Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources and Development
Resources
A resource is defined as anything in our environment that can satisfy our needs, provided it meets three key criteria:
- Technological Accessibility: It must be reachable through existing technology.
- Economic Feasibility: It must be cost-effective to utilize.
- Cultural Acceptability: It must align with cultural norms and values.

The transformation of resources involves a relationship between nature, technology, and institutions. People interact with nature through technology and form institutions to boost economic growth.
- Resources depend on human activities. People play a vital role as resources themselves.
- They change materials from the environment into resources and use them.
Thus, resources come from human actions. People are key to resources because they turn raw materials into useful assets to satisfy their needs. This illustrates the teamwork between the natural world and human creativity.
Classification of Resources
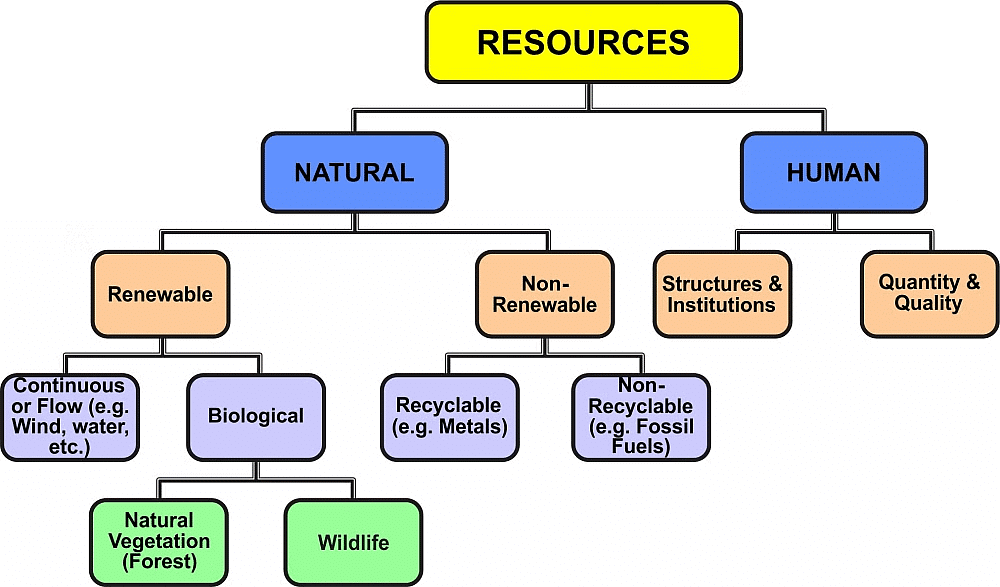
The resources can be classified as
1. On the Basis of Origin
- Biotic Resources: These are obtained from the biosphere and have life, such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc.
- Abiotic Resources: All those things that are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. Example: rocks and metals.
2. On the Basis of Exhaustibility
- Renewable Resources: The resources that can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical, or mechanical processes are known as renewable resources.
Example - solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. - Non-Renewable Resources: The resources that, once consumed, cannot be replaced are known as non-renewable resources. These resources take millions of years to form. Non-renewable resources are recyclable, such as metals and non-recyclable.
Example - Fossil fuels.
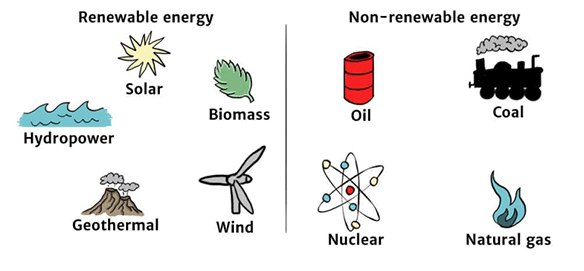 Renewable and Non- Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable and Non- Renewable Energy Sources
3. On the Basis of Ownership
- Individual Resources: These are owned privately by individuals.
- Community Owned Resources: Resources that are available to all community members.
- National Resources: These belong to the nation as a whole. All resources technically belong to the nation.
- International Resources: Resources found beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone in oceans. Accessing these requires permission from international institutions.
