Cheatsheet: Introduction to Business Economics | Business Economics for CA Foundation PDF Download
Overview
Business involves economic activities transforming inputs into outputs to create net value added, such as profit for commercial entities or social benefits for non-profits. It encompasses various sectors and decision-making processes to optimize limited resources.

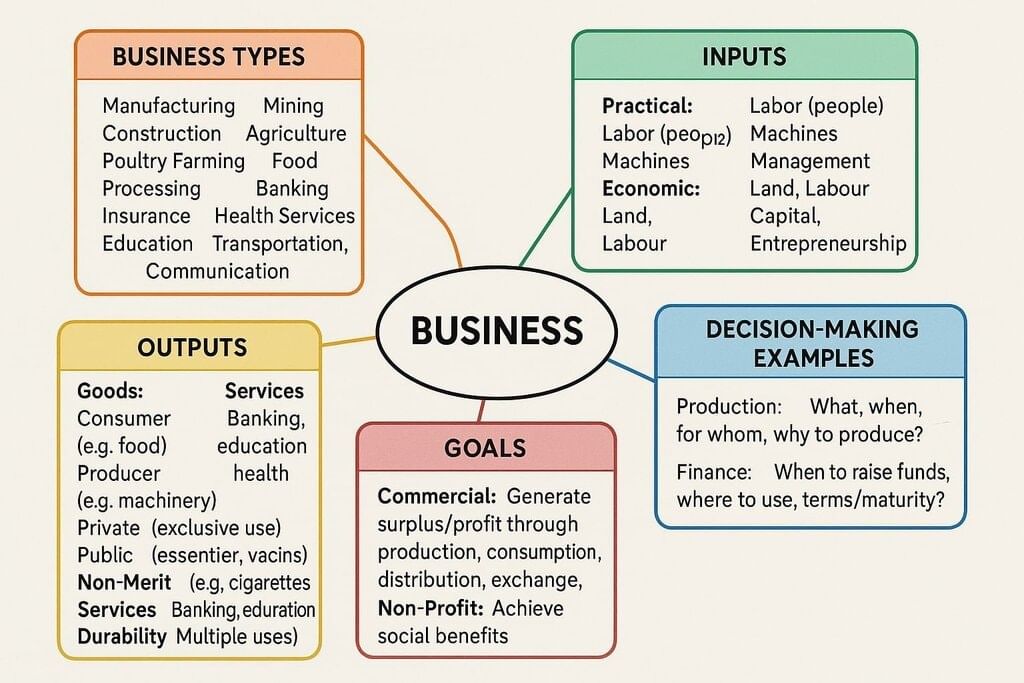
What is Economics?
Economics, derived from the Greek ‘Oikonomia’ (household), studies the allocation of limited resources to satisfy unlimited human wants. Known as ‘Political Economy’ until the 19th century, Adam Smith’s An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776) is a foundational work.
Scenario: Birthday Money
You receive ₹1000 for your birthday with options:
- Throw a party (full amount)
- Buy a dress (₹1000)
- Movie and dining
- Buy a book, save the rest
Limited funds force a choice, maximizing satisfaction.
