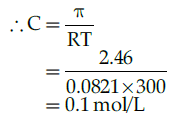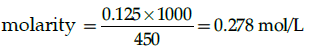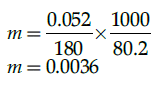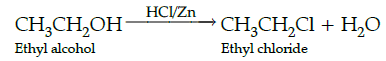Class 12 Chemistry: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term I (2021-22)- 2 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 90 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- The Question Paper contains three sections.
- Section A has 25 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section C has 6 questions. Attempt any 5 questions.
- All questions carry equal marks.
- There is no negative marking.
Section - A
Q.1: Nitrogen differs from the rest of group 15 elements due to:
(a) High electronegativity
(b) High ionization enthalpy
(c) Non- availability of d-orbitals
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Nitrogen different from the other members of this group due to its small size, high electronegativity, high ionisation enthalpy and non-availability of d-orbitals.
Q.2: The number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre of solution is called as:
(a) Molality
(b) Molarity
(c) Normality
(d) Solubility
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre of solution is called as molarity.
Q.3: Para isomers of isomeric dihalobenzene has higher melting point as compare to its ortho and meta isomers because of:
(a) loose crystal lattice structure
(b) difference in their mass
(c) change in position
(d) highly compact crystal lattice structure.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Higher number of molecules are packed compactly in crystal lattice, so more energy is required to break the bond leading to higher melting point.
Q.4: Ethylene dichloride is a gem-dihalide because:
(a) Cl group attached to adjacent carbon atom
(b) two carbon atoms
(c) it has both Cl present on same carbon atom
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Dichloride has both the halogen atoms attached on the same carbon atom, then it is called as gem dihalides or geminal dihalides.
Q.5: The correct reactant used which is oxidised to give acetone and phenol:
(a) 
(b)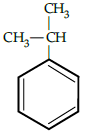
(c)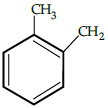
(d)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Cumene (isopropyl benzene) is oxidised in the presence of air to cumene hydroperoxide. It is later converted to phenol and acetone when treated with dilute acid.
Q.6: Octahedral voids are surrounded by:
(a) four spheres
(b) six spheres
(c) five spheres
(d) two spheres
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The triangular voids in the second layer are above the triangular voids in the first layer, and the triangular shapes of these do not overlap. One of them has the apex of the triangle pointing upwards and the other downwards. Such voids are surrounded by six spheres and are called as octahedral voids.
Q.7: Ethanol shows the boiling point of 351K while methoxymethane shows boiling point of only 248K. The high boiling point of ethanol is due to :
(a) presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(b) increase in size
(c) increase in molecular mass
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is absent in ethers.
Q.8: When phenol is treated with conc. H2SO4 acid followed by treatment with conc. HNO3, it gives:
(a) phenolic acid
(b) 2,4,6, trinitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol
(d) phenyl-methanoic acid
Correct Answer is Option (b)
It forms 2,4,6-trinitro phenol which is a different name for picric acid.
Q.9: The possible chemical reactions of sulphuric acid are due to which of its following characteristics:
(a) strong affinity for water
(b) ability to act as an oxidising agent.
(c) low volatility
(d) all of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
All the following reasons are responsible for chemical reactions of sulphuric acid : (a) low volatility (b) strong acidic character (c) strong affinity for water and (d) ability to act as an oxidising agent.
Q.10: Which of the following is not an example of osmosis:
(a) raw mangoes shrivel when pickled in brine
(b) wilted flowers revive when placed in fresh water
(c) blood cells collapse when suspended in saline water
(d) exchange of gases in lungs
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Exchanges of gases is an example of diffusion.
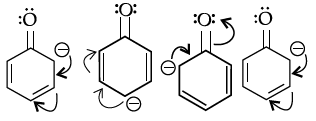
Q.11: Starting from the given structure: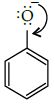
Choose the correct sequence of resonating structures.


(a) iii, ii, i, iv
(b) ii, iii, iv, i
(c) i, ii, iii, iv
(d) i, iii, iv, ii
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.12: Covalent solids do not show which of the following property:
(a) They are very hard and brittle.
(b) They have extremely high melting point.
(c) They do not conduct electricity.
