Chapter notes: Time | Mathematics Class 3 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Reading Time |

|
| Seconds |

|
| Time in a.m. and p.m. |

|
| Converting Hours to Minutes |

|
| Converting Days to Hours |

|
| 24-Hour Clock |

|
| Reading Timetables—Bus and Railway |

|
| Calendar |

|
| Leap Year |

|
Introduction
The chapter "Time" introduces the concept of measuring and understanding time through the use of clocks and calendars. It covers how to read and write time in both 12-hour and 24-hour formats, convert between different units of time, and interpret timetables. It also explains the use of a.m. and p.m. We can see that a clock has two hands. The longer hand is called the minute hand, and the shorter hand is called the hour hand. It has many big and small markings on its face. The bigger markings are for hours, and the smaller markings are for minutes. When the hour hand moves from one number to another, we call it one hour. The minute hand moves faster than the hour hand. It completes one full circle of the clock face in one hour.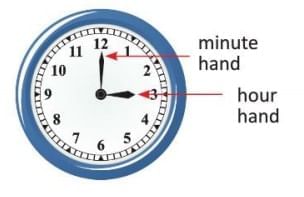
Reading Time
Reading the Hour Hand
- The hour hand shows the hour when the minute hand points at 12.
- It takes 12 hours for the hour hand to complete one full circle around the clock, and it does this twice in a 24-hour day.
- A day is split into four parts: morning (when the sun rises), afternoon (noon to evening), evening (when the sun sets), and night (evening to morning).
Example: If the hour hand is on 4and the minute hand is on 12, the time is 4:00 or 4 o'clock.
Reading the Minute Hand
- A clock has 60 markings, each marking one minute.
- Big markings (numbers 1–12) represent hours, with four smaller markings between them for minutes.
- Each big marking equals 5 minutes (multiply the number by 5).
- The minute hand completes one full circle (60 minutes) in one hour.
- Time can be read forward (minutes past the hour) or backward (minutes to the next hour).
Examples
- Example 1: If the minute hand is on 3 and the hour hand is past 11, the time is 11:15 (3 × 5 = 15 minutes), or quarter past 11.
- Example 2: If the minute hand is on 10 and the hour hand is past 5, the time is 5:50 or 10 minutes to 6 (12 – 10 = 2 × 5 = 10 minutes).
Seconds
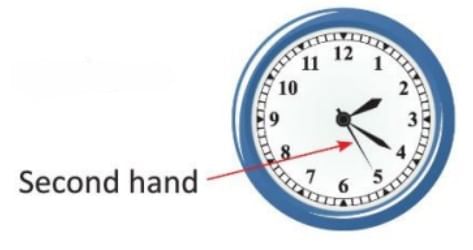
- Seconds are a smaller unit of time, with 60 seconds in one minute.
- Some clocks have a second hand, which is the thinnest and longest, moving one full circle in 60 seconds (1 minute).
- Time can be written using short forms: 'h' for hours, 'min' for minutes, and 's' for seconds.
- Example: A time of 3 hours, 15 minutes, and 30 seconds can be written as 3h 15min 30s.
Time in a.m. and p.m.
- Time is divided into a.m. (before midday, from midnight to noon) and p.m. (post meridiem, after midday, from noon to midnight).
- Using a.m. and p.m. avoids confusion between morning and evening times.
- 12 o'clock is written as 12 noon (midday) or 12 midnight, not with a.m. or p.m.
- 1 day = 24 hrs = 12 hours first half (a.m.) + 12 hours second half (p.m.)
- Special terms: quarter past (15 minutes), half past (30 minutes), quarter to (45 minutes).
Examples
- Example 1: 6:00 in the morning is 6:00 a.m., and in the evening, it is 6:00 p.m.
- Example 2: If the hour hand is between 4 and 5 and the minute hand is on 3, the time is 4:15 a.m. (morning) or 4:15 p.m. (evening), also called quarter past 4.
Converting Hours to Minutes
- One hour equals 60 minutes (1h = 60 min).
- To convert hours to minutes, multiply the number of hours by 60.
- For hours and minutes together, multiply hours by 60 and add the minutes.
Examples
- Example 1: 10 hours = 10 × 60 = 600 minutes.
- Example 2: 5 hours 45 minutes = (5 × 60) + 45 = 300 + 45 = 345 minutes.