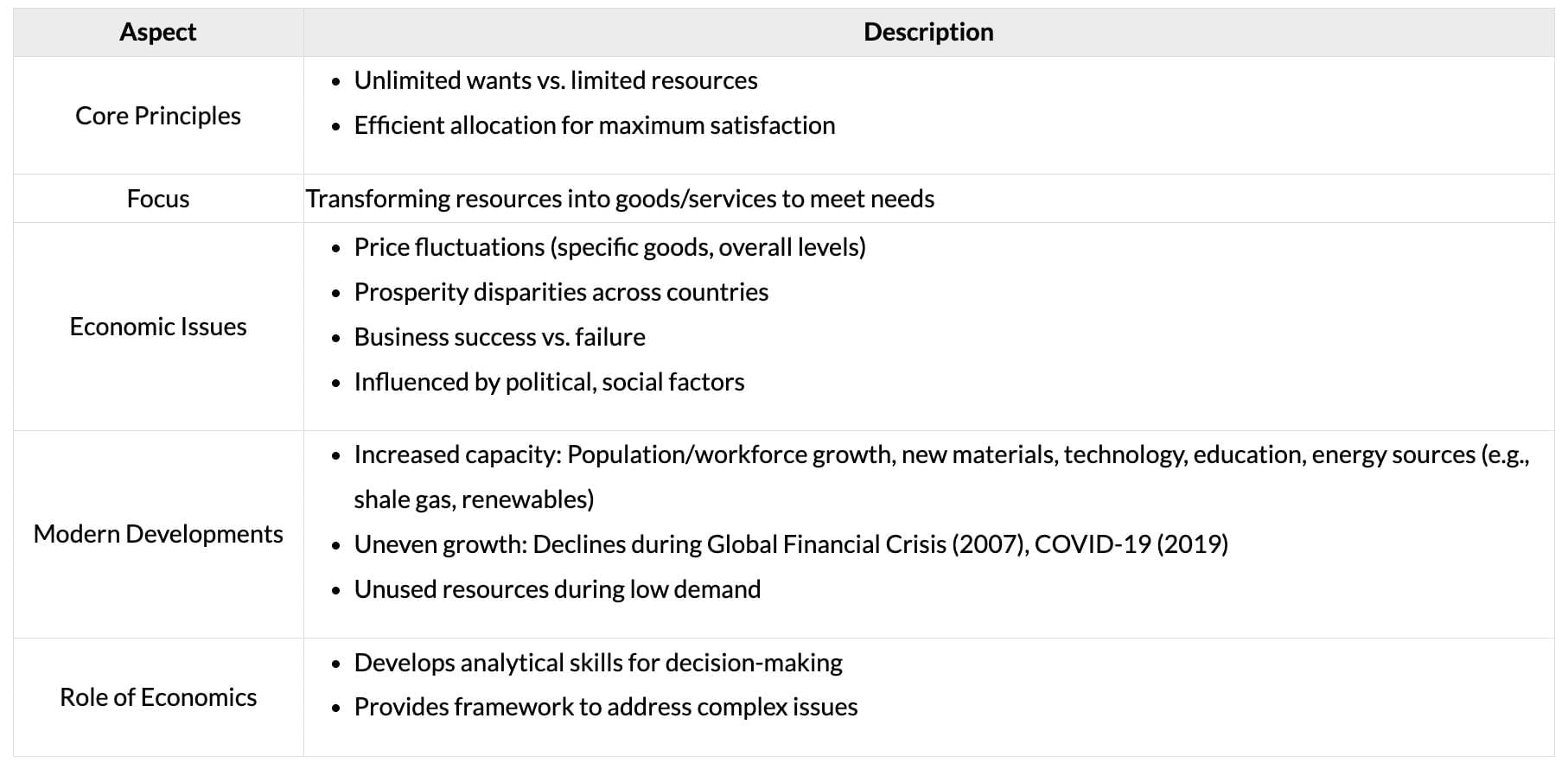
Meaning of Business Economics
Business Economics (Managerial Economics) applies economic analysis to optimize scarce resources for business decisions, integrating Microeconomics and Macroeconomics with practical tools.
