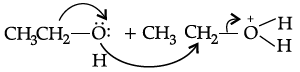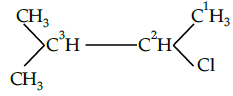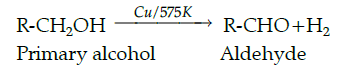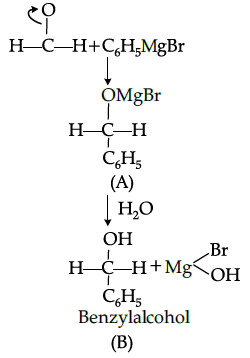Class 12 Chemistry: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term I (2021-22)- 3 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 90 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- The Question Paper contains three sections.
- Section A has 25 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section C has 6 questions. Attempt any 5 questions.
- All questions carry equal marks.
- There is no negative marking.
Section - A
Q.1: Which of the statements is incorrect for haloalkanes:
(i) Haloalkanes are extremely soluble in water.
(ii) Alkyl halides are colourless when pure.
(iii) Haloalkanes tend to dissolve in organic solvents.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) only (i)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii)
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Haloalkanes are very slightly soluble in water.
Q.2: How does the branching in haloalkanes affect its boiling point ?
(a) Increases with branching
(b) decreases with branching
(c) does not affect the branching
(d) initially increases then decreases
Correct Answer is Option (b)
This is because branching results in lesser surface area thus the Vander waals force of attraction decreases.
Q.3: IUPAC name of the following compound is: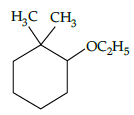 (a) 2-ethoxy-1-1-dimethylcyclohexane
(a) 2-ethoxy-1-1-dimethylcyclohexane
(b) 2,6 -dimethyl phenol
(c) 2 -ethoxy propane
(d) 1-ethoxy-2-methylcyclohexane
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.4: Which of the following is not the requirement while preparing ammonia by Haber’s process:
(a) A high pressure of 200 atm.
(b) A temp of nearly 700 K
(c) Catalyst iron oxide
(d) Reactants in solid state
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Only the rest three are required to maximise the yield of ammonia.
Q.5: Which is the correct sequence to be followed in Ostwald’s process:
(i) Formation of nitrogen dioxide
(ii) Formation of nitric acid
(iii) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(a) (i),(ii),(iii)
(b) (i),(iii),(ii)
(c) (iii),(ii),(i)
(d) (iii),(i),(ii)
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Ostwald’s process is used for the synthesis of nitric acid where catalytic oxidation of ammonia by atmospheric oxygen results in the formation of nitric oxide. The nitric oxide combines with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide is absorbed in water and forms nitric acid.
Q.6: The general formula for carbohydrate is:
(a) Cx-1(H2O)2y
(b) Cx (H2O)x
(c) C2x (H2O)y
(d) Cx+1 (H2O)y
Correct Answer is Option (b)
General formula for carbohydrate is (CH2O)n. Here n is the number of carbon atom in the molecule.
Q.7: Conc. nitric acid oxidises non -metals. Based on it, which of the following is wrongly paired ?
(a) Phosphorus –phosphoric acid
(b) Carbon -carbonic acid
(c) Sulphur - sulphuric acid
(d) Iodine – iodic acid
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Carbon is oxidised to carbon dioxide
Q.8: In preparation of phenol, benzene is sulphonated with oleum. Benzene sulphonic acid so formed is converted to sodium phenoxide on heating with:
(a) molten sodium chloride
(b) molten sodium hydroxide
(c) solid sodium hydroxide
(d) sodium nitrate with HCl
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Molten sodium hydroxide helps in acidification of sodium salts to give phenols.
Q.9: During preparation of alcohol, the addition of borane to the double bond involves addition of boron to:
(a) sp2 carbon carrying higher number of hydrogen atoms
(b) sp3 carbon carrying higher number of hydrogen atoms
(c) sp2 carbon carrying lower number of hydrogen atoms
(d) sp3 carbon carrying lower number of hydrogen atoms
Correct Answer is Option (a)
This is due to anti -Markovnikov’s rule.
