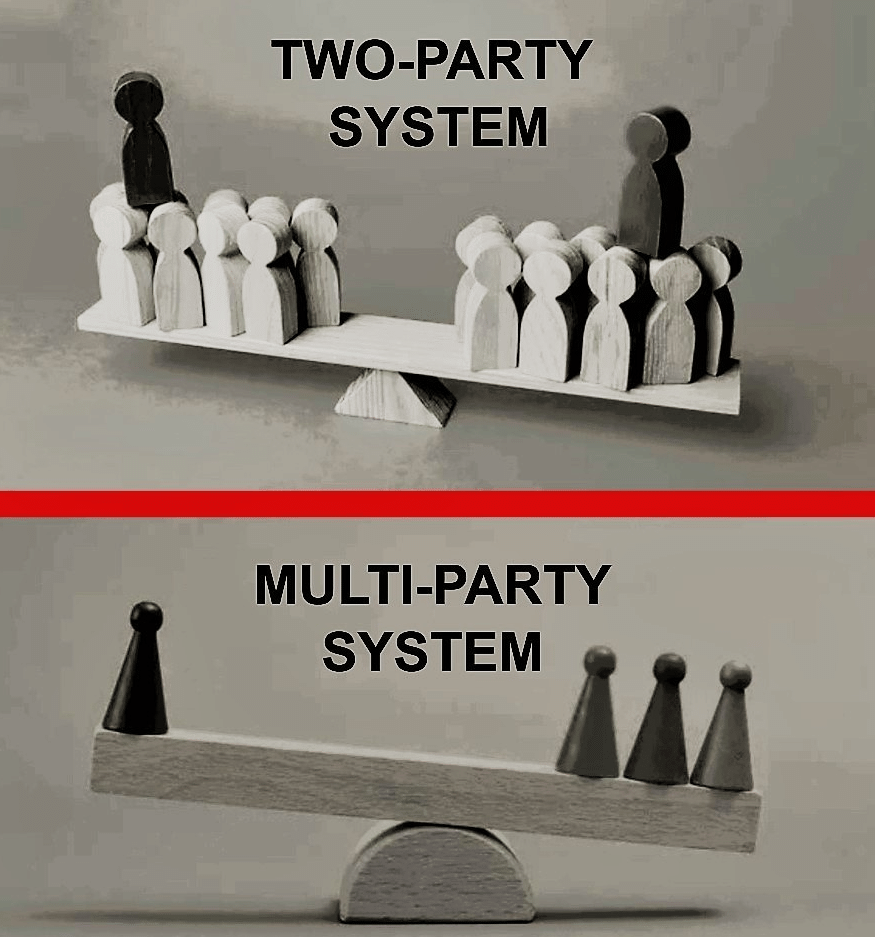
Multi-Party Systems:
- In countries where power distribution involves various parties, either independently or through alliances, a multi-party system prevails, as seen in India.
- Coalitions and alliances among multiple parties, like the National Democratic Alliance and the United Progressive Alliance in India, occur to contest elections and gain power.
- While multi-party systems may seem chaotic and potentially unstable, they facilitate diverse interests and opinions in governance.
Choosing the Ideal System:
- There is no one-size-fits-all answer to which system is superior as each country's political landscape is influenced by unique societal, regional, and historical factors.
- Various systems evolve over time based on a nation's circumstances, with no single system being universally applicable.
National Parties
- In democracies with a federal system, political parties typically fall into two categories: those that operate solely within a single federal unit and those that are active across multiple or all units of the federation.
- In India, there are country-wide parties known as "national parties" which have units in various states. These parties generally follow the same policies, programs, and strategies decided at the national level.
- All political parties in India must register with the Election Commission, which treats all parties equally but provides special facilities to large and established parties.
- The Election Commission has specific criteria for a party to be recognized, such as securing at least six percent of the total votes and winning a certain number of seats in elections.
- A party that meets the criteria in an election for a state legislative assembly is recognized as a state party, while a party that meets the criteria in Lok Sabha or assembly elections in four states is recognized as a national party.
Major National Parties in India
According to this classification, there are six recognized national parties in the country as per notification of the Election Commission of India issued in 2023.
 National Parties in India
National Parties in India
1. Aam Aadmi Party (AAP)
- Established on 26 November 2012 after the 2011 movement against corruption. The party was created with a focus on responsibility, honest governance, openness, and effective management.