Case Study: Worldwide Food Limited
CEO G. Ramamurthy proposes entering the soft drink industry:
- Pros: Expanding market, aligns with food business, high return potential
- Cons: Competition from White Soft Drinks Ltd., Black Nectar Ltd.; past failure of Swati Foods
- Decision: Requires analysis of market trends, competition, and timing

Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
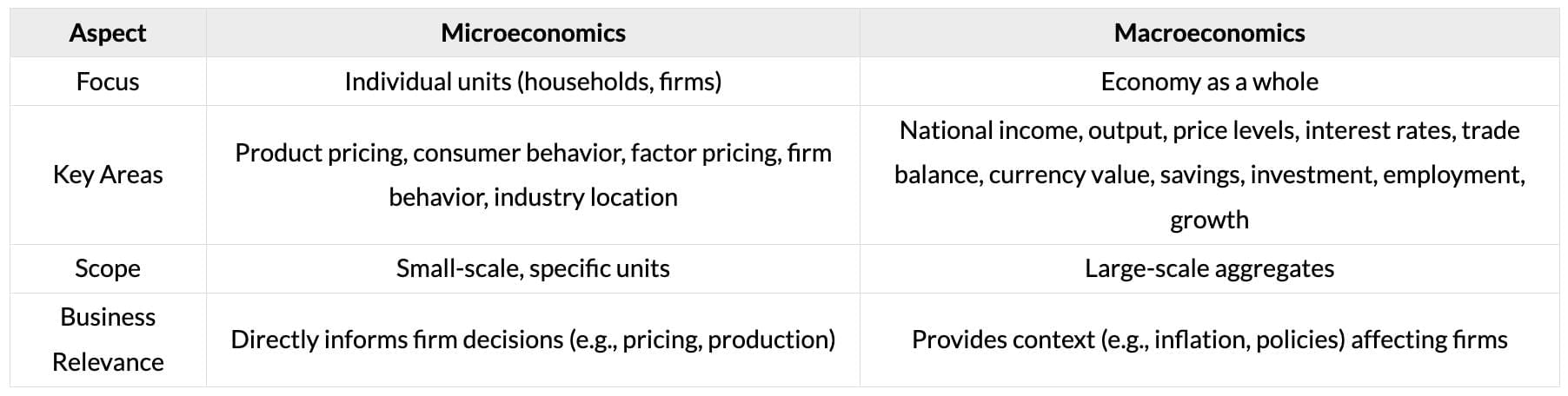
