Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
One Word Questions
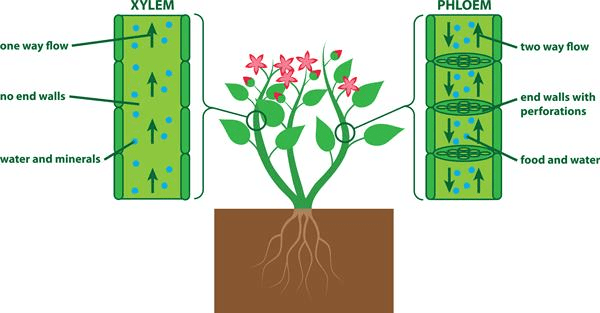
Name the conducting tissue in plants.
 Transportation in Plants
Transportation in PlantsName the components of xylem tissue.
Name the tissue which transports water and minerals in plants.
State the term used for loss of water in vapour form from the aerial part of the plants.
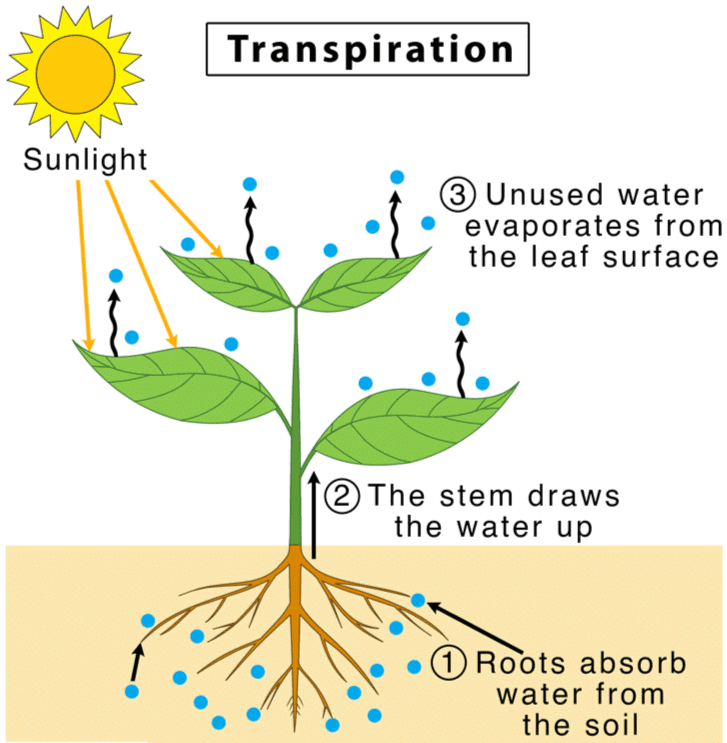
Define the term transpiration.
Define the ascent of sap.
Name the components of phloem tissue.
Which plant tissue is associated with translocation?
State the term used for transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Define the term translocation.
 Transpiration
Transpiration
Very Short Answer Type Questions
What is transpiration?
What is translocation?
Name a plant which does not have a transport system.
What is the role of stomata in transpiration?
Name the tissues responsible for the translocation of food in plants.
Name the process by which plants lose water.
Name that component of the vascular bundle which transports food from the leaves to different parts of a plant.
What is the transporting medium in higher plants?
What is the upward movement of water and minerals called?
Which process in plants creates a suction force to help the water column rise in plants?
Short Answer Type Questions
Write about the opening and closing of stomata.
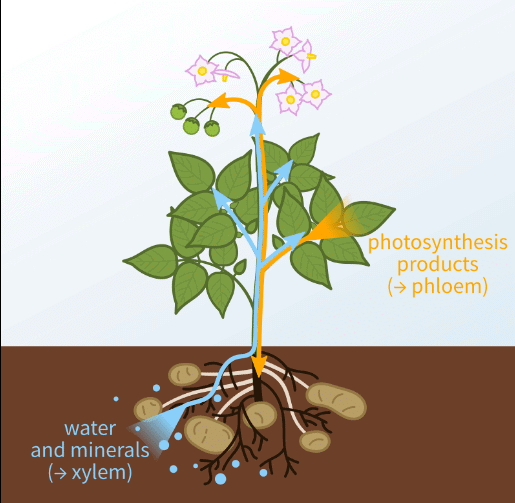
Why is transportation of materials necessary?