4. On the Basis of the Status of Development
- Potential Resources: These are found in a region but are not yet used.
- Developed Resources: Resources that have been assessed for their quality and quantity and are ready for use.
- Stock: Resources that have been identified but cannot be used due to a lack of technology.
- Reserves: These are resources that are assessed and can be used with current technology, but their use has not yet started.
Development of Resources
Resources are vital for human survival. It was believed that resources are free gifts of nature, so, human beings used them indiscriminately, and this has led to the following major problems:
(a) Depletion of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals.
(b) Accumulation of resources in a few hands divides society into rich and poor.
(c) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution, and land degradation.
- For a sustained quality of life and global peace, an equitable distribution of resources has become essential.
- To use resources judiciously, we need to adopt sustainable economic development.
- Sustainable economic development means development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of future generations.
Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, 1992
- Took place in June 1992 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- Addressed global environmental and socio-economic challenges.
- Adopted the Declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity.
- Supported global Forest Principles.
Agenda 21
- Approved at the 1992 Earth Summit.
- Concentrated on global sustainable development.
- Aims to achieve worldwide sustainable development.
- A key goal of Agenda 21 is for each local government to create its own local Agenda 21.
Resource Planning
- Resource planning is essential for the efficient and sustainable use of resources.
- India's diverse regions have varying availability of resources—some rich in certain resources but lacking in others.
- Example regions:
- Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh: Rich in minerals and coal.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Abundant in water resources, but underdeveloped infrastructure.
- Rajasthan: Rich in solar and wind energy, but water-scarce.
- Ladakh: Culturally rich but lacks water, infrastructure, and minerals.
- Balanced resource planning is needed at national, state, regional, and local levels to address these disparities.
Resource Planning in India
- Resource planning is a detailed processthat includes:
1. Identifying and listing resources across different regions. This involves surveying and mapping to assess the quantity and quality of these resources.
2. Establishing a planning system that employs suitable technology, skills, and organisations for resource development.
3. Ensuring that these resource development plans align with the broader national development goals. - Simply having resources isn't enough; we need technological and institutional progress for development.
- Many resource-rich regions are economically backward.
- Historically, the exploitation of these regions shows the need for technology and institutional growth.
- Since Independence, India has focused on resource planning for balanced development, integrating technology, human resources, and historical experiences.
- Resource planning has been a focus since the First Five-Year Plan. Resources alone do not guarantee development; technology and institutions are key.
- For instance, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal, while some areas with fewer resources are economically developed.
- The cold desert of Ladakh is isolated, rich in culture, but lacks water, infrastructure, and essential minerals.
Conservation of Resources
- Resources are essential for any development activity. Irrational consumption and over-utilization of resources can cause socio-economic and environmental issues. Resource conservation at various levels is crucial to prevent these problems.
- Historical Concern:
- Past leaders, like Gandhiji, highlighted the importance of conserving resources.
- Gandhiji believed there is enough for everyone’s needs, but not for greed, and saw greed and exploitative technology as major causes of resource depletion.
- He advocated for production by the masses as a way to ensure sustainable resource use
Land Resources
- Land is a natural resource of great importance. It supports vegetation, wildlife, human life, economic activities, transport, and communication.
- However, land is a limited resource, so careful planning is essential for its various uses.
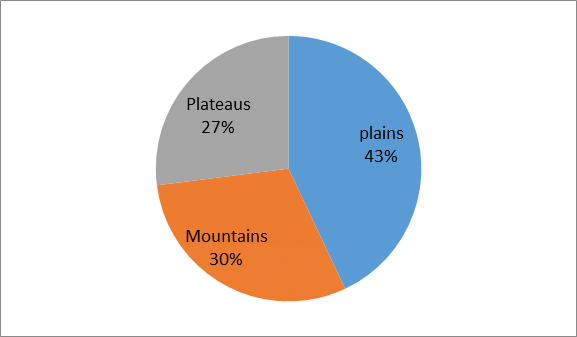 Land under Important Relief Features in India
Land under Important Relief Features in India
- About 43 per cent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry.
