Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Year 7 Physics (Cambridge) > Charge flow in circuits
Charge flow in circuits | Year 7 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Electrical Circuits |

|
| Components of a Circuit |

|
| Direction of Current |

|
| Circuit Representation |

|
Understanding Electrical Circuits
An electrical circuit is a closed loop that includes a power source, such as a cell or battery, and components through which electrons flow. It can be represented using circuit diagrams.
Components of a Circuit
- Cell/Battery Symbol: Represents the power source. A battery is made up of two or more cells connected together.
- Filament Lamp Symbol: Represents a light bulb. When connected in a circuit with a closed switch, it lights up.
- Switch Symbol: Controls the flow of current. When closed, it allows current to flow; when open, it interrupts the circuit.
Key Terms
- Current (I): Measures the flow of electrons in the circuit, similar to water flow in a pipe. It is measured in amperes (A).
- Potential Difference (V): Also known as voltage, it is the driving force that pushes electrons through the circuit, provided by the cell or battery. It is measured in volts (V).
- Resistance (R): Opposes the flow of electrons, similar to partial blockage in a pipe. It is measured in ohms (Ω).
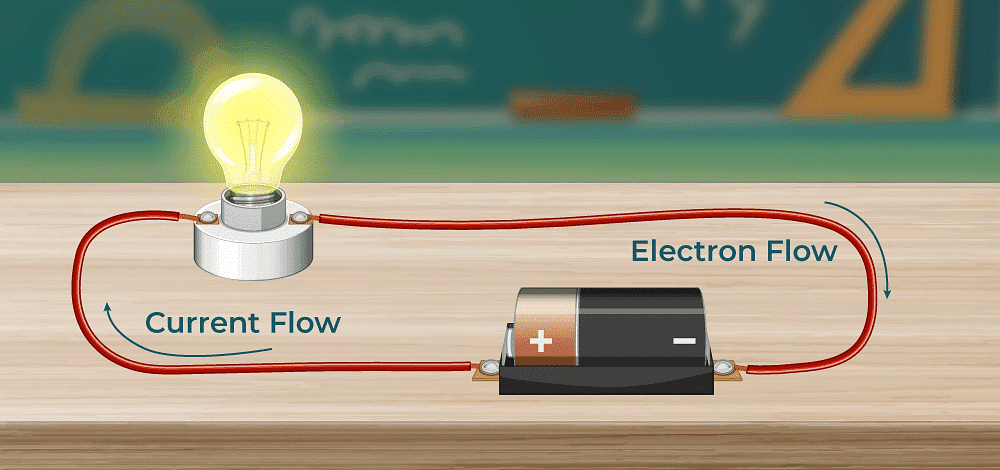
Direction of Current
- Current flows from the positive terminal (longer line) of the cell/battery to the negative terminal (shorter line), though historically, conventional current is considered to flow from positive to negative.
Question for Charge flow in circuitsTry yourself: Which component in an electrical circuit controls the flow of current?View Solution
Circuit Representation
- Simple Circuit: Contains a single power source, such as a cell, connected in a closed loop with components like lamps and switches.
- Complex Circuits: Use various components like resistors, capacitors, and diodes, represented by specific symbols in circuit diagrams.
Conclusion
Understanding electrical circuits involves grasping the roles of current, potential difference, and resistance. These concepts are crucial in explaining how electricity flows through different components in both simple and complex circuits.
The document Charge flow in circuits | Year 7 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 7 is a part of the Class 7 Course Year 7 Physics (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
14 videos|31 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Charge flow in circuits - Year 7 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 7
| 1. How does charge flow in electrical circuits? |  |
Ans. In electrical circuits, charge flows from the negative terminal of the power source to the positive terminal. This flow of charge is due to the movement of electrons.
| 2. What is the role of conductors and insulators in electrical circuits? |  |
Ans. Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electric charge, such as metals. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that do not allow the flow of electric charge, like rubber or plastic.
| 3. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits? |  |
Ans. In a series circuit, the components are connected end to end, creating a single path for the flow of current. In a parallel circuit, the components are connected in separate branches, providing multiple paths for the current to flow.
| 4. How does resistance affect the flow of current in a circuit? |  |
Ans. Resistance restricts the flow of current in a circuit. The higher the resistance, the lower the current that can flow through the circuit. This relationship is described by Ohm's Law, which states that current is inversely proportional to resistance.
| 5. What are the safety precautions to consider when working with electrical circuits? |  |
Ans. Some safety precautions to consider when working with electrical circuits include turning off the power source before making any adjustments, using insulated tools, and wearing protective gear such as gloves and goggles. It is also important to avoid overloading circuits and to follow proper wiring practices to prevent electrical hazards.
Related Searches















