Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Political Science Class 12 > Chapter Notes: US Hegemony in World Politics
US Hegemony in World Politics Class 12 Political Science
What Is Hegemony ?
Hegemony refers to a situation in which a nation is in a stronger position than the other nations in the world; the term "American hegemony" also refers to a situation along these lines. It places America in a stronger position than the rest of the world's nations. This hegemony dominated the fields of politics, economics, and culture.
Beginning of the ‘New World Order’ by the US
- In 1991, the US hegemony emerged as a result of the collapse of the USSR. It survived, all of its powers strengthened and unaltered.
- In August 1990, Iraq invaded Kuwait, which it later annexed. The United Nations ordered the forced liberation of Kuwait after numerous diplomatic initiatives to stop Iraq's assault failed. President George H.W. Bush of the United States welcomed this UN decision as the beginning of a "New World Order."
- During the First Gulf War, a coalition force of 6,60,000 soldiers from 34 nations destroyed Iraq. It was known as ‘Operation Desert Storm’ or ‘First Gulf War’.
- America was largely responsible for the war. It revealed the vast technological disparity between the US military's capabilities and those of other nations.
The Clinton Years
- In the 1992 US Presidential elections, Democratic candidate William Jefferson (Bill) Clinton defeated Republican candidate George H.W. Bush.
- It was widely considered during this time period that the US had become more focused on its internal affairs and had not yet fully engaged in global politics.
- Instead than focusing on "hard politics," the Clinton administration prioritised "soft issues" including the advancement of democracy, climate change, and international trade.
- However, the US showed its military power. First, in 1999 in retaliation to Yugoslavian acts against Kosovo's predominantly Albanian people. Second, in retaliation for the US embassies being bombed in Nairobi, Kenya, and Dar es Salaam.
- The US launched "Operation Infinite Reach," which consisted of several cruise missile attacks on Al-Qaeda terrorist targets in Afghanistan and Sudan.
9/11 and the Global War on Terror
- On 11th September 2001, four American commercial aircrafts were hijacked and flew into important buildings in the US.
- The first and second airlines collided with the World Trade Center's North and South Towers in New York, the third with the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, and the fourth with a field in Pennsylvania. These attacks became known as "9/11."
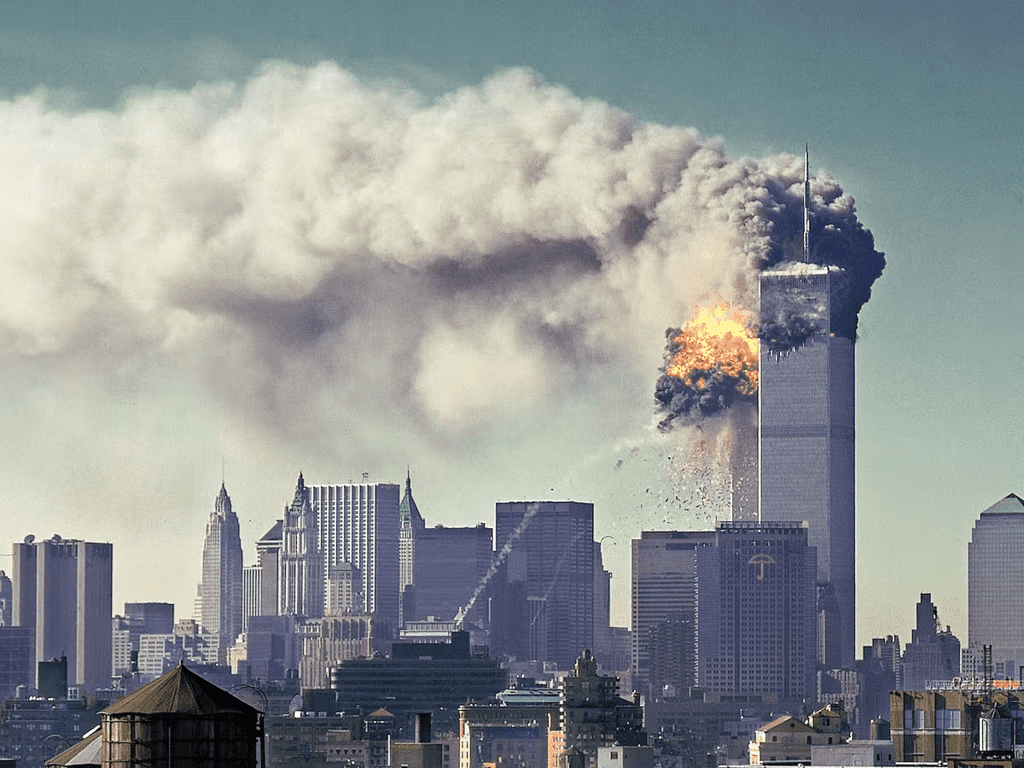 The twin tower bombing
The twin tower bombing
- The US response to 9/11 was swift and ferocious. George W Bush had succeeded Clinton in the US Presidency.
- The US launched ‘Operation Enduring Freedom’ as a part of its ‘Global War on Terror’.
- The operation was against all those suspected to be behind the 9/11 attack, mainly Al-Qaeda and the Taliban regime in Afghanistan.
- Arrests were made all over the world by the US forces often without the knowledge of the government of the persons being arrested.
- These persons were transported across countries and detained in secret prisons.
The Iraq Invasion
- On March 19, 2003, the US began Operation Iraqi Freedom, and more than 40 other nations soon followed.
- The purpose of the invasion was to prevent Iraq from developing Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
- As there was no evidence of WMD, it is speculated that the invasion was motivated by other objectives such as controlling Iraqi oilfields, etc.