Nature of Business Economics

Scope of Business Economics
Microeconomics and Internal Issues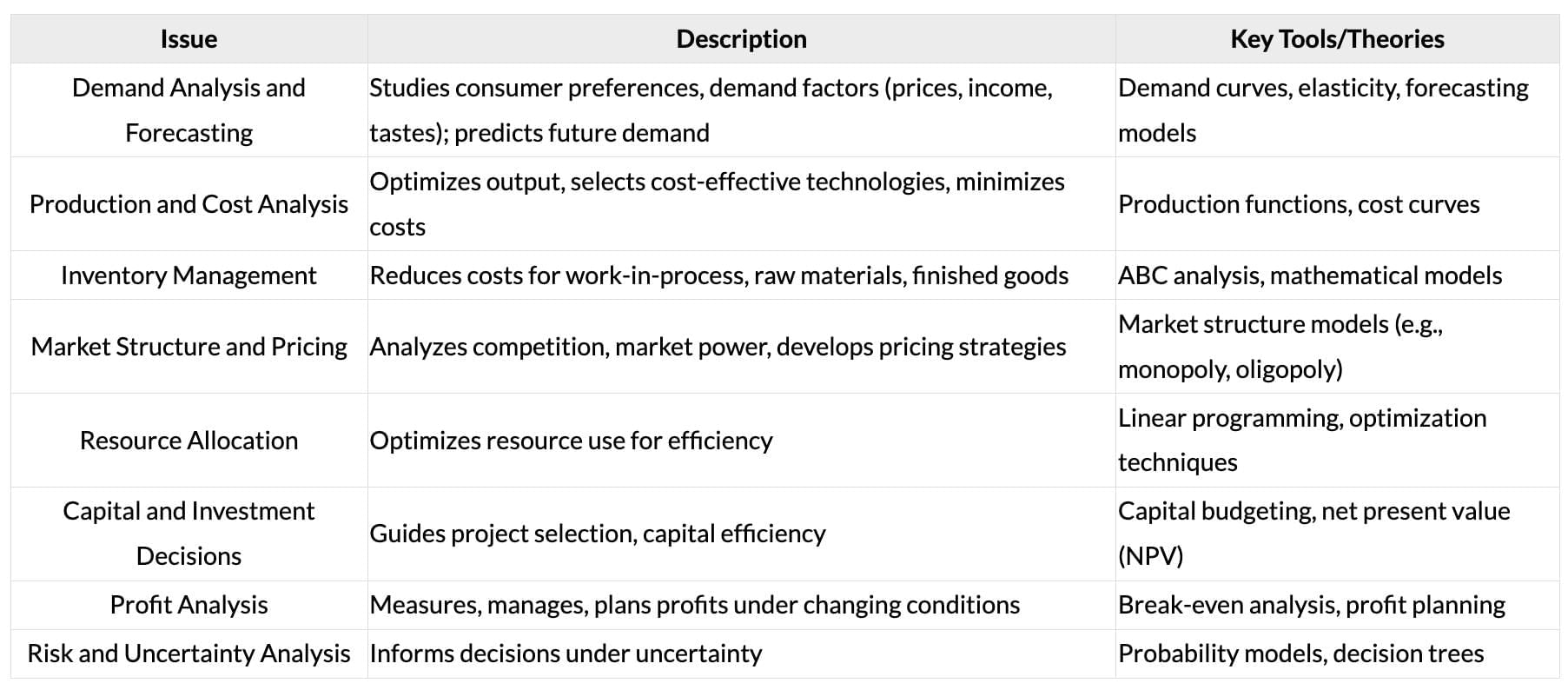
Macroeconomics and External Issues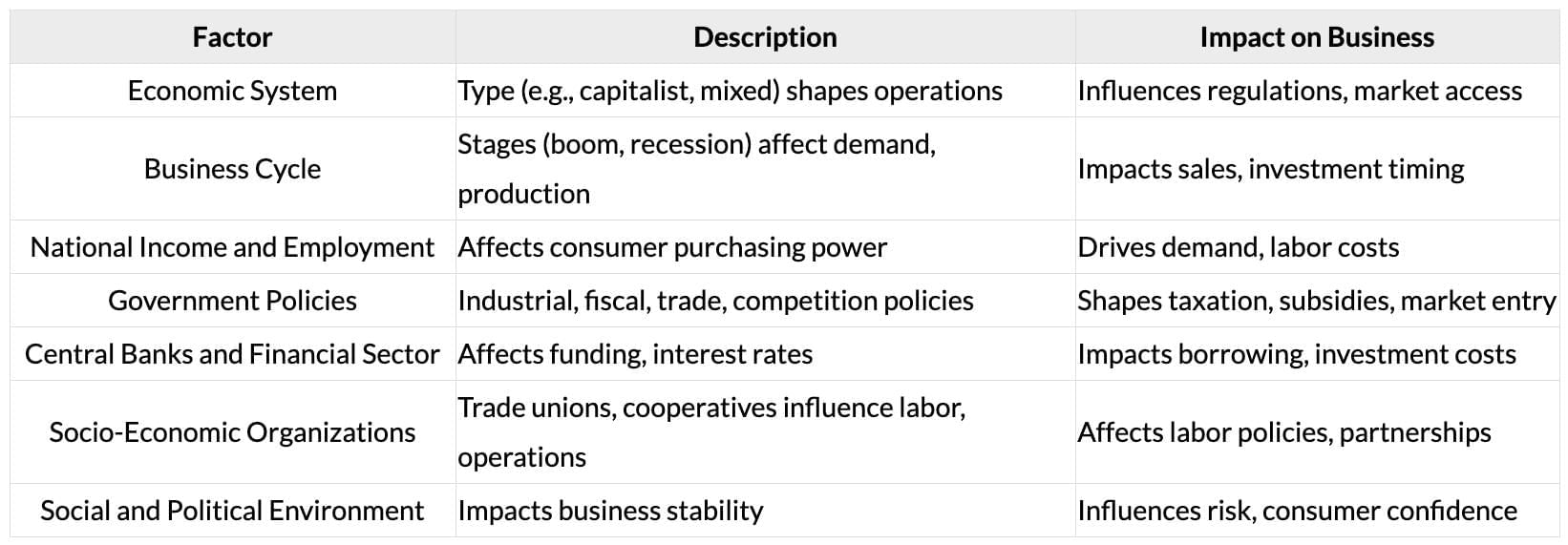
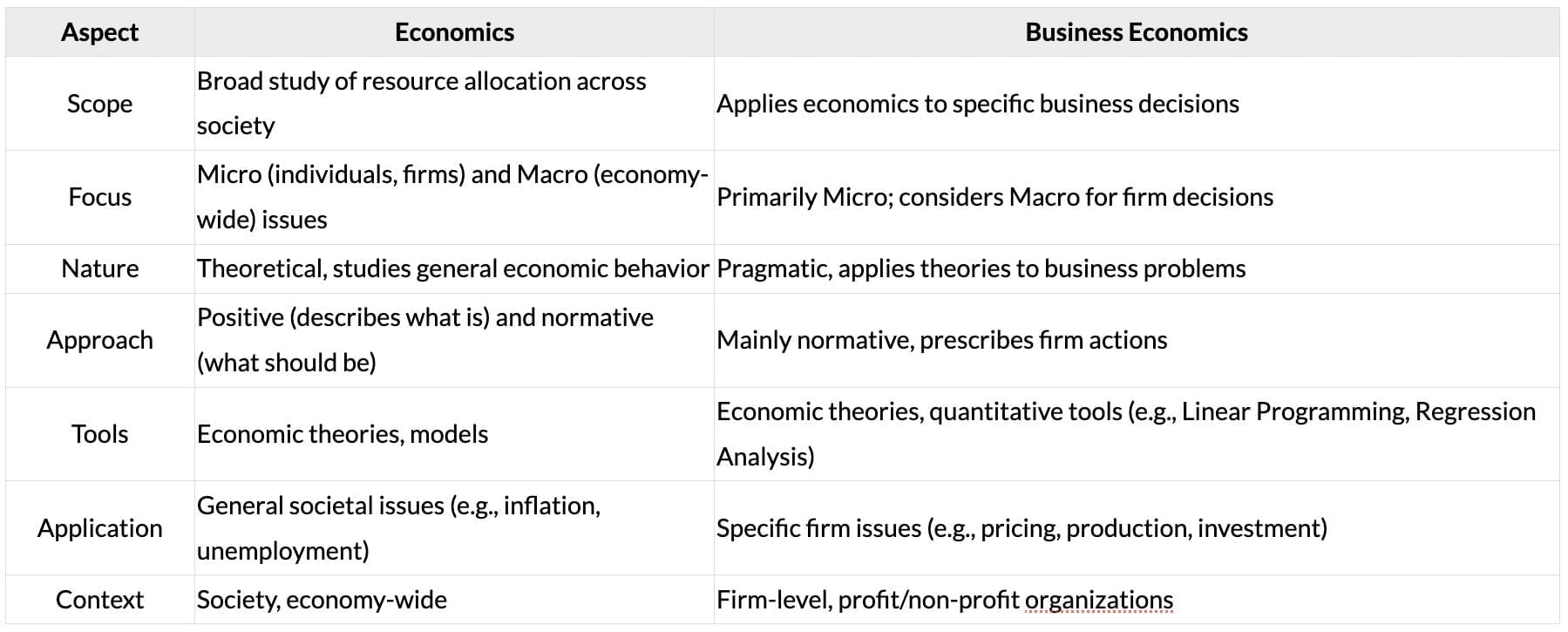
Difference Between Economics and Business Economics
|
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Introduction to Business Economics - Business Economics for CA Foundation
| 1. What is the definition of Economics and its importance in business? |  |
| 2. How does Business Economics differ from traditional economics? |  |
| 3. What are the primary distinctions between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics? |  |
| 4. What is the nature of Business Economics? |  |
| 5. What is the scope of Business Economics in the context of business decision-making? |  |
