Describe the transport of the following materials in plants:
Water
Food
Write the main difference between xylem and phloem.
How does transpiration help in the ascent of sap?
Long Answer Type Questions
Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State three reasons for your answer.
What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesized:
(a) Sugar
(b) Hormones
NCERT Questions
What are the components of the transport system in highly organized plants?
How is food transported in plants?
How are water and minerals transported in plants?
What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Fill in the blanks
In plants, food is transported through _________.
In plants, water is transported through _________.
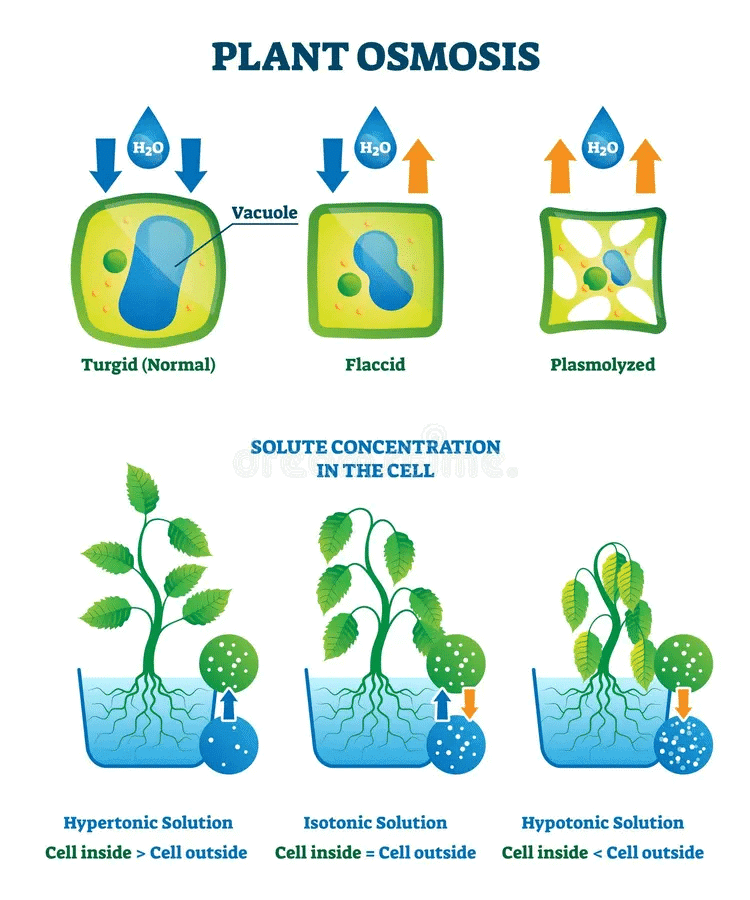
Water enters into the root hair from soil by _________.
Transport of water and minerals is called _________.
The water moving upward forms a column, which is maintained up to a certain height due to _________.
Vascular tissues in plants are _________ and _________.
During the day period, _________ and _________ help in the upward movement of sap from roots to leaves.
Transpiration mainly occurs through _________.
Guttation takes place through _________.
Translocation takes place through energy in the form of _________.
Water enters into sieve tubes containing sugar by the process of _________.
According to plant requirements, sugar is translocated from _________ osmotic pressure to _________ osmotic pressure areas.