- About 30 per cent of the total surface area of the country is mountainous which ensure the perennial flow of some rivers and provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects.
- About 27 per cent of the area of the country is the plateau region that possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Land Utilisation
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
- Forests: Large areas of land are set aside as forests.
- Land not available for cultivation: This includes barren land, wasteland, and land used for buildings, roads, and factories.
- Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land): This consists of permanent pastures, grazing lands, and land with miscellaneous tree crops and groves, as well as culturable waste land that has remained uncultivated for over 5 years.
- Fallow lands:
- Current fallow: Land that has not been cultivated for up to one year.
- Other than current fallow: Land that has remained uncultivated for 1 to 5 years.
- Net sown area: This refers to the land where crops are sown and harvested.
- Gross cropped area: This is the total area sown, including areas that are sown more than once in a year, plus the net sown area.
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land is determined by:- Physical factors: include topography, climate, and soil types.
- Human factors: cover population density, technology, culture, and traditions.
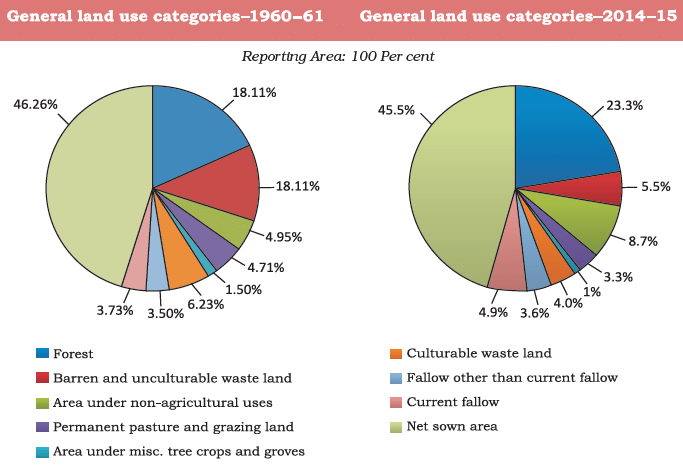
Geographical Overview
- Total area of India: 3.28 million sq km.
- Land use data is available for only 93% of this area, as many northeastern states, except Assam, have not fully reported their data. Additionally, certain regions of Jammu and Kashmir under Pakistan and China remain unsurveyed.
- The area of permanent pasture has decreased, raising concerns about feeding India’s large cattle population.
- Most lands classified as current fallow are of low quality or too expensive to cultivate, leading to cultivation only once or twice every two to three years.
- If these lands are included, the Net Sown Area (NSA) in India is about 54%of the total reporting area.
- Net Sown Area varies greatly by state: over 80% in Punjab and Haryana, but below 10% in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Forest area is significantly lower than the desired 33% of geographical area, as stated in the National Forest Policy (1952). Many people rely on forests for their livelihoods.
- Waste land includes rocky, arid, and desert regions; non-agricultural land is used for settlements, roads, railways, and industry.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
- Land degradation is a serious problem caused by human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and quarrying.
- About 95% of our basic needs for food, shelter, and clothing rely on land, highlighting the importance of conserving it for future generations.
- Human actions have not only led to the degradation of land but have also sped up the damage caused by natural forces.
- In regions like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha, mining has resulted in significant land degradation due to deforestation.
- In areas such as Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra, overgrazing is a major contributor to land degradation.
- Excessive irrigation in Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh causes waterlogging, increasing salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
- Mineral processing, such as grinding limestone for the cement industry and calcite for ceramics, produces a large amount of dust that hampers water absorption into the soil.
- Industrial waste is a significant source of land and water pollution in many regions.
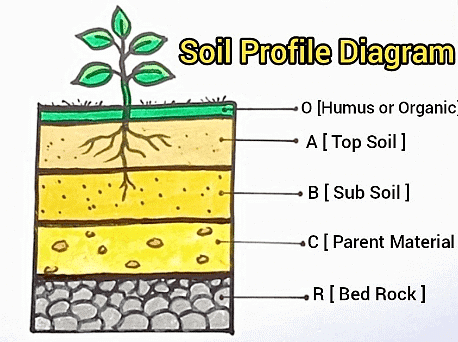
Soil as a Resource
Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
Factors responsible for Soil Formation
- It takes millions of years to create just a few centimetres of soil.
