Citizenship Class 11 Political Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Full and Equal Membership |

|
| Equal Rights |

|
| Citizen and Nation |

|
| Universal Citizenship |

|
| Global Citizenship |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
- Citizenship means full and equal membership in a political community, granting a collective political identity and state-provided rights.
- Citizens expect rights, help, and protection from their state, both at home and abroad.
- Refugees and illegal migrants, like Palestinian refugees, highlight the value of state membership, living precariously without guaranteed rights.
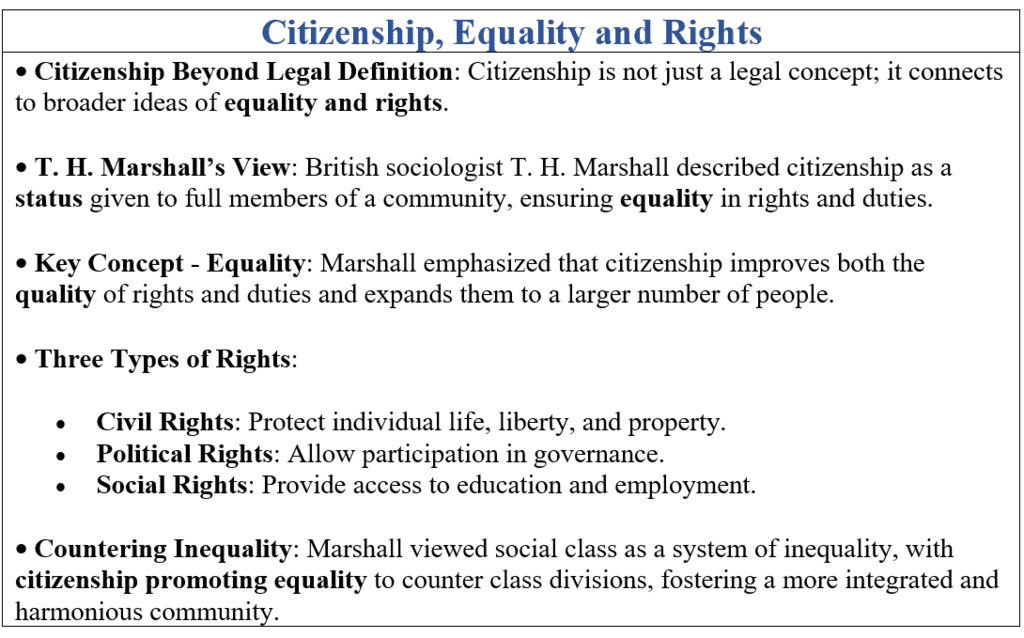
- Rights include political (e.g., voting), civil (e.g., free speech), and socio-economic (e.g., education), varying by state.
- Equality is central to citizenship in democracies.

- Rights were won through struggles, such as the French Revolution, anti-colonial movements, and South Africa’s fight for equal citizenship.
- Movements like India’s women’s and Dalit movements push for equal rights and opportunities.
- Citizenship also includes citizen–citizen obligations to contribute to community life and preserve culture and resources.
- Challenges to citizenship arise when groups feel their needs are ignored, spurring demands for inclusion.
Full and Equal Membership
- Full and equal membership in a political community raises questions about whether citizens should have equal rights and opportunities across all regions of a country.
- Freedom of movement, a key right of citizens, allows workers to migrate for jobs, such as I.T. professionals to Bangalore or nurses from Kerala, but can lead to tensions when locals resist outsiders competing for limited jobs or resources.
- Resistance to migrants, often expressed through demands like “Mumbai for Mumbaikars,” may prioritise local or state-based identity, sometimes leading to organised violence against outsiders.
- Debates arise over whether freedom of movement includes the right to live and work anywhere in the country, especially when locals resent competition for scarce jobs.
- Attitudes differ toward skilled versus poor, unskilled migrants, raising questions about whether all citizens should have equal rights to migrate and work regardless of their socioeconomic status.
- Disputes over migration and rights can be addressed in democratic societies through freedom of expression, including protests, forming groups, using media, or approaching courts, provided actions do not harm others or the state.
- Courts may rule on disputes or urge government action, but resolving issues relies on negotiation and discussion rather than force, aligning with the democratic principle of ensuring full and equal membership for all citizens.
Equal Rights
- Equal rights in citizenship raise the question of whether all citizens, regardless of wealth, should be guaranteed basic rights and a minimum standard of living by the state.
- Urban poor, such as slum-dwellers and squatters, face harsh living conditions (e.g., cramped housing, no sanitation) but contribute significantly to the economy as hawkers, traders, or labourers.
- Slum-dwellers are often viewed negatively, blamed for straining city resources or spreading crime, despite receiving minimal services like water or sanitation.
- Awareness of the urban poor’s conditions is growing, with policies like the 2004 national policy on urban street vendors aimed at protecting vendors from harassment while regulating their work.
- Slum-dwellers are organising to demand rights, including the right to vote, which is challenging due to the lack of a fixed address for voter registration.
- Tribal people and forest dwellers face threats to their livelihoods from population growth, commercial interests (e.g., mining), and tourism, raising questions about balancing their rights with national development.
- Ensuring equal rights is complex, as different groups have unique needs, and uniform policies may not address these disparities effectively.
- Equal citizenship requires policies that consider diverse needs to promote equality, not just apply the same rules to all.
- Changing economic and social conditions demand evolving interpretations of citizenship rights, with equal rights and protection as guiding principles for government policies.
 Citizenship, Equality and Rights
Citizenship, Equality and Rights
Citizen and Nation
- The concept of the nation-state emerged in the modern era, with early claims of sovereignty and citizen rights during the French Revolution in 1789.
- A nation-state defines a territory with a unique culture and shared history, expressed through symbols like the flag, national anthem, or national language.
National Identity and Inclusivity
- Modern states include people of diverse religions, languages, and cultural traditions, aiming to provide a shared political identity for all citizens.
- Democratic states strive for an inclusive national identity so all citizens feel part of the nation, but some groups find it easier to identify with the state than others.
- In practice, national identity may favour certain groups, affecting who is granted citizenship, even in countries like the United States, known for its immigrant heritage.
Challenges of Assimilation
- In France, a secular and inclusive nation, citizens must assimilate into the national culture and language in public life while keeping personal beliefs private.
- Defining public versus private spheres causes controversies, such as Sikh boys wanting to wear turbans or Muslim girls wearing headscarves in schools, which some schools banned as religious symbols.
- Assimilation is easier for those whose practices align with the majority, creating challenges for minority groups.
Citizenship Criteria
- Citizenship criteria differ across countries; for example, Israel and Germany may prioritise religion or ethnic origin when granting citizenship.
In Germany, children of Turkish workers born and raised there face debates over automatic citizenship, showing restrictions in inclusive democracies.
India’s Approach to Citizenship
- India defines itself as a secular, democratic nation-state, shaped by an independence movement uniting diverse religions, regions, and cultures.
- Despite the Partition in 1947, Indian leaders were committed to a secular and inclusive nation-state, as outlined in the Indian Constitution.
- The Indian Constitution ensures full and equal citizenship for diverse groups like the Scheduled Castes, the Scheduled Tribes, women, and remote communities in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Citizens can retain personal beliefs, languages, and cultural practices while enjoying equal rights.
- Citizenship in India is acquired by birth, descent, registration, naturalisation, or inclusion of territory, as per Part Two of the Constitution and related laws.
- The Constitution prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth, and protects religious and linguistic minorities.
- The Republic Day parade in Delhi symbolises India’s effort to include diverse regions, cultures, and religions.
Ongoing Struggles and Evolution
- Despite inclusive provisions, struggles continue, such as those by the women’s movement, Dalit movement, and people displaced by development projects, who feel denied full citizenship rights.
- Democratic citizenship is an ongoing project, evolving as societies change and marginalised groups raise new demands.
- In a democratic state, these demands are addressed through negotiation, reflecting the dynamic nature of citizenship and its rights.