(d) They are orderly collection of positive ions surrounded by free electrons.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Covalent bond is formed between adjacent atoms throughout the crystal. They are orderly collection of positive ions surrounded by free electrons is the characteristic of metallic solids.
Q.13: An ionic compound has a unit cell consisting of A ion at the corner of a cube and B ions on the centres of the faces of the cube. The empirical formula of the compound would be:
(a) AB
(b) A2B
(c) AB3
(d) A3B
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Contribution by A ions at the contribution B ion at the centres of all the six faces of the cube = 6 x 1/2 = 3
∴ the formula of the the compound AB3
Q.14: Liquid A and liquid B forms minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition. Which of the following supports the given statement:
(a) A-B interaction is stronger than those between A-A or B-B
(b) A-B interaction is weaker than that between A-A or B- B.
(c) vapour pressure of solution increases as more number of molecules of liquids A and B can escape from solution.
(d) vapour pressure of solution decreases as less number of molecules of either liquids A or B escape from solution
Correct Answer is Option (a)
If A-B interactions is less than A-A or B-B, the vapour pressure will be more and the result will be positive deviation. The solutions which show positive deviation form minimum boiling azeotropes.
Q.15: Which of the following carbohydrate do not follow the general formula of glucose:
(a) rhamnose
(b) cane sugar
(c) glucose
(d) fructose
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Rhamnose is C6H12O5 which does not fit the general formula C2(H2O)2.
Q.16: Which of the following solution is not ideal in behaviour:
(a) n- hexane and n-heptane
(b) bromoethane and chloroethane
(c) benzene and toluene
(d) benzene and n-hexane
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
Q.17: What does (i), (ii) and (iii) represent: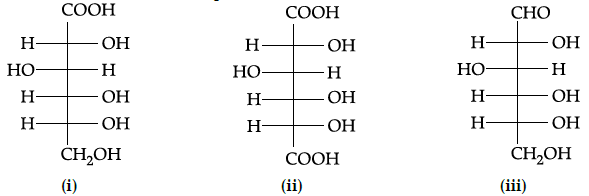
(a) gluconic acid, glucose and saccharic acid
(b) glucose, saccharic acid and gluconic acid
(c) glucose, gluconic acid and saccharic acid
(d) gluconic acid, saccharic acid and glucose
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Based on functional group and their position, gluconic acid , saccharic acid and glucose is the correct answer.
Q.18: Which of the following is not an essential amino acids ?
(a) Arginine
(b) Isoleucine
(c) Valine
(d) Alanine
Correct Answer is Option (d)
It can be synthesized in body, hence called as non-essential amino acid.
Q.19: While preparing alcohols from Grignard’s reagent, the first and second step are as respectively:
(a) hydrolysis and nucleophilic addition
(b) nucleophilic addition, substitution
(c) hydrogenation, nucleophilic substitution
(d) nucleophilic addition, hydrolysis
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct yields an alcohol.
Q.20: A point in crystal lattice represents one constituent particle which may be:
(a) An atom
(b) A molecule
(c) An ion
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
A point in crystal lattice represents one constituent particle which can be atom/molecule or an ion.
Q.21: The oxo-acid of fluorine is/are:
(a) HOF
(b) HOFO
(c) HOFO4
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Due to high electronegativity and small size, fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF.
Q.22: What is not true:
(a) Rhombic sulphur is formed by evaporation.
(b) Mononclinic sulphur is formed by melting.
(c) Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur has S8 molecules.
(d) monoclinic sulphur is stable at room temperature.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.23: Which of the following formula represents the density of a cubic unit cell ?
(a) 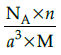
(b) 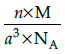
(c) 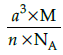
(d) 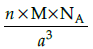
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Mass of unit call = n × m (n=number of atoms per unit cell)
Mass of an atom present in unit all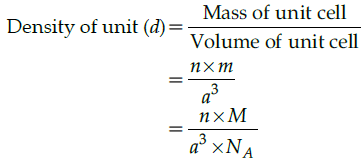
Q.24: Osmotic pressure of a sugar solution in 2.46 atmosphere at 27 °C. What will be the concentration of solution in g/litre ?
