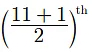Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Assertion and Reason Questions - Statistics
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Question 1:
Assertion (A): If the value of mode and mean is 60 and 66 respectively, then the value of median is 64.
Reason (R): Median = (mode + 2 mean)
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Median = 1/3 (mode + 2 mean)
= 1/3 (60 + 2 x 66) = 64
Question 2:
Assertion (A): If the number of runs scored by 11 players of a cricket team of India are 5, 19, 42, 11, 50, 30, 21, 0, 52, 36, 27 then median is 30.
Reason (R): Median 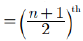 value, if n is odd.
value, if n is odd.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Arranging the terms in ascending order, 0, 5, 11, 19, 21, 27, 30, 36, 42, 50, 52
Median value =
= 6th value = 27
Question 3:
Assertion (A): The arithmetic mean of the following given frequency distribution table is 13.81.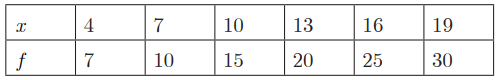
Reason (R): 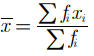
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion and reason are true, reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 4:
Assertion (A) : Class width = upper class limit – lower class limit
Reason (R) : Class mark =(Upper Class Limit+ Lower Class Limit)/2
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Question 5:
Assertion (A) : Frequency is the number of times a particular observation occurs in data.
Reason (R) : Data can be grouped into class intervals such that all observations in that range belong to that class.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Question 6:
Assertion (A) : The mode of the call received on 7 consecutive day 11,13,13,17,19,23,25 is 13.
Reason (R) : Mode is the value that appears most frequent;
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
Question 7:
Assertion (A) : The runs scored by a batsman in 5 ODIs are 31,97,112, 63, and 12. The standard deviation is 25.79.
Reason (R) : Total sum of number in data sets./ total number in data sets.
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Assertion and Reason Questions - Statistics
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in the assertions and reason type questions in statistics? |  |
| 2. How do assertions and reasons relate to statistical reasoning in exams? |  |
| 3. What strategies can be used to effectively answer assertions and reason questions in statistics? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of an assertion and reason type question in statistics? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to differentiate between assertions and reasons in statistical examinations? |  |