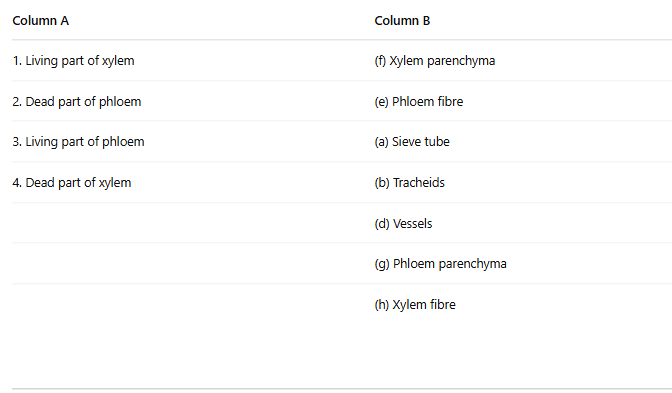
Match the Columns
Answers and Explanation
Answers: One Word Questions:
Name the conducting tissue in plants.
Answer: Xylem and Phloem
Explanation: Xylem conducts water and minerals, while phloem conducts food (mainly sugars).
Name the components of xylem tissue.
Answer: Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem parenchyma, Xylem fibres
Explanation: Tracheids and vessels are involved in the conduction of water, while xylem parenchyma stores food and xylem fibres provide structural support.
Name the tissue which transports water and minerals in plants.
Answer: Xylem
Explanation: Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the other parts of the plant.
State the term used for the loss of water in vapour form from the aerial part of the plants.
Answer: Transpiration
Explanation: Transpiration is the process through which plants lose water vapour mainly from the stomata of leaves.
Define the term transpiration.
Answer: The process by which plants lose water vapour to the atmosphere, mainly through the stomata in leaves.
Explanation: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant and driving the upward movement of water and minerals.
Define the ascent of sap.
Answer: The upward movement of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves through the xylem.
Explanation: This process is driven by transpiration pull, root pressure, and capillary action.
Name the components of phloem tissue.
Answer: Sieve tubes, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, Phloem fibres
Explanation: Sieve tubes and companion cells are involved in food transport, while phloem parenchyma stores food, and phloem fibres provide support.
Which plant tissue is associated with translocation?
Answer: Phloem
Explanation: Phloem is responsible for the translocation of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
State the term used for the transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Answer: Translocation
Explanation: Translocation is the process of transporting food (mainly sugars) through the phloem from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Define the term translocation.
Answer: The process by which food is transported from the leaves to other parts of the plant via the phloem.
Explanation: This ensures that all plant parts receive the necessary nutrients for growth.
Answers: Very Short Answer Type Questions:
What is transpiration?
Answer: The process by which plants lose water vapour to the atmosphere through the stomata.
Explanation: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant and driving the upward movement of water and minerals.
What is translocation?
Answer: The transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant through phloem.
Explanation: Phloem facilitates this process by moving sugars produced during photosynthesis.
Name a plant which does not have a transport system.
Answer: Chlamydomonas
Explanation: Chlamydomonas is a simple plant that lacks a vascular system for transporting water, minerals, and food.
What is the role of stomata in transpiration?
Answer: Stomata are openings in the leaf that allow water vapour to escape, aiding in transpiration.
Explanation: The stomata regulate the amount of water lost by controlling their opening and closing.
Name the tissues responsible for the translocation of food in plants.
Answer: Phloem
Explanation: Phloem transports food (mainly sugars) produced in the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Name the process by which plants lose water.
Answer: Transpiration
Explanation: Through transpiration, plants release water vapour through the stomata.
Name that component of the vascular bundle which transports food from the leaves to different parts of a plant.
Answer: Phloem
Explanation: Phloem carries food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
What is the transporting medium in higher plants?
Answer: Water
Explanation: Water transports nutrients, minerals, and food throughout the plant via xylem and phloem.
What is the upward movement of water and minerals called?
Answer: Ascent of sap
Explanation: This process involves the upward movement of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves through xylem.
Which process in plants creates a suction force to help the water column rise in plants?
Answer: Transpiration
Explanation: Transpiration creates a suction force, or negative pressure, that pulls water up through the xylem.
Answers: Short Answer Type Questions:
Write about the opening and closing of stomata.
Answer: Stomata open when guard cells fill with water, causing them to swell and create an opening. When the guard cells lose water, the stomata close. This regulates water loss and gas exchange.