(a) 26.6 g/litre
(b) 38.8 g/litre
(c) 24.2 g/litre
(d) 34.2 g/litre
Correct Answer is Option (d)
T=27 + 273 = 300 K
Osmotic Pressure π = CRT
Molar mass of sucrose (C12H22O11)=342
Osmotic pressure in g / liter=0.1342 g/litre =34.2 g/litre
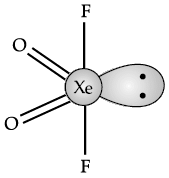
Q.25: The shape of XeO2F2 is:
(a) Trigonal bipyramidal
(b) Trigonal planar
(c) See-saw
(d) T-shaped
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In XeO2F2, there is one lone pair of electron at equation position. Due to lone pair-bond pair interaction, the shape of XeO2F2 distorted from trigonal bipyramidal to sea-saw. It is represented as below:
Section - B
Q.26: Which is the correct relation between mole fraction and molality ?
(a) 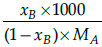
(b) 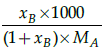
(c) 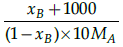
(d) 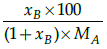
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Mole fraction is the ratio of moles of solute to moles of solvent. Molality is number of moles of solute per mass of solvent.
Q.27: Which of the following is dependent on temperature ?
(a) mass %
(b) parts per million
(c) molarity
(d) molality
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Molarity is the ratio of the amount of solvent moles to the volume of solution in litres, and as the volume increases with increasing temperature, the molarity decreases with rise in temperature.
Q.28: Which of the following unit is used in medicine and pharmacy:
(a) mass by volume percentage
(b) parts per million
(c) mass percentage
(d) molarity
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The unit is used as it is easy concentration unit since it is easy to measure volumes of solvents and solutions rather than their weights.
Q.29: Find the molarity of a solution having 5 g of NaOH is 450 ml of solution:
(a) 0.125 mol
(b) 0.278 mol/L
(c) 27.8 mol/L
(d) 450 mL
Correct Answer is Option (b)
moles of NaOH = 5/40 = 0.125 mol
volume of solution in litres= 450/1000
Q.30: A solution of glucose is prepared with 0.052 g of glucose in 80.2 g of water. (Kf = 1.86 K kg/mol and Kf = 5.2 K kg/mol).Molality of the given solution is:
(a) 0.0052 m
(b) 0.0036 m
(c) 0.0006 m
(d) 1.29 m
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.31: When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will:
(a) boil above 100°C and freeze above 0°C
(b) boil below 100°C and freeze above 0°C
(c) boil above 100°C and freeze below 0°C
(d) boil below 100°C and freeze below 0°C
Correct Answer is Option (c)
This is in relation with colligative property elevation of boiling point.
Q.32: Colligative properties are:
(a) dependent only on the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s and solute’s identity.
(b) dependent only on the identity of the solute and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s identity.
(c) dependent on the identity of the solvent and solute and thus on the concentration of the solute.
(d) dependent only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solute’s identity.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions.
Q.33: Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them. The concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1M, 0.5 M and 0.2 M respectively. Freezing point will be highest for the fruit juice:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) All have same freezing point
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Lower the molar mass, higher is the freezing point.
Q.34: Identify which of the following is a colligative property:
(a) freezing point
(b) boiling point
(c) osmotic pressure
(d) all of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Osmotic pressure, lowering of vapour pressure, elevation in boiling point, depression in freezing point are colligative property.
Q.35: The vapour pressure of a liquid can be lowered by:
(a) decreasing the temperature
(b) adding a non- volatile solute
(c) either of the two
(d) None of the two
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.36: On hydrolysis of proteins ________________ is obtained.
(a) α- amino acids
(b) β−amino acids
(c) γ-amino acids
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Hydrolysis of proteins by boiling aqueous acid or base produces α - amino acids.
Q.37: Choose the wrong pair:
(a) CH3 -alanine
(b) HO-CH2 - serine
(c) C6H5 -OH - Phenylalanine
(d) H – glycine
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Phenylalanine – C6H5 -CH2 -
Q.38: A compound may have excess metal ion if a negative ion is absent from its lattice position, leveing a hole, which is occupied by electron This defect belongs to:
(a) Stoichiometric defect
(b) Non-Stoichiometric defect
(c) Line defect
(d) Frenkel defect
Correct Answer is Option (b)
This defect is metal excess defect due to anion vacancies. Since, in this defect, metal is in excess so, it belongs to non-stoichiometric defect in which the ratio of cations and anions present in the compound differs from that required by ideal chemical formula of the compound.
