Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Case Based Questions - Understanding Economic Development
Q1:
Rajesh works in a bank as a bank manager. He goes regularly to his bank and attends his bank services from 9.00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. He gets his salary at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, he also gets provident fund as per the rules laid down by the government. He also gets earned leaves, sick leaves and casual leaves. Apart from leaves, he receives medical and other allowances. Rajesh does not go to bank on Saturdays and Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When he joined bank, he was given an appointment letter stating all the terms and conditions of work and his job is secure. Ram is Rajesh’s neighbour. He is a daily wage labourer in a nearby grocery shop. He goes to the shop at 7:00 am in the morning and works till 10:00 p.m. in the evening. He gets no other allowances apart from his wages. He is not paid for the days he does not work. He has therefore no leave or paid holidays. Nor was he given any formal appointment letter saying that he has been employed in the shop. He can be asked to leave anytime by his employer if his job is not found satisfactory. His job is not secure. Rajesh works in the organized sector whereas Ram works in an unorganized sector. Q. In the urban areas, unorganised sector comprises mainly of
Q2:
Rajesh works in a bank as a bank manager. He goes regularly to his bank and attends his bank services from 9.00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. He gets his salary at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, he also gets provident fund as per the rules laid down by the government. He also gets earned leaves, sick leaves and casual leaves. Apart from leaves, he receives medical and other allowances. Rajesh does not go to bank on Saturdays and Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When he joined bank, he was given an appointment letter stating all the terms and conditions of work and his job is secure. Ram is Rajesh’s neighbour. He is a daily wage labourer in a nearby grocery shop. He goes to the shop at 7:00 am in the morning and works till 10:00 p.m. in the evening. He gets no other allowances apart from his wages. He is not paid for the days he does not work. He has therefore no leave or paid holidays. Nor was he given any formal appointment letter saying that he has been employed in the shop. He can be asked to leave anytime by his employer if his job is not found satisfactory. His job is not secure. Rajesh works in the organized sector whereas Ram works in an unorganized sector. Q. Which of the following statements is an example of unorganised sector activities?
Q3:
Rajesh works in a bank as a bank manager. He goes regularly to his bank and attends his bank services from 9.00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. He gets his salary at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, he also gets provident fund as per the rules laid down by the government. He also gets earned leaves, sick leaves and casual leaves. Apart from leaves, he receives medical and other allowances. Rajesh does not go to bank on Saturdays and Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When he joined bank, he was given an appointment letter stating all the terms and conditions of work and his job is secure. Ram is Rajesh’s neighbour. He is a daily wage labourer in a nearby grocery shop. He goes to the shop at 7:00 am in the morning and works till 10:00 p.m. in the evening. He gets no other allowances apart from his wages. He is not paid for the days he does not work. He has therefore no leave or paid holidays. Nor was he given any formal appointment letter saying that he has been employed in the shop. He can be asked to leave anytime by his employer if his job is not found satisfactory. His job is not secure. Rajesh works in the organized sector whereas Ram works in an unorganized sector. Q. Which of the following statement is not true with respect to organized sector?
Q4:
Rajesh works in a bank as a bank manager. He goes regularly to his bank and attends his bank services from 9.00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. He gets his salary at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, he also gets provident fund as per the rules laid down by the government. He also gets earned leaves, sick leaves and casual leaves. Apart from leaves, he receives medical and other allowances. Rajesh does not go to bank on Saturdays and Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When he joined bank, he was given an appointment letter stating all the terms and conditions of work and his job is secure. Ram is Rajesh’s neighbour. He is a daily wage labourer in a nearby grocery shop. He goes to the shop at 7:00 am in the morning and works till 10:00 p.m. in the evening. He gets no other allowances apart from his wages. He is not paid for the days he does not work. He has therefore no leave or paid holidays. Nor was he given any formal appointment letter saying that he has been employed in the shop. He can be asked to leave anytime by his employer if his job is not found satisfactory. His job is not secure. Rajesh works in the organized sector whereas Ram works in an unorganized sector. Q. In the rural areas, the unorganized sector mostly comprises of
Q5:
There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector. The secondary sector covers activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature but has to be made and therefore some process of manufacturing is essential. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services. The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. Q. Which of the following is an example of tertiary activities?
Q6:
There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector. The secondary sector covers activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature but has to be made and therefore some process of manufacturing is essential. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services. The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. Q. Match the following list of occupations with their sectors: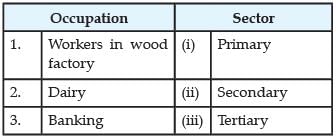
Q7:
There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector. The secondary sector covers activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature but has to be made and therefore some process of manufacturing is essential. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services. The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. Q. Production of a commodity, mostly through ways of manufacturing is an activity of which sector?
Q8:
There are many activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector. The secondary sector covers activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature but has to be made and therefore some process of manufacturing is essential. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. The various production activities in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors produce a very large number of goods and services. Also, the three sectors have a large number of people working in them to produce these goods and services. The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. Q. Which of the following statement is not true?
|
64 videos|445 docs|87 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
