Universal Citizenship
- Refugees and illegal migrants include people smuggled from Asia or Africa to Europe or America, or those displaced by war or famine, like in Darfur, Sudan, Palestinians, Burmese, or Bangladeshis.
- TV often shows images of people forced to leave their homes due to war or famine.
- People assume those who live and work in a country, or apply for citizenship, should get full membership, but states set criteria in their laws.
- States use their power to keep unwanted visitors out with walls or fences.
- Despite restrictions, migration happens due to wars, persecution, famine, or other reasons.
- Stateless people, not accepted by any state and unable to return home, live in camps or as illegal migrants, unable to work, educate children, or own property.
- The U.N. has a High Commissioner for Refugees to help these people.
- Deciding how many refugees to accept is a tough humanitarian and political problem for states.
- Many countries accept those fleeing persecution or war, but worry about security risks or too many people.
- India gave refuge to persecuted people, like the Dalai Lama and his followers, in 1959.
- People from neighbouring countries enter India, and many remain stateless for years, with few gaining citizenship.
- Statelessness challenges the promise of democratic citizenship to provide rights and identity to all.
- Wars or political disputes redefine borders, causing people to lose homes, political identities, and security.
- Without a state to grant citizenship, people lack an alternative identity.
- Suggestions for global citizenship are made to provide a universal identity, which to be discussed later.
Global Citizenship
- Examples like the 2004 South Asia tsunami relief, international terrorist networks, and the UN’s work to prevent bird flu show we live in an interconnected world.
- New communication tools like the internet, TV, and cell phones let us learn about global events instantly, unlike in the past when news took months to spread.
- Watching disasters and wars on TV creates shared sympathies among people across countries.
- Supporters of global citizenship say these shared feelings, like help for tsunami victims, show a growing global society, encouraging a universal identity.
- National citizenship assumes states provide rights and protection for a dignified life, but states face problems they can’t solve alone.
- Questions arise about whether state-guaranteed rights are enough or if human rights and global citizenship are needed for better protection.
- Global citizenship could help solve problems crossing borders, like migration or statelessness, by ensuring basic rights and protection for all, regardless of location.
- Socio-economic inequalities within countries threaten equal citizenship, which only local governments and people can fully solve.
- Global citizenship complements national citizenship by reminding us to strengthen ties with people worldwide and work together across borders.
Conclusion
- Citizenship is a dynamic relationship that goes beyond legal status, involving both individual rights and collective responsibilities.
- As we face modern challenges, from local disputes to global issues, our commitment to equality and inclusion will shape the future of citizenship.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Citizenship Class 11 Political Science
| 1. What is full and equal membership in the context of citizenship? |  |
| 2. How do equal rights relate to citizenship? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of universal citizenship? |  |
| 4. What does global citizenship entail? |  |
| 5. How can individuals actively participate in promoting citizenship rights? |  |
