- Early Progress: Soon after its inception, AAP became the second largest party in the Delhi Legislative Assembly elections. It later formed a government with the backing of the Indian National Congress (INC).
- Expansion: Following the 2022 Gujarat Legislative Assembly elections, AAP also became a significant player in Gujarat politics, marking its presence as the third front.
- Present Status: Currently, AAP is in power in Punjab and Delhi, governing these states.
- National Presence: In the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, AAP secured a seat in the Lok Sabha, reflecting its national ambitions and reach.
2) Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
- Formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram. Aims to represent and gain power for the bahujan samaj, which includes dalits, adivasis, OBCs, and religious minorities.
- Derives inspiration from the thoughts and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar Ramaswami Naicker, and Babasaheb Ambedkar.

- Advocates for the rights and well-being of dalits and oppressed individuals.
- Primarily operates in Uttar Pradesh and holds a significant presence in neighboring regions like Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Delhi, and Punjab.
- Has formed governments in Uttar Pradesh multiple times, aligning with different political parties as needed.
- In the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, the BSP garnered approximately 3.63% of the votes and secured 10 seats in the Lok Sabha.
3) Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
- Founded in 1980 by reviving the former Bharatiya Jana Sangh, established by Syama Prasad Mukherjee in 1951.
- Goal: To construct a robust and contemporary India by taking inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values, along with Deendayal Upadhyaya’s concepts of integral humanism and Antyodaya.

- Idea: Cultural nationalism (or 'Hindutva') is a significant aspect in its view of Indian nationhood and politics.
- Objectives: Advocates for complete territorial and political integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India, a uniform civil code for all citizens regardless of religion, and a prohibition on religious conversions.
- Expansion: Witnessed a substantial rise in its support during the 1990s. Initially concentrated in the north and west, as well as urban regions, the party broadened its base to include the south, east, the north-east, and rural areas.
- Achievements: Assumed power in 1998 as the head of the National Democratic Alliance (NDA), comprising various regional parties. Emerged as the largest party with 303 members in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections. Currently leads the ruling NDA government at the Centre.
4) Communist Party of India – Marxist (CPI-M)
- Founded in 1964. Believes in Marxism-Leninism.
Supports socialism, secularism, and democracy and opposes imperialism and communalism.

- Accepts democratic elections as a useful and helpful means for securing the objective of socio-economic justice in India.
- Enjoys strong support in West Bengal, Kerala, and Tripura.
- The party was in power in West Bengal without a break for 34 years.
- In the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, it won about 1.75 per cent of votes and 3 seats.
5) Indian National Congress (INC)
- Popularly known as the Congress Party.
- One of the oldest parties globally, established in 1885 with numerous divisions.

- Significantly influential in Indian politics post-independence, both nationally and at state levels.
- Guided by Jawaharlal Nehru, aimed to shape a modern, inclusive democratic nation.
- Ruled the country from 1977 to 1980 and then from 1980 to 1989.
- Post 1989, faced a decline in support but remains a substantial presence nationwide.
- Identified as a centrist party, upholding secularism and advocating for the welfare of marginalized communities.
- Endorses new economic policies with a focus on human-centric approaches.
- Led the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) government from 2004 to 2019.
- In the 2019 Lok Sabha election, secured 19.5% of the votes and 52 seats.
6) Nationalist People's Party (NPP)
- Formed in July 2013 under the leadership of P.A Sangma.
- NPP is the first political party from North East India to achieve national party status.

