Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Assertion and Reason Questions - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Direction: Each of these questions contains an Assertion followed by Reason. Read them carefully and answer the question on the basis of following options. You have to select the one that best describes the two statements.
Question 1:
Assertion: Stannous chloride is a powerful oxidising agent which oxidises mercuric chloride to mercury.
Reason: Stannous chloride gives grey precipitate with mercuric chloride, but stannic chloride does not do so.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Stannous chloride SnCl2 is a strong reducing agent. It first reduces mercuric chloride (HgCl2) to Mercurous Chloride (greyish) and finally to mercury.SnCl2 + 2HgCl2 → Hg2Cl2 + SnCl2
HgCl2 + SnCl2 →2Hg + SnCl4
So, in above reaction, stannous Chloride is acting as reducing agent that reduces Hg(II) toHg(I) and then Hg(0).
Question 2:
Assertion: In a reaction.
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq)+ Cu (s)
Zn is a reductant but itself get oxidized.
Reason: In a redox reaction, oxidant is reduced by accepting electrons and reductant is oxidized by losing electrons.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Reducing agent is an element or compound that loses an electron to an electron recipient in a redox chemical reaction. A reducing agent is thus oxidized when it loses electrons in the redox reaction. Reducing agents "reduce" oxidizing agents. Oxidizers "oxidize" reducers
Question 3:
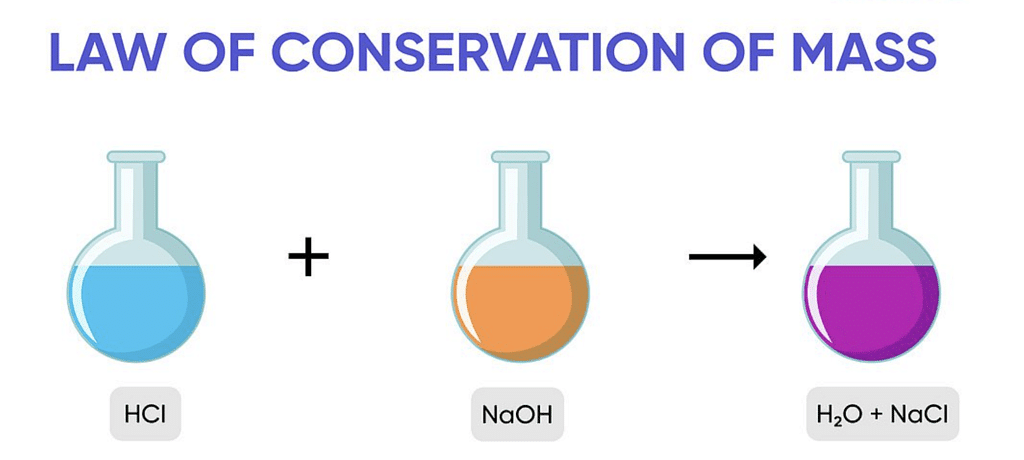
Assertion: The balancing of chemical equations is based on law of conservation of mass.
Reason: Total mass of reactants is equal to total mass of products.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The balancing of chemical equations is based on law of conservation of mass. The Law of conservation of mass states that mass can be neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.Total mass of reactants is equal to total mass of products.
Thus, both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Example of law of conservation of mass
Question 4:
Assertion (A): A chemical reaction becomes faster at higher temperatures.
Reason (R): At higher temperatures, molecular motion becomes more rapid.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A). A chemical reaction becomes faster at higher temperatures because at high temperature, the movement of particles are greater.
Question 5:
Assertion (A): To dilute sulphuric acid, acid is added to water and not water to acid.
Reason (R): Specific heat of water is quite large.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
The mixing of water to an acid is highly exothermic in nature. If water is added to an acid it produces very large amount of heat which can break the container and some times even causes burnings. So it is advised to add concentrated acid to water very slow manner.
Question 6:
Assertion(A): Brown fumes are produced when lead nitrate is heated.
Reason (R): Nitrogen dioxide gas is produced as a by product due to the decomposition of lead nitrate.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
When lead nitrate is heated strongly, NO and O. In this decomposition reaction, the colourless compound lead nitrate forms a yellow compound, lead monoxide, and brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas are evolved.
Question 7:
Assertion(A): Pungent smelling gas is produced when sulphur burns in air.
Reason (R): Sulphur trioxide is formed on reaction of sulphur with oxygen.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Since Reason mentioned is false because when sulphur burns in air then sulphur reacts with oxygen to form sulphur dioxide which gives the pungent smell.
Question 8:
Assertion: The following chemical equation,
2C6H6 + 7/2O2 → 4CO2 + 3H2O
is a balanced chemical equation.
Reason: In a balanced chemical equation, the total number of atoms of each element may or may not equal on both side of the equation.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Both Assertion and Reason are false. Both Assertion and Reason are false. In a balanced chemical equation, the total number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides of the equation. The correct balanced chemical equation is, 2C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O
Question 9:
Assertion: In the following chemical equation,
CuO (s) + Zn (s) → ZnO (s)+ Cu (s)
Zinc is getting oxidised and copper oxide is getting reduced.
Reason: The process in which oxygen is added to a substance is called oxidation whereas the process in which oxygen is removed from a substance is called reduction.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. Because the reaction involves both oxidation and reduction in which, CuO is reduced to Cu and Zn is oxidised to ZnO.
Question 10:
Assertion (A): Sodium metal is stored under Kerosene.
Reason (R): Metallic sodium melts when exposed to air.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false. Sodium is a very reactive metal. It is kept in kerosene to prevent it from coming in contact with oxygen and moisture present. If this happens, it will react with the moisture present in air and form sodium hydroxide. This is a strongly exothermic reaction, and lot of heat is generated.
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Assertion and Reason Questions - Chemical Reactions and Equations
| 1. What is the difference between a chemical reaction and a chemical equation? |  |
| 2. How can we determine the type of chemical reaction based on a chemical equation? |  |
| 3. Why is balancing a chemical equation important? |  |
| 4. How can we balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of chemical equations? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|