Q.39: Mark the incorrect statement:
(a) The solution which obey Raoult’s law are called non-ideal solution.
(b) The vapour pressure of the ideal solution always lies between the vapour pressure of the pure components.
(c) For ideal solution ΔHmixing = 0
(d) For non-ideal solution ΔHmixing ≠ 0
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The solutions which obey Raoult’s law are called ideal solutions.
Q.40: Peroxide effect in unsymmetrical alkenes applies to the addition of:
(a) HCl
(b) HBr
(c) HI
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Peroxide effect in unsymmetrical alkenes applies to the addition of HBr only and not to the addition of HI or HCl, It is due to following reasons.
- HCl is very stafle due to stronger H- Cl ford (430 KJ mol1) than H-Br find (378 KJ mol-1) and is not broken symmetrically by the free radicals generated by pesoxide.
- H-I fond (297 KJ mol-1) is weaker than H-Br bond and undergoes homolysis readily to form I° free radical. But I° free radicals have greater tendency to combine amongst themselves to from I2 molecules rather than add to the
bond.
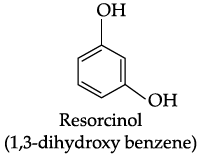
Q.41: The structural formula of resorcinol is:
(a) 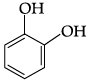
(b) 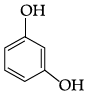
(c) 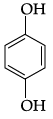
(d)
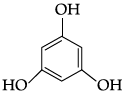
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.42: Which of the following hydrides of halogen can be used for Etching of glass ?
(a) HF
(b) HCl
(c) HBr
(d) HI
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The tendency of HF is to dissolve the glass after reaction with it. This property of HF can be used for Etching of glass.
Q.43: Find the product

(a) C2H4
(b) C2H5Cl
(c) (C2H5)2 Zn
(d) CH3CHO
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.44: Mark the odd one out:
(a) Proline
(b) Lysine
(c) Valine
(d) Alanine
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Alanine is non-essentials amino acid while other amino acids (proline, Lysine and Valine are essential amino acids
From Q. 45 to Q. 49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
Q.45: Assertion (A): In one dimensional close packed arrangement, the coordination number is 2.
Reason (R): Each sphere is in contact with two of its neighbours.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The number of nearest neighbours of a particle is called its coordination number. Thus, in one dimensional close packed arrangement, the coordination number is 2.
Q.46: Assertion (A): Except nitrogen, no other element forms pπ - pπ bonds.
Reason (R): Nitrogen show anomalous property due to small size and high electronegativity
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
N has unique ability to form pπ - pπ with itself and other elements having small size and high electro negativity.
Q.47: Assertion (A): Ag CN forms isocyanide when react with haloalkanes while KCN form alkyl cyanides.
Reason (R): KCN is ionic while Ag CN is covalent in nature thus providing different ions in solution.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In KCN, the linking is generally through carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom while in case of Ag CN, linking is through nitrogen which is free to donate electrons.
Q.48: Assertion (A): SN2 reaction proceeds with inversion of configuration.
Reason (R): SN1 reaction are accompanied by racemisation.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In case of optically active alkyl halides, the nucleophile attaches itself on the side opposite to the place where halogen atom is present. This results in inversion of configuration.
Q.49: Assertion (A): Elements of group 16 generally show lower value of first ionisation enthalpy as compared to the group 15 elements.
Reason (R): Larger amount of energy is required to remove electrons from group 16
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Due to extra stable half-filled p- orbitals electronic configurations of group 15 elements, larger amount of energy is required to remove electrons.
Section - C
Q.50: Match the following: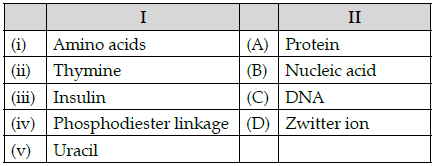
Which of the following is the best matched options?