- It believes in the diversity of India and understands that different regions face unique development challenges.
- The main idea of the party is to provide education and jobs to everyone and empower all parts of society.
- NPP has formed the government in Meghalaya and has a presence in various North Eastern States.
- In the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, NPP won one seat in the Lok Sabha.
State Parties
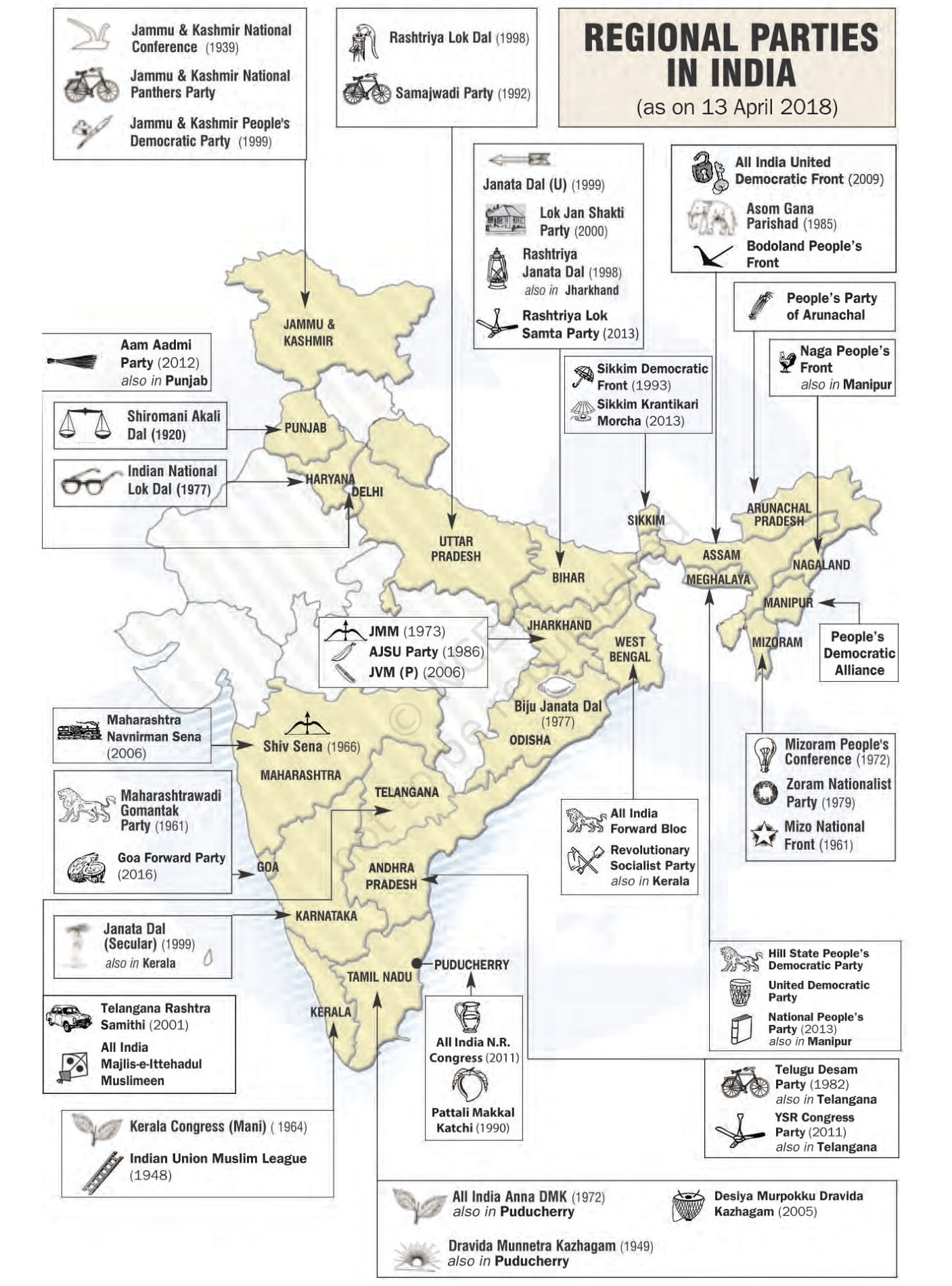
- Apart from the national parties, most major parties in the country are classified as 'State parties' by the Election Commission.
- These State parties are often referred to as regional parties, but they may not necessarily have a regional ideology or outlook.
- Some of these parties, like the Samajwadi Party and Rashtriya Janata Dal, have a national level political organization with units in multiple states.
- Certain State parties, such as Biju Janata Dal, Sikkim Democratic Front, Mizo National Front, and Telangana Rashtra Samithi, are conscious of their state identity.
- Over the past three decades, the number and strength of these State parties have increased, making the Indian Parliament more politically diverse.
- No single national party has been able to secure a majority in the Lok Sabha without forming alliances with State parties, until 2014.
- This has contributed to the strengthening of federalism and democracy in the country.
Challenges to Political Parties
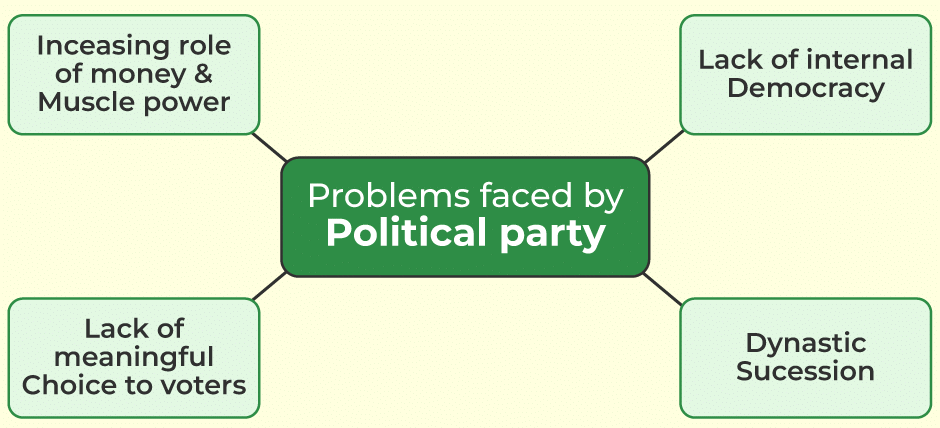
1. Lack of Internal Democracy
- One of the main challenges faced by political parties is the lack of internal democracy.
- Many parties concentrate power in a few leaders at the top, resulting in a lack of transparency and decision-making power for ordinary members.
- Leaders assume greater power and make decisions on behalf of the party, making it difficult for those who disagree with the leadership to continue in the party.
2. Limited Opportunities for Ordinary Workers to Rise to the Top in a Party
- Leaders often favor people close to them or their family members, leading to unfair advantages and a lack of adequate experience or popular support in positions of power.
3. Growing Role of Money and Muscle Power in Parties
- Parties tend to nominate candidates who can raise large amounts of money, leading to the influence of rich individuals and companies on party policies and decisions.
- There is concern about the increasing influence of rich individuals and big companies in democratic politics.
4. Parties often do not Provide a Meaningful Choice to Voters
- Ideological differences among parties have declined in recent years, making it difficult for voters to choose between significantly different policies or leaders.
- The same set of leaders often shift from one party to another, limiting the possibility of electing different leaders.
a) Lack of transparency and decision-making power for ordinary members b) Growing role of money and muscle power in parties c) Limited opportunities for ordinary workers to rise to the top in a party d) Parties often do not provide a meaningful choice to voters
How can Parties be Reformed?
Political parties face significant challenges, and reforms are necessary to address these issues.
- The key question is whether parties are willing to reform and, if not, whether they can be compelled to do so.
- In democracies, political leaders, who often resist change, hold the power to make decisions.
However, recent efforts and suggestions in India have been made to reform political parties:
1. Anti-Defection Law:
- A constitutional amendment prevents elected MLAs and MPs from switching parties, curbing defection.

