Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Causes of Wind |

|
| Air Pressure |

|
| Why are roofs blown off in the wind? |

|
| Characteristics of Wind: |

|
| Storm |

|
| Effects of a Cyclonic Storm |

|
| Key Words |

|
| Activity 1: |

|
| Activity 2: |

|
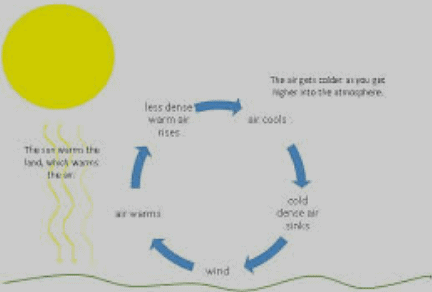
Wind is the movement of air in the atmosphere, caused by a difference in temperatures between different regions on the Earth. Uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun is the main cause of temperature difference.
Causes of Wind
Air absorbs different amounts of heat, making it warm in some places and cool in others. Warm air rises and cool air sinks, setting up a current of air that we call wind.
Hot Air Balloons:
Hot air balloons use the fact that hot air rises. Consists of a huge balloon with a light basket attached to it, in which people can sit. Fans are used to fill the balloon with air and also heat the air as needed. The balloon rises when the air inside is heated and descends when it is cooled.
Seasonal Winds:
Heating and cooling on Earth happens regularly with a change in seasons. Sets up seasonal winds such as monsoon winds. During summer, land becomes very hot compared to the ocean, and air over the land gets heated and rises. Cooler rain-bearing winds from over the ocean blow towards the land, and these are called monsoon winds.
Air Pressure:
Wind is closely related to the pressure of the air at a place. Air pressure is the weight of the air pressing down on the Earth's surface. Differences in air pressure cause wind to blow from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
Storms:
Strong winds that occur during a thunderstorm are called gusts. Tornadoes are a type of storm that are characterized by spinning winds that form a funnel shape. Hurricanes are large, intense storms that form over warm ocean water. Thunderstorms are storms that produce lightning and thunder and are often accompanied by heavy rain, strong winds, and hail.
Air Pressure
The pressure exerted by air on objects in the atmosphere. Factors affecting air pressure: height of a place and temperature. Air moves from areas of higher pressure to areas of lower pressure, causing wind. Moving air causes variations in pressure.
Moving Air and Lift
Moving air can provide lift due to variations in pressure. Pressure is lower where air moves faster and higher where air moves slower. When air flows horizontally, a strip with faster air above and slower air below experiences a lift.
Experiment: Blow over a strip of paper and observe it being pushed up. Forces acting on the paper: gravity pulling it down and pressure differences. Blowing air above the paper reduces pressure on top, causing higher pressure below to push the paper up.
Why are roofs blown off in the wind?
When there is a strong wind, the pressure on top of the roof is lower than the pressure below. This creates an imbalance of forces, causing the roof to get dislodged and blown away.
Types of winds:
- Local winds are caused by temperature differences in a small area.
- Global winds are caused by the rotation of the Earth and differences in pressure.
Effects of storms:
- Storms can cause damage to buildings, trees, and power lines.
- They can also cause flooding and landslides.
Preventing damage from storms:
- Secure loose objects and remove dead branches from trees.
- Reinforce windows and doors.
- Have an emergency kit ready.
Characteristics of Wind:
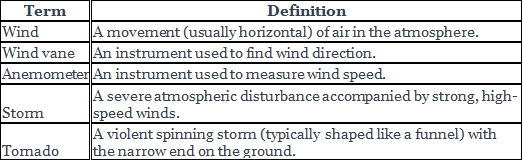
Wind has two important characteristics: direction and speed. Wind direction can be gauged using an instrument called the wind vane or weather vane. The front and rear parts of a wind vane are designed in a way that the arrow aligns itself in the direction from which the wind is blowing. A rooster-shaped wind vane can also be used to determine wind direction. Wind speed is measured using an instrument called an anemometer. Cup anemometers are mainly used by meteorological stations, and the rate of rotation of cups is directly proportional to wind speed.
Impact of Wind:
Wind can have both positive and negative impacts on our daily lives. Wind can be harnessed to generate electricity, power windmills, and even sail boats. However, strong winds can lead to power outages, damage to buildings and infrastructure, and even cause harm to people and animals. Strong winds can also cause storms, such as hurricanes, cyclones, and typhoons, which can be extremely dangerous and cause widespread damage.
Anemometer
An anemometer is an instrument used to measure wind speed. An anemometer can be easily made with simple materials such as plastic cups, straws, a pencil, and a ball pin. The procedure to make an anemometer involves punching holes in the cups and passing straws through them, aligning them to intersect at the center, and attaching them to a pencil with a ball pin.
Wind energy
Wind energy is the energy produced by wind turbines. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy. Wind energy is a clean and renewable source of energy and is becoming increasingly popular worldwide.
Effects of wind and storms
Strong winds can cause damage to property and infrastructure. Storms can cause flooding, landslides, and power outages. It is important to take precautions during storms and follow safety guidelines issued by authorities.
Storm
Storms are severe atmospheric disturbances accompanied by very strong, high-speed winds. They occur when different types of air masses meet, such as dry air mass meeting a moist air mass or a cold air mass meeting a warm air mass. Storms can range from moderate to very severe and can cause large-scale destruction of life and property.
Types of Storms
There are two main types of storms: cyclones and tornadoes. Let's explore each of them.
Cyclones
Cyclones develop over the ocean near the equator, where the waters are warm. In different regions, cyclones are known by different names such as hurricanes in North America and the Caribbean, typhoons in Eastern Asia, and cyclones in India.
The formation of a cyclone involves several steps:
Warm air over the oceans, containing a lot of water vapor, rises, creating a region of low pressure. Colder air from the surroundings rushes in, causing the formation of a spiral, which is influenced by the Earth's rotation. The spiraling winds spin anti-clockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere.
The cyclone consists of the eye (center) and spiraling winds that gain very high speeds. Multiple small storm systems can merge to become a larger storm. A full-fledged cyclone can have wind speeds ranging from 120 km/h to 280 km/h, spreading over hundreds of kilometers. The path of a cyclone is difficult to predict, but it can be tracked using satellites. The damage caused by a cyclone depends on its wind speeds and is categorized on the Saffir-Simpson Scale, ranging from Category 1 (mild) to Category 5 (devastating). When a cyclone's eye hits land, it is referred to as making a landfall.
[Case Study: Cyclone Fani]
Cyclone Fani hit the eastern coast of India on May 3, 2019, and was one of the most powerful cyclones in the last 20 years. The state of Odisha faced the brunt of the storm, but the government's effective disaster management planning and execution helped in evacuating thousands of people to safer areas. The number of deaths was minimized due to accurate tracking and advance warning provided by the Indian Meteorological Department. However, significant damage to property occurred, and many people had to rebuild their lives and livelihoods.
Tornadoes
Tornadoes are another type of storm characterized by a rapidly rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud. They often appear as a twisting funnel-shaped cloud extending from the sky to the ground. Tornadoes are usually smaller in size compared to cyclones but can be extremely destructive. They form under specific atmospheric conditions and are associated with severe thunderstorms. Tornadoes are known for their strong winds that can exceed 300 km/h and cause significant damage in their path.
Effects of a Cyclonic Storm
Cyclones can be very dangerous to human life and property. Cyclonic storms produce very high waves, storm surge, and storm tide, which can be very dangerous for fishermen to go out into the seas. The damage caused by a cyclonic storm depends on the category of the storm, ranging from Category 1 to Category 5. Safety measures should be taken to prevent injuries and damage during a cyclonic storm.

