Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
Very Short Answer Questions :
Q1. Name the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
Ans: Nephron
Q2. Name the structure that stores urine temporarily.
Ans: Urinary bladder
Q3. Name the U-shaped tubule of the nephron.
Ans: Loop of Henle
Q4. What is the main drawback of artificial kidneys?
Ans: There is no reabsorption of useful substances
Q5. Name the tube that passes out urine from the urinary bladder.
Ans: Ureter
Q6. Name the chief nitrogenous waste materials in human beings.
Ans: Ammonia, Urea, Uric acid
Q7. What is the advantage of the presence of two kidneys in man?
Ans: If one kidney fails, man can live on the other kidney
Q8. Name two parts of a nephron.
Ans: Bowman's capsule and nephric tubule
Q9: Where does ultrafiltration occur in the nephron?
Ans: Bowman's capsule
Q10. Name three parts of the nephric tubule.
Ans: PCT, loop of Henle, DCT
Q11. Define glomerulus.
Ans: A tuft of capillaries is present in the cavity of Bowman's capsule.
Q12. Give the technical term for passing the useful substances from nephric filtrate back into blood in blood capillaries.
Ans: Selective reabsorption.
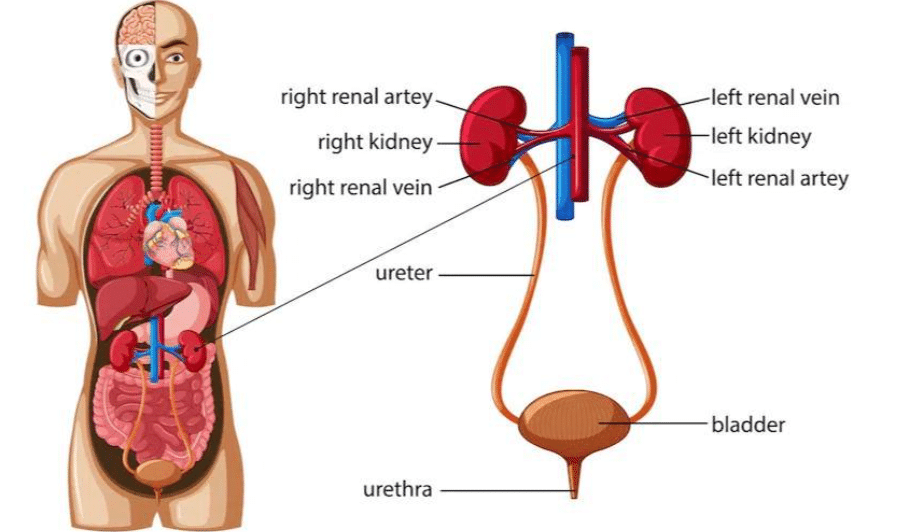 Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System
Short Answer Questions :
Q1. Define :
(a) Osmoregulation
(b) Haemodialysis
(c) Malpighian body
Ans: (a) Osmoregulation: It is the process by which organisms maintain the balance of water and salts in their bodies. This regulation is crucial for cellular function and overall homeostasis.
(b) Haemodialysis: This is a medical procedure used to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly. It involves passing blood through a machine that filters out harmful substances.
(c) Malpighian body: It refers to a part of the nephron in the kidneys, consisting of the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule. This structure is essential for the filtration of blood and the formation of urine.
Q3. Differentiate between the ureter and urethra.
Ans: Ureter and urethra are both parts of the urinary system, but they serve different functions:
Ureter:
- There are two ureters, one for each kidney.
- They transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Ureters are muscular tubes that help move urine through peristalsis.
Urethra:
- It is a single tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- The urethra is shorter in females than in males.
- It also serves as a passage for semen in males.
Q4. What will happen if there is no tubular reabsorption in the nephrons of kidneys?
Ans: If there is no tubular re-absorption in the nephrons of the kidneys, several critical issues arise:
- The body would lose essential substances such as glucose, amino acids, and salts.
- Excess water would not be reabsorbed, leading to a significant increase in urine volume.
- This could result in severe dehydration and an imbalance of electrolytes in the body.
- Accumulation of waste products in the blood would occur, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Overall, the body's ability to maintain homeostasis would be severely compromised.
Q5. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Ans: The regulation of urine production involves several key processes:
- Kidneys filter waste from the blood, producing urine.
- Each kidney contains many nephrons, which are the basic filtration units.
- As urine forms, substances like glucose, amino acids, and salts are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
- The amount of water reabsorbed depends on the body's need for water and the concentration of waste.
- Urine travels from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder, where it is stored.
- When the bladder fills, nerve signals trigger the urge to urinate, allowing control over when to release urine through the urethra.