- While this has reduced defections, it also limits dissent, as MPs and MLAs must adhere to party leadership.
2. Affidavit Requirement:
- The Supreme Court mandates that election candidates disclose their assets and any pending criminal cases through affidavits.
- This has increased transparency, though there is no mechanism to verify the accuracy of the information.
Affidavit: A signed document submitted to an officer, where a person makes a sworn statement regarding her personal information.
3. Election Commission Orders:
- Political parties are required to hold internal elections and file income tax returns.
- Although this is sometimes just a formality, it has encouraged some level of internal democracy.
4. Regulation of Internal Party Affairs: Proposals include laws requiring parties to maintain membership registers, adhere to their constitutions, establish independent authorities for disputes, and hold open elections for top positions.
5. Gender Quotas: A proposed mandate for political parties to allocate at least one-third of their election tickets to women and ensure representation in decision-making bodies.
6. State Funding of Elections: The government could provide financial support for election expenses, either in kind or based on a party's previous electoral performance.
While these suggestions have not been universally accepted, they could lead to improvements if implemented. However, there is caution against over-regulating political parties, as it may lead to legal evasion.
Defection: Changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected (to a legislative body) to a different party.
Alternative Approaches:
1. Public Pressure: Citizens, pressure groups, movements, and the media can exert pressure on political parties to reform by using petitions, publicity, and agitation.
2. Public Participation: For meaningful political reform, more citizens need to actively participate in politics rather than merely criticize it. Improving democracy requires greater involvement in the political process.
Reforms in political parties are crucial for strengthening democracy, but achieving them requires both internal willingness and external pressure.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Notes - Political Parties
| 1. Why are political parties important in a democracy? |  |
| 2. How many political parties should a country have for effective governance? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between national and state political parties? |  |
| 4. What are some challenges faced by political parties today? |  |
| 5. How can political parties be reformed to better serve democracy? |  |
