Converting Days to Hours
- One day equals 24 hours.
- To convert days to hours, multiply the number of days by 24.
- For days and hours together, multiply days by 24 and add the hours.
Examples
- Example 1: 4 days = 4 × 24 = 96 hours.
- Example 2: 2 days 10 hours = (2 × 24) + 10 = 48 + 10 = 58 hours.
24-Hour Clock
- The 24-hour clock is used in places like railway stations, airports, and hospitals, running from midnight to midnight.
- Time is written as hours: minutes (e.g., 14:30) or as four digits (e.g., 1430 hours).
- Midnight is 00:00 or 0000 hours (start of the day) or 24:00 or 2400 hours (end of the day).
- Numbers less than 10 have a zero before them (e.g., 06:40).
- Noon is 12:00 or 1200 hours.
- After 12:00, add hours to represent p.m. times (e.g., 1:00 p.m. = 13:00).
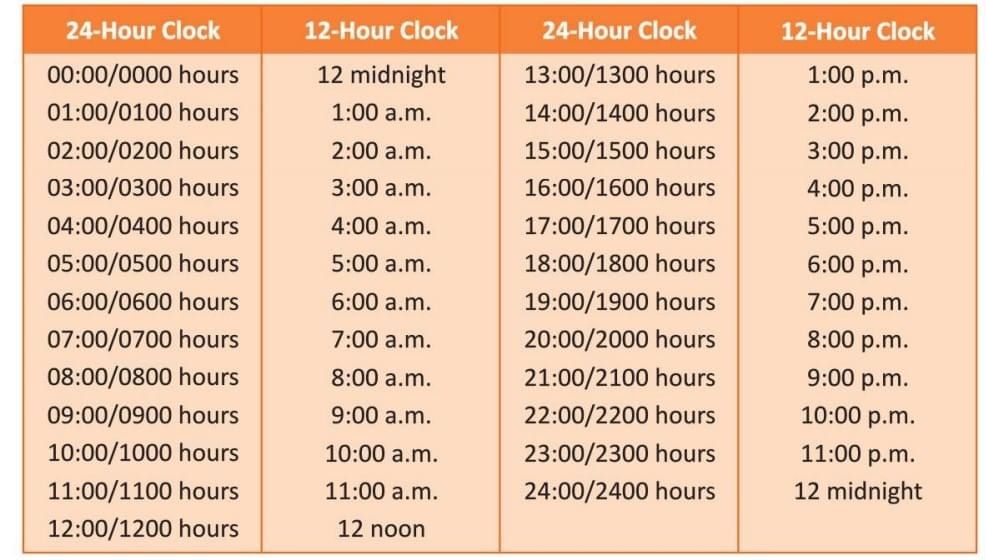 Example: 15:00 hours is 3:00 p.m. (15:00 - 12:00 = 3:00).
Example: 15:00 hours is 3:00 p.m. (15:00 - 12:00 = 3:00).
Conversion of 24-Hour Clock Time to 12-Hour Clock Time
- For 0000–0059 hours, add 12:00 a.m.
- For 0100–1159 hours, add a.m. directly.
- For 1200–1259 hours, add p.m. directly.
- For 1300–2359 hours, subtract 12:00 and add p.m.
- Example 1: 0045 hours = 12:45 a.m. (0045 + 1200 = 1245).
- Example 2: 1430 hours = 2:30 p.m. (1430 - 1200 = 0230).
Conversion of 12-Hour Clock Time to 24-Hour Clock Time
- For 12:00–12:59 a.m., subtract 12:00.
- For 1:00 a.m.–12:59 p.m., write as is.
- For 1:00 p.m.–11:59 p.m., add 12:00.
- Example 1: 12:20 a.m. = 00:20 (1220 - 1200 = 0020).
- Example 2: 5:45 p.m. = 17:45 (0545 + 1200 = 1745).
Advantages of 24-Hour Clock over 12-Hour Clock
- It avoids confusion between morning and evening (e.g., 19:00 is clearly evening, unlike 7:00).
- It makes calculating time duration easier.
- Example: The duration between 09:30 and 14:30 is 5 hours (1430 - 0930 = 0500), simpler than 9:30 a.m. to 2:30 p.m.
Reading Timetables—Bus and Railway
- Timetables help plan activities like travel by showing departure and arrival times.
- They are used for buses, trains, and other public transport.
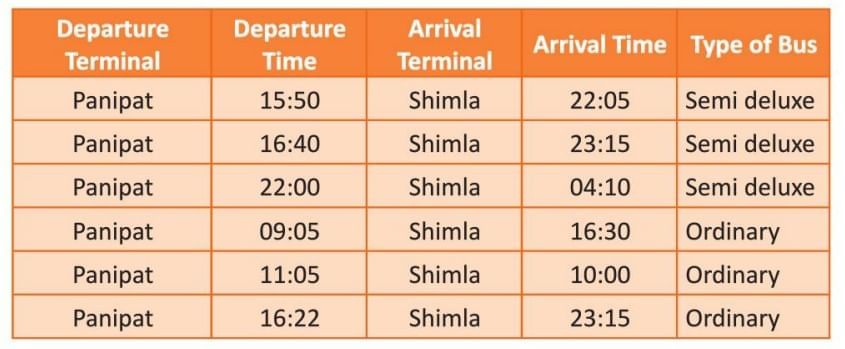
Example 1: Mr Kaushal staying in Panipat planned a holiday to Shimla. He decided to travel by bus. Look at the timetable and answer the questions that follow.
(a) If Mr Kaushal and his family want to reach Shimla early in the morning, at what time should they leave from Panipat?(b) If they take the ordinary bus from Panipat at 11:05, at what time will they reach Shimla?
Solution:
(a) To reach Shimla early in the morning, Mr Kaushal and his family should leave Panipat at 22:00 by the semi deluxe bus.(b) If they take the ordinary bus from Panipat at 11:05, they will reach Shimla at 10:00 the next morning.
Calendar

- A week has 7 days: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
- A year has 52 weeks and 1 day, totalling 365 days.
- There are 12 months: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December.
- Dates are written as day, month, year (e.g., 7 November 2017 or 7/11/2017).
- Example: The date 15 August is written as 15/08/2025.
Leap Year
- A leap year has 366 days, with February having 29 days instead of 28.
- It occurs every four years (e.g., 2016, 2020).
- Example: 2020 was a leap year with 366 days, and February had 29 days.
|
67 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Chapter notes: Time - Mathematics Class 3 ICSE
| 1. What is the difference between a.m. and p.m. in time notation? |  |
| 2. How do you convert hours to minutes? |  |
| 3. How do you convert days to hours? |  |
| 4. How do you convert 24-hour clock time to 12-hour clock time? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using a 24-hour clock over a 12-hour clock? |  |