- Due to the loss of about 3000 US military men and significantly larger Iraqi casualties, the US invasion of Iraq was both a military and political failure.
Meaning of Hegemony
- The word ‘hegemony’ means the leadership or predominance of one state over others by virtue of its military, economic, political power and cultural superiority.
- Gaining power is the main goal of politics. Countries and groups of countries are continually competing for power in international politics.
- It is important to understand the distribution of power among the countries of the world in order to understand world politics.
- During the Cold War Era, there were two superpowers, the US and the USSR. But after the disintegration of USSR, only a single power was left i.e. the US.
- A "unipolar system" is occasionally used to describe the global order in which a single superpower or hyperpower dominates.
Hegemony as Hard Power
- Hegemony relates to the relations, patterns and balances of military capability between states.
- The base of US power lies in the overwhelming superiority of its military power. It is both absolute and relative.
- The military dominance of the US is not just based on higher military spending but on a qualitative gap.
- However, the US invasion of Iraq still demonstrates the limits of American power because it failed to compel the Iraqi population to submit to the US-led coalition's occupation forces.
Hegemony as Structural Power
- An open world economy needs a hegemon or dominant power to enable its development and continuation, according to the theory underlying this type of hegemony.
- In this sense, hegemony is reflected in the role played by the US in providing global public goods. The best examples of global public goods are Sea-Lanes of Communication (SLOCs), Internet, roads, etc.
- The economic preponderance of the US is inseparable from its structural power, which is the power to shape the global economy in a particular way.
- Another example of the structural power of the US is the academic degree called the Masters in Business Administration (MBA). The idea of teaching skills for business is uniquely American.
Hegemony as Soft Power
- In this type of hegemony, it implies class ascendancy in the social, political and particularly ideological spheres.
- It suggests that a dominant power not only possess military power but also ideological resources to shape the behaviour of competing and lesser powers.
- The US predominance in the world is based not only on its military power and economic powers but on its cultural presence.
- Instead of using hard power, the US was successful throughout the Cold War by using structural power and soft power.
What are the Constraints on American Power?
There are three constraints on American power.
- The institutional architecture of the America is the first constraint.
- The second constraint is domestic in nature and stems from the open nature of American society. There is a deep scepticism regarding the purposes and methods of government in American political culture.
- The third constraint on American power is the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) which is only organisation in the international system that could possibly moderate the exercise of American power.
India’s Relationship with the US
- India's closest friendship during the Cold War was with the Soviet Union.
- India made the decision to liberalise its economy and include it into the global economy over time. This made India an attractive trading partner for many nations, including the US.
- Two new factors emerged in Indo-US relations in recent years. They include :
1. Technological dimension
2. The role of the Indian-American diaspora. - There are three different strategies to decide what kind of relationship India should have with USA. They are as follows :
1. Those Indian analysts who see international politics in terms of military power, prefer that India should maintain its distance from US and should focus upon increasing its own national power.
2. Other analysts see the growing convergence of interests between US and India as a historic opportunity for India.
3. A third group of analysts advocate that India should take the lead in establishing the coalition of countries from developing world. - It would be impossible to govern Indo-US relations with only one strategy. There should be a blending of US foreign policy approaches.
How to Overcome the Hegemony?
- It's crucial to realise that the US military cannot be balanced by a single power. There are numerous strategies that can be effective in challenging the hegemony.
- According to the Bandwagon Strategy, it is suggested that instead of engaging in activities opposed to the hegemonic power, it is advisable to extract benefits by operating within the hegemonic system.
- Hide Strategy implies staying as far removed from the dominant power as possible. China, Russia and the European Union are many examples of this behaviour.
- Another idea holds that non-state entities may oppose American hegemony more so than other states. It is anticipated that a combination of non-governmental organisations (NGOs), social movements, and public opinion would pose threats to US hegemony.
The document US Hegemony in World Politics Class 12 Political Science is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Political Science Class 12.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
34 videos|433 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on US Hegemony in World Politics Class 12 Political Science
| 1. What is hegemony? |  |
Ans. Hegemony refers to the dominance or leadership of one country or group over others, particularly in terms of politics, economy, and culture. It involves the ability to shape and control the actions and behavior of other nations or actors to align with the interests of the dominant power.
| 2. How did the US establish a hegemony and initiate the 'New World Order'? |  |
Ans. Following the end of the Cold War, the US emerged as the sole superpower with unmatched military, economic, and political influence. The term 'New World Order' was used by President George H.W. Bush to describe a world where the US would lead and promote democracy, free markets, and global cooperation.
| 3. How did events like 9/11 and the Iraq Invasion affect US hegemony? |  |
Ans. The 9/11 attacks led to the US launching the Global War on Terror, which significantly expanded its military presence and intervention in various regions. The Iraq Invasion in 2003, based on flawed intelligence, eroded global support for US actions and raised doubts about its motives and ability to maintain international order.
| 4. What are the constraints on American power? |  |
Ans. While the US has immense power, it faces several constraints on its ability to exercise hegemony. These include the rise of other global powers like China, increasing regional conflicts and instabilities, economic interdependence, international institutions, public opinion, and resistance from non-state actors.
| 5. How can hegemony be overcome? |  |
Ans. Overcoming hegemony requires a combination of efforts at the domestic, regional, and international levels. Building strong and inclusive regional organizations, promoting multilateralism and cooperation, fostering economic interdependence, addressing the root causes of conflicts, and promoting a more equitable international order can help reduce the dominance of any single power.
Related Searches





















