Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Due to higher enthalpy of formation in the solid state and due to higher hydration enthalpy in the aqueous solution, alkaline earth metals uniformally form bipositive ions.
Due to increased nuclear charge and smaller size, alkaline earth metals form compounds which are less ionic than the corresponding compounds of the alkali metals.
Oxides and Hydroxides
1. Oxides
The oxides of alkaline earth metals MO, are obtained either by heating the metal in dioxygen or by thermal decomposition of their carbonates.
2M + O2 → 2 MO (M = Be, Mg, Ca)
MCO3 → MO + CO2 (M = Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba)
- All the oxides have rock salt structure. The enthalpy of formation of these oxides are quite high and consequently they are very stable.
Metal oxide BeO MgO CaO SrO BaO
ΔfH° 550 590 623 590 545 - They have high melting point, have very low vapour pressure, are very good conductors of heat and are chemically inert. These oxides are used for lining furnaces and hence are used as refractory materials. Due to small size of beryllium ion, BeO is covalent but still has high melting point because of its polymeric nature. Each atom is tetrahedrally coordinated to four other oxygen atoms.
2. Hydroxides
The hydroxides of Ca, Ba and Sr are obtained either by treating the metal with cold water or by reacting the corresponding oxide with water. The reaction of these oxides with water is also called slaking.
M + 2 H2O → M(OH)2 + H2
MO + H2O → M(OH)2
Be(OH)2 and Mg (OH)2 being insoluble are obtained from suitable metal ion solution by precipitation with OH‾ ion.
BeCl2 + 2 NaOH → Be(OH)2 ↓ + 2 NaCl
MgSO4 + 2 NaOH → Mg(OH)2 ↓ + 2 Na2SO4
Properties of hydroxides
- Basic character: Due to small size and high ionization of Be, Be(OH)2 is amphoteric. It dissolves both in acids and bases.
Be(OH)2 + 2 HCl → BeCl2 + 2 H2O
Be(OH)2 + 2 NaOH → Na2BeO2 + 2 H2O
The hydroxides of Mg, Sr, Ca and Ba are basic. Their basic strength increases as we move down the group.
Reason: Basic character of these hydroxide is due to their low ionization enthalpy. Because of low ionization enthalpy, the M-O bond in MOH is weak and thus breaks to give OH‾ ions in solution. On moving down the group, the ionic size increases and ionization enthalpies further decreases. As a result, M-O bond becomes weaker and weaker down the group and hence the basic character also increases down the group.
The hydroxides are less basic than the corresponding alkali metal hydroxides because of higher ionization enthalpies , smaller ionic size and greater lattice energies. - Solubility in water: Alkaline earth metal hydroxides are less soluble in water as compared to the alkali metal hydroxides. The solubility of the alkaline earth metal hydroxide in water increases with increase in atomic number down the group. Both lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy decreases down the group as the size of the cation increases but lattice enthalpy decreases more rapidly than the hydration enthalpy and hence the solubility increases down the group.
Halides
Preparation: The alkaline earth metals combine directly with halogens at appropriate temperature forming halides, MX2.
These halides can also be prepared by the action of halogen acids on metals, metal oxides, hydroxide and carbonates.
M + 2 HX → MX2 + H2
MO + 2 HX → 2MX2 + H2O
M(OH)2 + 2 HX → MX2 + 2 H2O
MCO3 + 2 HX → MX2 + CO2 + H2O
Properties
- All beryllium halides are essentially covalent and are soluble in organic solvents. They are hydroscopic, and fume in air due to hydrolysis. On hydrolysis, they produce acidic solution.
BeCl2 + 2 H2O → Be(OH)2 + 2 HCl - The halides of all other alkaline earth metals are ionic. Their ionic character increases as the size of the metal Ion increases.
As the ionic character increases or the covalent character decreases, their tendency towards hydrolysis decreases.
BeCl2 > MgCl2 > CaCl2 > SrCl2 > BaCl2 - Except BeCl2, all other chlorides of group 2 form hydrates but their tendency to form hydrates decreases.
- The hydrated chlorides ,bromides and iodides of Ca, Ba and Sr can be dehydrated on heating but those of Be and Mg undergo hydrolysis.
MgCl2· 6 H2O → MgO + 2 HCl + 5 H2O
CaCl2·6 H2O → CaCl2 + 6 H2O - BeF2 in highly soluble in water due to the high hydration enthalpy of the small Be2+ ion. The Other fluoride are almost insoluble in water.
The chlorides, bromides and iodides of all of the elements i.e. Mg, Ca, Ba, Sr are ionic, have lower melting point than the fluorides and are readily soluble in water. The solubility decreases somewhat with increasing atomic number. - Except BeCl2 and MgCl2, the other chlorides of alkaline earth metal impart characteristic colours to flame.
Structure of BeCl2
In the solid phase, BeCl2 has polymeric chain structure with chloride bridges.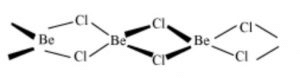
The polymeric structure of BeCl2 is due to its electron deficient nature.Be has only 4 electrons in the valence shell and hence can accept two electron pair to complete its octet. Each Be atom is tetrahedral surrounded by 4 chlorine atoms. Two of the chlorine atoms are bonded by two covalent bonds while the other two by co-ordinate bonds.
In the vapour phase it tends to form a chlorine bridged dimer which dissociates into the linear triatomic monomer at high temperature.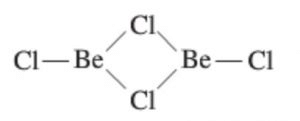
Uses
- Calcium fluoride or fluorspar is the only large scale source of fluorine.
- CaCl2 is widely used for melting ice on roads, particularly in very cold countries.
