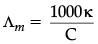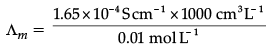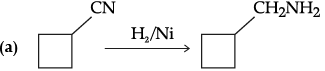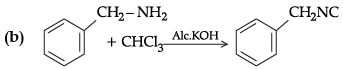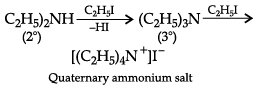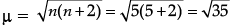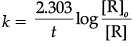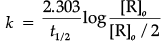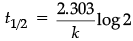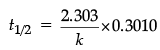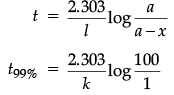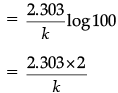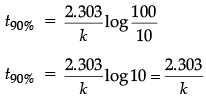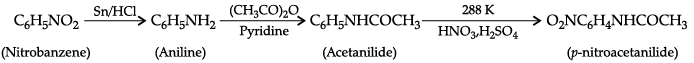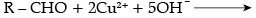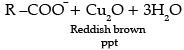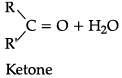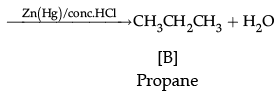Class 12 Chemistry: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 4 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A - Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B - Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C- Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Section - A
Q.1. Attempt any two question
(a) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their property indicated:
CH3 CH2CH3, CH3CH2NH2, CH3CH2OH. (dipole moment)
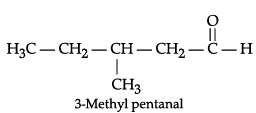
(b) Draw the structure of 3-methylpentanal.
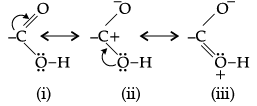
(c) Draw the resonating structures of carboxylic acid.
(a) CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CH2NH2 < CH3CH2OH
Since O is more electronegative than N, therefore, dipole moment of ethyl alcohol is higher than that of ethyl amine. Propane however, has the least dipole moment since it is almost a non-polar molecule.
(b)(c) Carboxylic acid has three resonating structures.
Q.2.: The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 × 10–4 S cm–1. Calculate molar conductivity of the solution.
= 16.5 S cm2 mol–1
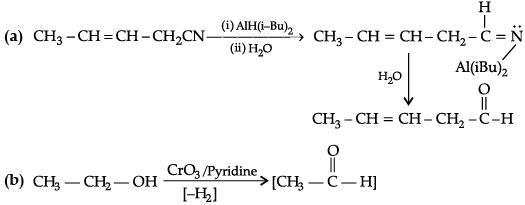
Q.3. Write the major product (s) in the following :
(a) CH3 – CH = CH – CH2 – CN 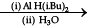
(b) CH3 – CH2 – OH 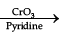
Section - B
Q.4: Account for the following:
(a) Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution but platinum does not.
(b) Salt bridge is used in electrochemical process.
(a) Electrode potential of Fe is more than electrode potential of Cu. So, Fe displaces Cu from copper sulphate while electrode potential of Pt is less than Cu. Due to this reason, Pt cannot displace Cu from copper sulphate.
(b) In an electrochemical cell, a salt bridge is used to keep solution electrically neutral and allow the flow of ions from one cell to another so that reaction can not stop, otherwise due to accumulation of ions on cathode and anode can stop reactions.
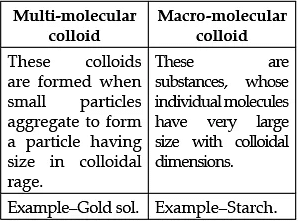
Q.5. (a) Write one difference between multi-molecular colloid and macro-molecular colloid.
(b) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(c) Write one similarity between physisorption and chemisorption.
(a)
(b) Dispersed phase-liquid and Dispersion medium-liquid.
(c) Both are surface phenomena/both increase with increase in surface area (or any other correct similarity)
Q.6. Complete the following chemical reactions :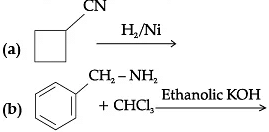
(c) Why aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine?
OR
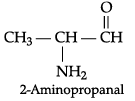
(a) Write the IUPAC name of : 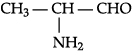
(b) Draw the structure of 3-methylpentanal.
(c) Why is it difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkyl halides?
(c) Cyclohexylamine is more basic than aniline because aniline is a resonance hybrid of various resonance structures. As a result, in aniline the electron donating capacity of nitrogen for protonation is considerably decreased than cyclohexylamine.
OR
(a)(b)
(c) Ammonolysis of alkyl halides does not give single amine but gives a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
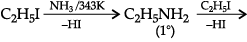
Q.7. Consider the standard electrode potential values (M2+/M) of the elements of the first transition series.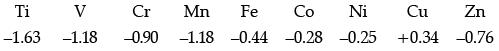
Explain:
(a) E° value for copper is positive.
(b) E° value of Mn is more negative as expected from the trend.
(c) Cr3+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+.
(a) The high energy to transform Cu(s) to Cu2+(aq) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy.
(b) Mn2+ has d5 configuration (stable half-filled configuration)
(c) d5 to d3 occurs in case of Cr2+ to Cr3+. (More stable t2g3) while it changes from d6 to d5 in case of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
Q.8. Account for the following:
(a) CuCl2 is more stable than Cu2Cl2.