Safety Measures during a Cyclone
A cyclone can be tracked, and a warning can be given well before it comes close to land. Preparation should be made before the storm, including listening to news updates and stocking up on food, water, batteries, emergency lights, and candles. Dead trees and branches should be removed, and loose roofing should be secured. Fishermen should not venture out to sea.
Tornado
A tornado is a spinning air column typically shaped like a funnel, with wind speeds of over 500 km/h, destroying virtually everything in its path. Tornadoes develop from thunderstorms and are formed mostly on land, usually narrow, about 0.5 km wide, and rarely move beyond 20 km.
Safety Measures During and After a Tornado
- Stay indoors and take shelter in a building.
- Avoid taking shelter under a tree as it can be uprooted.
- Avoid touching anything that may be exposed to electricity lines.
- Watch out for flying debris; most injuries in a tornado are due to flying debris.
- Never try to outrun a tornado.
Key Words
Activity 1:
Demonstrating Air Pressure
Aim: To show that air exerts pressure.
Materials needed: Thin metal can with an air-tight cap, stove/Bunsen burner, kitchen sink/washbasin, tongs, small thick towel.
Method:
Fill the can up to one-third with water.
Heat the can without the cap, allowing steam to escape.
Use tongs to remove the can from the stove, quickly cover the opening with the towel, and tightly close the cap.
Take the can to the sink and hold it under tap water.
Observation: The can slowly crumples up.
Conclusion: Heating the can produces steam, which pushes out most of the air. As it cools, the steam condenses, creating a near vacuum inside the can. The external air pressure then crushes the can, demonstrating that air exerts pressure.
Activity 2:
Aim: Showing air expands on heating
Materials needed: Small plastic bottle, balloons, hair dryer, plastic mug, hot water
Method:
1. Cover the mouth of the plastic bottle with the uninflated balloon.
2. Heat the plastic bone with a hair dryer and observe the balloon.
3. Hold the plastic bone under cold water or place it in a refrigerator and observe the balloon.
4. Heat some water and pour it into a plastic mug.
5. Dip the plastic bottle (with the balloon) into the hot water.
6. Observe the balloon and cool the bottle again with cold water or a refrigerator.
Observation: The balloon inflates when heated and deflates when cooled.
Conclusion: Air expands when heated and contracts when cooled.
|
139 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|