- Anhydrous CaCl2 is also used as a desiccant ( drying agent in laboratory)
- Anhydrous MgCl2 is used in the electronic extraction of magnesium.
Solubility and thermal stability of Oxo salts
The salt containing one or more atoms of oxygen such as oxides, hydroxides, carbonate, bicarbonate, nitrite, nitrate, sulphates, oxalates and phosphates are called oxo salts.
Sulphates
The sulphates of alkaline earth metal are prepared by the action of sulphuric acid on metals, metal oxides, hydroxides and carbonates.
M + H2SO4 → MSO4 + H2
MO + H2SO4 → MSO4 + H2O
Properties
- The sulphate of alkaline earth metal are all white solids. Beryllium, magnesium and calcium sulphate crystallise in the hydrated form i.e. BeSO4·4H2O, MgSO4·7H2O, CaSO4·2H2O but sulphates of Strontium and barium crystallise without water of crystallisation.
- The solubility of sulphates in water decreases down the group i.e. Be > Mg > > Ca > Sr > Ba.
BeSO4 and MgSO4 are highly soluble, CaSO4 is sparingly soluble but the sulphates of Sr, Ba and Ra are insoluble.
Reason: The magnitude of the lattice enthalpy remains almost constant as the sulphate ion is so big that small increase in the size of cation from Be to Ba does not make any difference. The hydration enthalpy decreases from Be2+ to Ba2+ as the size of the cation increases down the group. Hence the solubility of sulphates of alkaline earth metal decreases down the group mainly due to decreasing hydration enthalpy from Be2+ to Ba2+. The high solubility of BeSO4 and MgSO4 is due to the high hydration enthalpy because of smaller size of Be2+ and Mg2+ ions.
Stability: The sulphates of alkaline earth metals decompose on heating giving their corresponding oxides and SO3.
MSO4 → MO + SO3
The temperature of decomposition of these sulphates increases as the electropositive character of the metal or the basicity of the metal hydroxide increases down the group.
Uses
- The almost negligible solubility of BaSO4 in water is used in the detection and estimation of SO42‾ ions.
- Barium meal is used to obtain a shadow of the stomach on an X-ray film which is useful in diagnosing stomach ulcers.
Carbonates and bicarbonates
Alkaline earth metal carbonates metal carbonates are obtained as white precipitate when
- calculated amount of carbon dioxide is passed through the solution of alkali metal hydroxide
M(OH)2 + CO2 → MCO3 + H2O - sodium or ammonium carbonate is added to the solution of alkaline earth metal salt such as CaCl2.
CaCl2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2 NaCl
Properties
- All carbonates are ionic but beryllium carbonate is prone to hydrolysis. It contains the hydrated ion, [Be(H2O)4]2+ rather than Be2+ and hence is precipitated only in an atmosphere of CO2.
BeCO3 + 4 H2O ⇔ [Be(H2O)4]2+ + CO32- - Solubility: The carbonates of magnesium and other alkaline earth metals are sparingly soluble in water and their solubility decreases down the group from Be to Ba.
Reason: As we move down the group, the lattice enthalpy of carbonates remain approximately the same. Carbonate ion is so large that relatively small changes in the size of the cation from Be2+ to Ba2+ do not make any difference. The hydration enthalpies of the metal cation decreases from Be2+ to Ba2+.
The solubility of carbonates of alkaline earth metal decreases down the group mainly due to decreasing hydration enthalpies of the cations from Be2+ to Ba2+.
All the carbonates of alkaline earth metal are more soluble in the presence of CO2 due to the formation of corresponding bicarbonates.
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2 - Stability: The carbonates of all alkaline earth metal decompose on heating to form corresponding metal oxide and carbon dioxide.
MCO3 → MO + CO2
The temperature of decomposition i.e. thermal stability of these carbonates, however, increases down the group as electropositive character of the metal or the basicity of metal hydroxides increases from Be(OH)2 and Ba(OH)2.
Preparation Of bicarbonates
The bicarbonates of alkaline earth metal are prepared by passing CO2 through a suspension of metal carbonate in water.
MCO3 + CO2 + H2O → M(HCO3)2
All the bicarbonates of alkaline earth metal are stable only in solution and have not been isolated in the pure state.
Uses
- The cations of group V of qualitative analysis are precipitated as their insoluble carbonates from the solution of their soluble salts by adding (NH4)2CO3 in presence of NH4Cl and excess of NH4OH.
- The soluble carbonates i.e. carbonates of alkali metals and NH4+ ions are detected by precipitating them as insoluble magnesium carbonate.
- CaCO3 is used in Solvay – ammonia process for manufacture of Na2CO3, in glass making and in cement manufacture.
Nitrates
Alkaline earth metal nitrates are prepared in solution and can be crystallized as hydrated salt by the action of HNO3 on oxides, hydroxides and carbonates.
MO + 2 HNO3 → M(NO3)2 + H2O
M(OH)2 + 2 HNO3 → M(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
MCO3 + 2 HNO3 → M(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
Tendency to form hydrates decreases with increasing size and decreasing hydration enthalpy down the group.
All nitrates are soluble in water and decompose on heating to give the corresponding oxides with evolution of NO2 and O2.
Strontium and barium nitrate are used in pyrotechnics for giving red and green flames.
Oxalates
The oxalates of calcium, Strontium and barium are sparingly soluble in water but their solubility increases from Ca to Ba. Beryllium oxalate is soluble in water.
|
366 videos|833 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the common characteristics of compounds of the alkaline earth metals? |  |
| 2. How do compounds of the alkaline earth metals differ from those of the alkali metals? |  |
| 3. What are some important applications of compounds of the alkaline earth metals? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the role of alkaline earth metal compounds in biological systems? |  |
| 5. Are compounds of the alkaline earth metals toxic? |  |
