- Factors such as relief, parent rock, climate, vegetation, and time play significant roles in soil formation.
- Temperature changes, the movement of water, wind, and glaciers all help shape the soil.
- Chemical and organic changes occurring in the soil are also vital for its development.
Based on these factors, soils in India are classified into different types according to their colour, thickness, texture, age, and chemical and physical properties.
Classification of Soils
On the basis of the factors responsible for soil formation, color, thickness, texture, age, chemical and physical properties, the soils of India can be classified in different types:
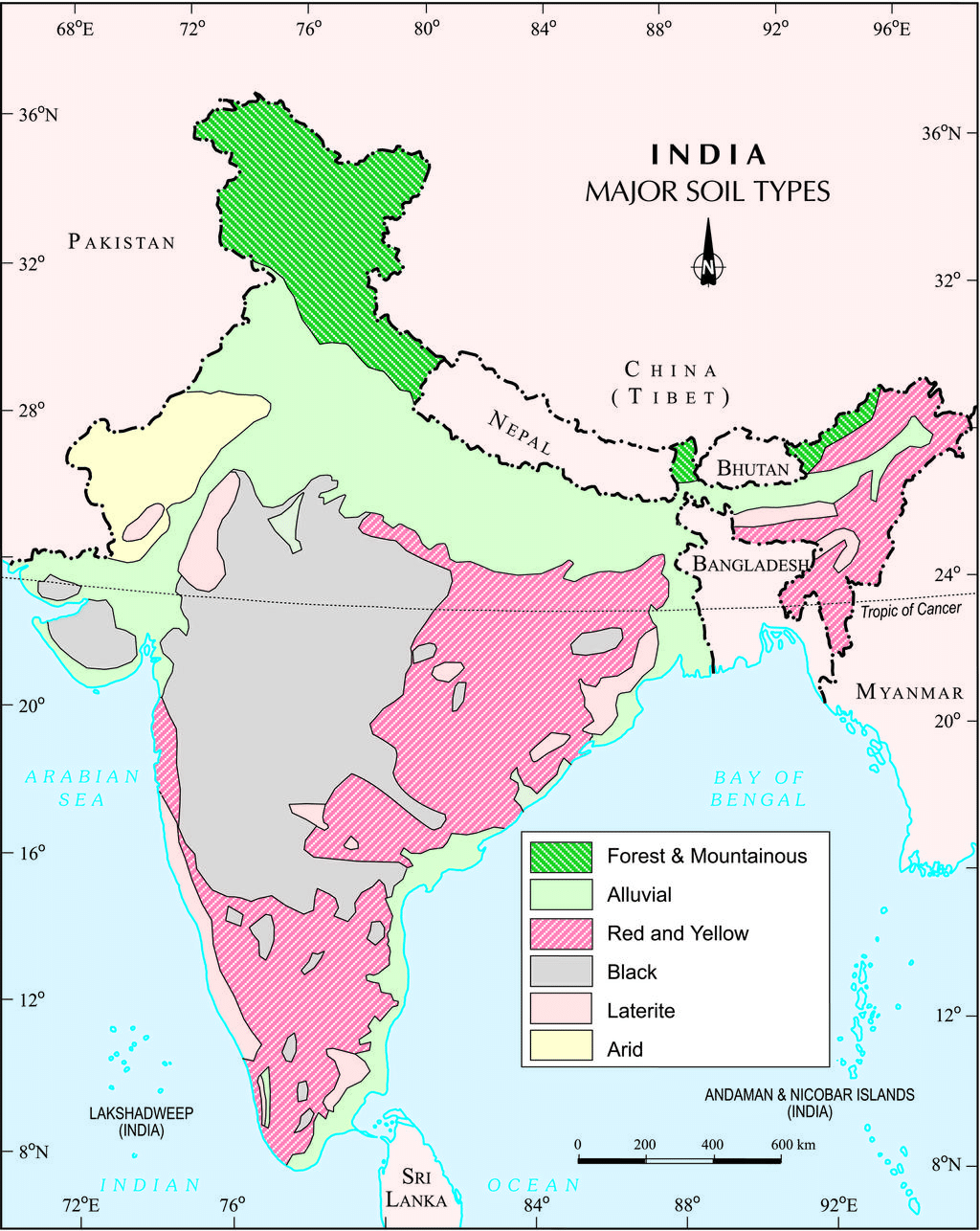 India: Major Soil Types
India: Major Soil Types
1. Alluvial Soils
- Alluvial soil is the most widespread and vital type of soil found in India, mainly located in the northern plains.