(a) i-A, v- D, iii- C, iv-B
(b) i-D, ii-C, iii- A, iv-B
(c) i-D, v- D, iii- A, iv-B
(d) i-A, ii- C, iii- D, iv-B
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Amino acids form proteins and exist as zwitter ion, Thymine is a nitrogenous base in DNA, Insulin is a protein, phosphodiester linkage is found in nucleic acids and also in DNA Uracil is nitrogenous base found in RNA which is a nucleic acid.
Q.51: Which of the following analogies is correct?
(a) Nitrogen: 1s22s22p3 :: Argon:1s22s22p6
(b) Carbon: maximum compounds :: Xenon: no compounds
(c) XeF2: Linear :: ClF3: Trigonal planar
(d) Helium: meteorological observations :: Argon: metallurgical processes
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Nitrogen: 1s22s22p3 :: Argon:1s22s22p6 is configuration of Neon not Argon.
Carbon: maximum compounds :: Xenon: no compounds , Xenon forms compounds. XeF2: Linear :: ClF3: Trigonal planar , ClF3 is T shaped not trigonal planar.
Q.52: Complete the following analogy: Same molecular formula but different structures: A:: Non superimposable mirror images: B
(a) A:Isomers, B: Enantiomer
(b) A: Enantiomers, B: Racemic mixture
(c) A: Stereoisomers, B: Retention
(d) A: Isomers, B: Sterioisomers
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Isomers have same molecular formula but different structure. Enantiomers are non superimposable mirror images.
CASE 1 : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55.
Early crystallographers had trouble solving the structures of inorganic solids using X-ray diffraction because some of the mathematical tools for analyzing the data had not yet been developed. Once a trial structure was proposed, it was relatively easy to calculate the diffraction pattern, but it was difficult to go the other way (from the diffraction pattern to the structure) if nothing was known a priori about the arrangement of atoms in the unit cell. It was important to develop some guidelines for guessing coordination numbers and bonding geometries of atoms in crystals. The first such rules were proposed by Linus Pauling, who considered how one might pack together oppositely charged spheres with different radii. Pauling proposed from geometric considerations that the quality of the “fit” depended on the radius ratio of the anion and the cation. If the anion is considered as the packing atom in the crystal, then the smaller cation fills the interstitial sites (“holes”). Cations will find arrangements in which they can contact the largest number of anions. If the cation can touch all of its nearest neighbouring anions then the fit is good. If the cation is too small for a given site, that coordination number will be unstable and it will prefer a lower coordination structure. The table below gives the ranges of cation/anion radius ratios that give the best fit for a given coordination geometry.
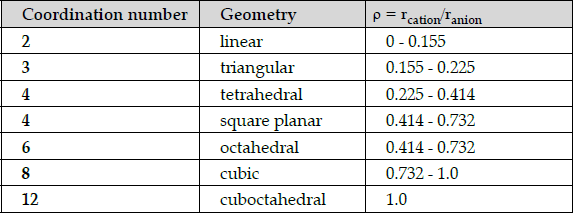
Q.53: The radius of Ag+ ion is 126 pm and of I-ion is 216 pm. The coordination number of Ag+ion will be:
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 8
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The radius of Ag+ ion is 126 pm and of I- ion is 216 pm. The coordination number of Ag+ ion is:
ρ = rcation/ranion = 126/ 216 = 0.58.
Radius ratio lies in the range 0.414 – 0.732, so has coordination number 6 or 4 according to the table.
Since none of the options is 4, so the answer is 6.
Q.54: A solid AB has square planar structure. If the radius of cation A+ is 120 pm, calculate the maximum possible value of anion B-.
(a) 240 pm
(b) 270 pm
(c) 280 pm
(d) 290 pm
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Square planar means ratio is between 0.414 – 0.732.
If radius of cation is 120 pm then anion should be in the range
ρ = rcation/ranion.
0.414 = 120/ x so x = 289.8 = 290 pm.
0.732 = 120/ x so x = 163.9 = 164 pm.
Q.55: A “good fit” is considered to be one where the cation can touch:
(a) All of its nearest neighbouring anions
(b) Most of its nearest neighbouring anions
(c) Some of its nearest neighbouring anions
(d) None of its nearest neighbouring anions
Correct Answer is Option (a)
|
159 docs|4 tests
|