Q6. What happens to glucose that enters the nephron along with filtrate during excretion in human beings? State two vital functions of the kidney.
Ans: When glucose enters the nephron with the filtrate, it undergoes a process called reabsorption. This means that the body takes back the glucose it needs, preventing its loss in urine. The nephron selectively reabsorbs glucose along with other essential substances like amino acids and salts. The kidneys serve two vital functions:
- Filtration: They filter waste products and excess substances from the blood, forming urine.
- Regulation: They help maintain the body's fluid and electrolyte balance, ensuring homeostasis.
Q7. Name the organ system responsible for excretion.
Ans: The organ system responsible for excretion in humans is the excretory system. It consists of:
- Kidneys: Two organs that filter blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Urinary bladder: A storage organ for urine.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine is expelled from the body.
This system plays a crucial role in removing waste products and maintaining the body's fluid balance.
Q8. Name the major excretory product of human beings.
Ans: The major excretory product of human beings is urea. This nitrogenous waste is produced during the breakdown of proteins and is primarily eliminated through urine.
- Urea is formed in the liver from ammonia, which is toxic.
- It is transported to the kidneys, where it is filtered from the blood.
- Excess water and other waste products are also removed in urine.
The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and ensuring that harmful substances are excreted efficiently.
Q9. Name three nitrogenous wastes produced during the metabolism.
Ans: Three main types of nitrogenous wastes produced during metabolism are:
- Urea - A less toxic compound formed from ammonia, primarily excreted by mammals.
- Uric acid - A more concentrated waste product, excreted by birds and reptiles to conserve water.
- Ammonia - A highly toxic waste, primarily excreted by aquatic organisms due to its solubility in water.
Long Answer Questions :
Q1. Describe the structure of the human nephron.
Ans: The human nephron is the basic functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. Its structure includes:
- Bowman's capsule: A cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus and collects the filtrate.
- Glomerulus: A network of tiny blood vessels where filtration occurs, separating waste from blood.
- Proximal convoluted tubule: The first segment of the nephron, where most reabsorption of nutrients like glucose and amino acids occurs.
- Loop of Henle: A U-shaped section that concentrates urine and helps conserve water.
- Distal convoluted tubule: The segment where further reabsorption and secretion of ions take place.
- Collecting duct: The final part of the nephron that collects urine and transports it to the renal pelvis.
Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons, working together to filter blood and regulate water and electrolyte balance.
Q2. Explain the structure of the excretory system and nephron with the help of a well-labelled diagram.
Ans: 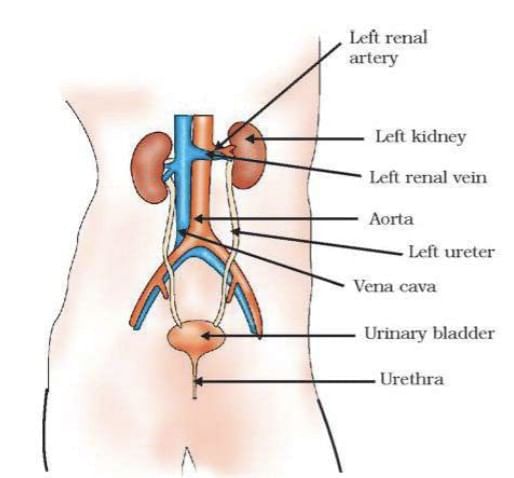 Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System
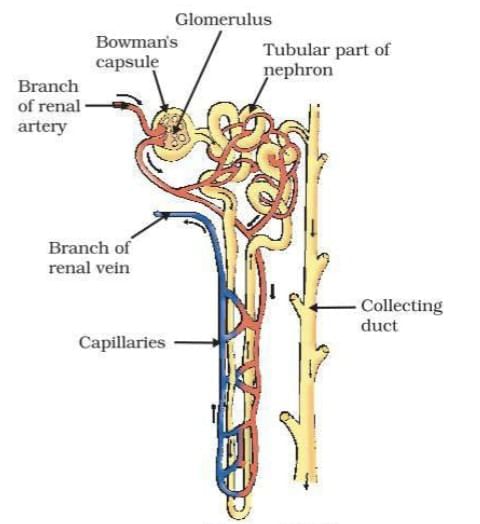 Nephron Structure
Nephron Structure
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| 1. What is excretion, and why is it important in humans and plants? |  |
| 2. What are the main excretory organs in humans? |  |
| 3. How do plants excrete waste? |  |
| 4. What role do the kidneys play in the excretion process? |  |
| 5. What are some common waste products that humans excrete? |  |

