- It is formed by the deposits from the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers, and is also seen in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and the eastern coastal plains (deltas of Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri rivers).
- The soil consists of sand, silt, and clay in different amounts, with coarser particles near the piedmont areas like Duars, Chos, and Terai.
- Alluvial soils are divided by age into old alluvial (Bangar) and new alluvial (Khadar):
- Bangar: Contains more kanker nodules, is coarser, and less fertile.
- Khadar: Finer particles, more fertile, and better suited for farming.
- These soils are very fertile, rich in potash, phosphoric acid, and lime, making them ideal for growing sugarcane, paddy, wheat, and pulse crops.
- Regions with intensive cultivation and high population density often feature alluvial soils.
- Alkaline soils in drier areas can become productive with appropriate treatment and irrigation.
 Alluvial Soil
Alluvial Soil
2. Black Soil
- Black Soil, also known as regur soil, is identified by its black colour.
- This soil is excellent for cultivating cotton, which is why it is often referred to as black cotton soil.
- The formation of black soil is affected by the climate and the parent rock material, primarily derived from lava flows.
- It is commonly found in the Deccan trap region, which includes areas like Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
- This type of soil extends southeast through the Godavari and Krishna valleys.
- Black soil is made up of clayey material and is known for its ability to retain moisture.
- It is rich in essential nutrients like calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime, but is typically low in phosphoric content.
- In hot weather, this soil develops deep cracks, which helps with aeration.
- When wet, it becomes sticky and is challenging to work with, unless tilled after the first shower or during the pre-monsoon period.
 Black Soil
Black Soil
3. Red and Yellow Soils
 Red Soil
Red Soil
- Red soil develops on crystalline Igneous rocks.
- Found in areas with low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau, as well as in parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, the southern parts of the middle Ganga plain, and along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
- These soils acquire a reddish color due to iron diffusion in crystalline and metamorphic rocks, appearing yellow in hydrated form.
4. Laterite Soils
 Laterite Soil
Laterite Soil
- Laterite Soil derives its name from the Latin word 'later', meaning brick.
- Develops under tropical and subtropical climates with alternating wet and dry seasons.
- Result of intense leaching due to heavy rainfall.
- Typically deep to very deep, acidic (pH < 6.0), and generally deficient in plant nutrients.
- Found predominantly in southern states, Western Ghats region of Maharashtra, Odisha, parts of West Bengal, and North-east regions.
- In areas with deciduous and evergreen forests, lateritic soils are humus-rich; in sparse vegetation or semi-arid environments, they are humus-poor.
- Prone to erosion and degradation due to landscape position.
- Useful for growing tea and coffee, especially in Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu with proper soil conservation techniques.
- Red laterite soils in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala are particularly suitable for crops like cashew nut.
5. Arid Soils
- Arid soils can be red or brown in colour.
- They are mostly sandy and contain salt.
- In certain regions, high salt levels allow common salt to form through evaporation.
- The dry climate and high temperatures lead to quick evaporation, resulting in low levels of humus and moisture.
- As calcium increases, the Kankar layer forms in the lower soil, making it hard for water to seep in.
- These soils tend to have low levels of phosphoric content.
- During hot weather, they develop deep cracks that help aerate the soil.