(b) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(c) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
OR
Out of the following metal ions:
Cr2+, Cu2+, Cu+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn3+
(a) Why Cr2+ is a a strong reducing agent?
(b) Which of the following ions is unstable in aqueous solution?
(c) Why Mn+3 is a strong oxidising agent?
Give suitable reason in each.
(a) In CuCl2, Cu is in +2 oxidation state which is more stable due to high hydration enthalpy as compared to Cu2Cl2 in which Cu is in +1 oxidation state.
(b) Due to lanthanoid contraction.
(c) Because HCl is oxidised to chlorine.
OR
(a) Electronic configuration of Cr+2 changes from d4 to d3 and have a half-filled t2g level.
(b) Cu+ in an aqueous medium energy is required to remove one electron from Cu+ to Cu2+, high hydration energy of Cu2+ compensates for it. Therefore Cu+ ion in an aqueous solution is unstable.
2Cu+ → Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s)
(c) Electronic configuration changes from Mn3+ to Mn2+ results in the half filled d5 configuration, which has extra stability.
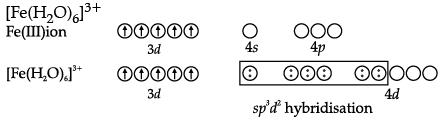
Q.9. (a) For the complex [Fe(H2O)6]3+, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
(b) Which of the following will not behave as ligand?
H2O, NH3, CO and CH4.
OR
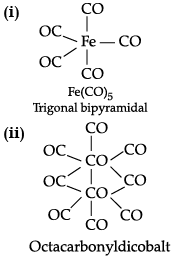
(a) Draw the structure of:
(i) Pentacarbonyl iron (0)
(ii) Octacarbonyldicobalt(0)
(b) What is synergic effect?
(a)
Since, H2O is a weak field ligand, it cannot cause pairing of electrons. Therefore, the number of unpaired electrons is 5.
= 5.92 BM
Thus, it is strongly paramagnetic (due to presence of unpaired electrons).
In [Fe(H2O)6]3+, outer d-orbitals are used in hybridization to form high spain complex.
(b) CH4 will not act as ligand because it does not contain any lone pair of electrons to donate for central metal ion of a coordination sphere.
OR
(a)
It has bridged structure in which two cobalt atoms bound to eight carbon monoxide ligand.
(b) The Metal – Carbon π-bond in metal carbonyls which is formed by the donation of an electron pair from a filled π-orbital of metal into the vacant anti bonding p-orbital of CO, strengthens the M–C σ-bond. This is called synergic effect and is usually observed in metal carbonyls.
Q.10. (a) Write the rate law for a first order reaction. Justify the statement that half life for a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
(b) For a first order reaction, show that the time required for 99% completion of a first order reaction is twice the time required for the completion of 90%.
(a) For a first order reaction
where [R]o = initial concentration, [R] = conc. after time t
When half of the reaction is completed, [R] = [R]o/2. Representing, the time taken for half of the reaction to be completed, by t1/2, equation becomes:
⇒
⇒
⇒ t1/2 = 0.693/k
The above equation shows that half-life of first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
(b) For a first order reaction
= 4.606/k
and
t99%/t90% = 2
t99% = 2 x t90%
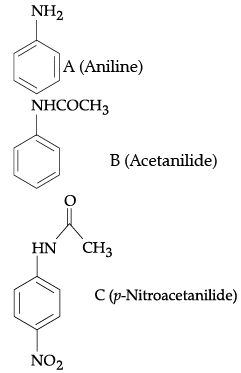
Q.11. Write the structure of A, B and C in the following reactions: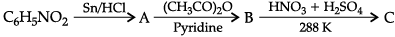
OR
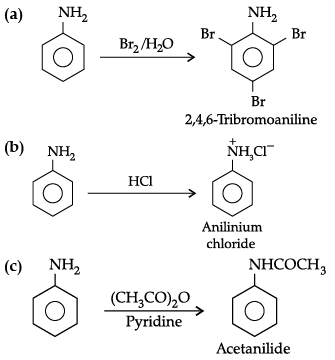
Write the structures of main products when aniline reacts with the following reagents:
(a) Br2 water
(b) HCl
(c) (CH3CO)2O / pyridine
OR
Section - C
Q.12. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 W. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 W. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
(a) What is the conductivity of 0.02M KCl solution?
(b) What will happen to the conductivity of cell with the dilution?
(c) What is the nature of cell constant of a conductivity cell?
(d) What are the factors on which conductivity depends?
OR
Why does the conductivity of solution of different electrolytes in the same solute at a given temperature differ? Also, write the SI unit for conductivity of a solution.
(a) Both aldehydes and ketones can be prepared by oxidation of alcohols.
(b) On heating an aldehyde with Fehling’s reagent, a reddish brown precipitate is obtained. Aldehydes are oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion. Aromatic aldehydes do not respond to this test.
(c)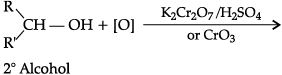
(d)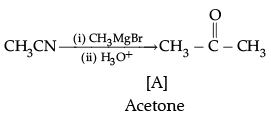
OR
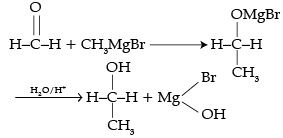
The number of C-atoms can be increased in the chain by Grignard reaction.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|