Explanation: This process controls transpiration and helps maintain homeostasis in the plant.
Why is transportation of materials necessary?
Answer: Transport is necessary to deliver water, minerals, and nutrients to all parts of the plant for growth, energy, and metabolism.
Explanation: Without transport systems, plants would not be able to carry out vital processes like photosynthesis or growth.
Describe the transport of the following materials in plants:
Water: Water is transported through xylem from the roots to the leaves.
Food: Food (mainly sugars) is transported through phloem from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Explanation: Water is essential for photosynthesis and nutrient transport, while food supplies energy for growth and development.
Write the main difference between xylem and phloem.
Answer: Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports food (mainly sugars).
Explanation: Xylem consists of dead cells and moves substances upwards, while phloem consists of living cells and moves substances in multiple directions.
How does transpiration help in the ascent of sap?
Answer: Transpiration creates a negative pressure that pulls water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves.
Explanation: This process is vital for maintaining water supply and nutrient transport in the plant.
Answers: Long Answer Type Questions:
Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State three reasons for your answer.
Answer: No, the plant will not remain healthy.
(1) Blocking the stomata will prevent transpiration, leading to water retention and poor cooling of the plant.
(2) It will restrict gas exchange, affecting photosynthesis.
(3) Without transpiration, water will not move up through the plant, causing dehydration of the plant tissues.
What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants? Where in plants are the following synthesized:
(a) Sugar: Synthesized in the leaves during photosynthesis.
(b) Hormones: Synthesized in the apical meristem, roots, and other growing tissues.
Answer: Translocation is the transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant via phloem. It is essential for distributing nutrients required for growth, reproduction, and energy storage.
Answers: NCERT Questions
What are the components of the transport system in highly organized plants?
Answer: The components are xylem and phloem.
Explanation: Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports food.
How is food transported in plants?
Answer: Food is transported through the phloem from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Explanation: Phloem carries sugars produced during photosynthesis to various parts for growth and storage.
How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Answer: Water and minerals are transported through xylem from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Explanation: Xylem transports water and dissolved minerals, supporting the plant's hydration and nutrient needs.
What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer:
Xylem: Transports water and minerals upwards from the roots to the leaves.
Phloem: Transports food (sugars) from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Explanation: Xylem consists of dead cells and only moves substances upwards, while phloem consists of living cells and moves substances in multiple directions.
Answers: Fill in the blanks:
In plants, food is transported through phloem.
In plants, water is transported through xylem.
Water enters into the root hair from soil by diffusion.
Transport of water and minerals is called ascent of sap.
The water moving upward forms a column, which is maintained up to a certain height due to root pressure.
Vascular tissues in plants are xylem and phloem.
During the day period, cohesion force and transpiration pull help in the upward movement of sap from roots to leaves.
Transpiration mainly occurs through stomata.
Guttation takes place through hydathodes.
Translocation takes place through energy in the form of ATP.
Water enters into sieve tubes containing sugar by the process of osmosis.
According to plant requirements, sugar is translocated from higher osmotic pressure to lower osmotic pressure areas.
Answers: Match the Following
1. Living part of xylem - (f) Xylem parenchyma
Explanation: Xylem parenchyma is the living part of xylem tissue involved in storage and lateral transport of water.
2. Dead part of phloem - (e) Phloem fibre
Explanation: Phloem fibers are dead cells in the phloem that provide structural support.
3. Living part of phloem - (a) Sieve tube
Explanation: Sieve tubes are the living parts of phloem that transport food (sugars) throughout the plant.
4. Dead part of xylem - (b) Tracheids, (d) Vessels, (h) Xylem fibre
Explanation: Tracheids, vessels, and xylem fibers are the dead elements of xylem that are involved in the conduction of water and providing structural support.
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Life Processes
| 1. What is transportation in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the two types of transportation in plants? |  |
| 3. How does the transportation of water take place in plants? |  |
| 4. What are the factors that affect the transportation of water in plants? |  |
| 5. Why is transportation in plants important? |  |

