- With proper irrigation, these soils can support farming, as seen in western Rajasthan.
 Arid Soil
Arid Soil
6. Forest Soils
- These soils are found in hilly and mountainous areas with plenty of rainfall and forests.
- The texture of these soils differs depending on the mountainous region where they develop.
- They are typically loamy and silty on valley sides and coarse-grained on the upper slopes.
- In the snow-covered regions of the Himalayas, these soils undergo denudation and are acidic with low humus content.
- The soils located in the lower parts of the valleys, especially on river terraces and alluvial fans, are quite fertile.
 Forest Soil
Forest Soil
Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
- Soil Erosion: This is the process of losing soil cover and having it washed away. Soil formation and erosion usually happen together, keeping a balance. However, this balance can be disrupted by human actions, like deforestation, over-grazing, construction, mining, and natural forces such as wind, glaciers, and water.
- Gully Erosion: When water flows over clay-rich soils, it cuts deep channels, making the land unsuitable for farming. Such areas are often called bad land or ravines, particularly in the Chambal basin.
- Sheet Erosion: This occurs when water spreads over large areas, washing away the topsoil.
- Wind Erosion: Wind can blow loose soil off flat or sloped land, taking away the top layer of soil.
- Defective Farming Methods: Poor farming practices can lead to soil erosion. For instance, ploughing up and down slopes creates channels that allow water to flow quickly, causing erosion.
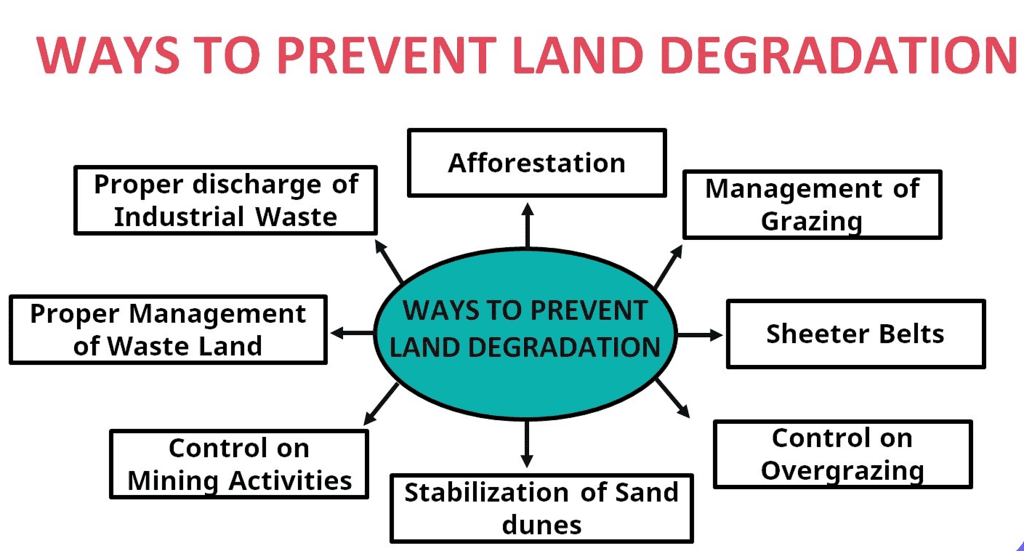
- Contour Ploughing: This method involves ploughing along the contours of the land to slow down water flow and reduce erosion.
- Terrace Cultivation: This technique involves cutting steps into slopes to create terraces, which help to limit erosion. It is commonly found in the Western and Central Himalayas.
- Strip Cropping: This involves dividing large fields into strips with grass sections between them to reduce wind impact and erosion.
- Shelter Belts: Rows of trees are planted to act as barriers, stabilising sand dunes and desert areas. This is especially effective in western India, where these belts have significantly helped in stabilising the landscape.
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources and Development
| 1. What is resource planning and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How are land resources classified? |  |
| 3. What is soil erosion and how can it be prevented through soil conservation? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of soil as a resource? |  |
| 5. How does resource planning contribute to sustainable development in India? |  |

