Q.10: Which of the following is not the correct statement in relation to vapour pressure:
(a) The lowering of vapour pressure depends only on the concentration of the solute particles.
(b) The lowering of vapour pressure is independent of the identity of solute particles.
(c) In non- volatile solutes, the lowering of the vapour pressure depends on the sum of the mole fraction of different solutes.
(d) vapour pressure of the solvent decreases in the presence of non-volatile solute.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Vapour pressure of the solvent increases in the presence of non-volatile solute.
Q.11: Peptide linkage:
(i) is a bond formed between COOH and -NH2 group
(ii) is a bond between two amino acids
(iii) it’s a connection between two proteins What is untrue about peptide linkage:
(a) only (i)
(b) only (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Peptide linkage (−CO−NH−) is not a bond between two amino acids.
Q.12: What happens when glucose reacts with bromine water:
(a) glucose gets reduced to gluconic acid
(b) it form oxime.
(c) glucose gets oxidised to gluconic acid.
(d) it forms oxalic acid
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Bromine water is a mild oxidising agent.
Q.13: Which of the following is not the right pair as per the uses of various nitrogen compounds:
(a) Pickling of stainless steel-nitric acid
(b) Refrigerant-liquid nitrogen
(c) In the manufacture of ammonia-dinitrogen
(d) Preparing nitrates used in explosives-dinitrogen
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Nitric acid is the nitrates that is used to prepare explosives.
Q.14: Formation of ortho hydroxy benzoic acid from phenol using sodium hydroxide is:
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Reimer Tiemann reaction
(c) Esterification
(d) Williamson synthesis
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Phenoxide ion generated by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide. Further it undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide to form ortho hydroxybenzoic acid as the main reaction product.
Q.15: Helium is used in filling balloons for meteorological observation because:
(a) it is non – inflammable and light gas.
(b) it is a good oxidising agent
(c) it is a good reducing agent.
(d) all of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Helium gas is lighter than air due to its lower density that help to float balloons. Helium gas is completely inert which doesn’t react with other compounds in the chemical reaction.
Q.16: Which of the following colligative property is directly proportional to molarity:
(a) Lowering of vapour pressure
(b) Elevation of boiling point
(c) Osmotic pressure
(d) Depression of freezing point
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the molarity of the solution at a given temperature.
Q.17: The concentration of pollutants in water is expressed in:
(a) μ g / mL
(b) ω /v
(c) v/v
(d) ω/ω
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The concentration of pollutants in water is expressed in mg/mL.
Q.18: Deacon’s process is used for the manufacture of:
(a) dinitrogen
(b) dioxygen
(c) sulphuric acid
(d) chlorine
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Deacons process involves oxidation of hydrogen chloride gas by atmospheric oxygen in presence of CuCl2 as catalyst at 723 K to produce chlorine.
Q.19: Choose the correct relation:
(a) p1∝2x1
(b) 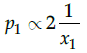
(c) p1∝x1
(d) 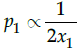
Correct Answer is Option (c)
According to Raoult’s law, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction.
Q.20: Primary alkyl groups form ____________ on dehydration while __________ is formed on dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohol.
(a) ethers, alkenes
(b) alkenes, ethers
(c) ethers, phenols
(d) alkenes, phenols
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Dehydration of primary alcohols gives ether while dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohol gives alkenes.
Q.21: Among halogens, which is a radioactive element:
(a) Bromine
(b) Iodine
(c) Astatine
(d) fluorine
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Astatine and tennessine are radioactive elements among halogen.
Q.22: What is the half life of radon?
(a) 10 days
(b) 4.56 days
(c) 3.82 days
(d) 5.46 days
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Half life of a radioactive substance refers to the amount of time that it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay into a more stable form.
Q.23: Which of the following compounds of hydrogen does not from hydrogen bonding ?
(a) NH3
(b) H2O
(c) HCl
(d) HF
Correct Answer is Option (c)
HCl does not form hydrogen bonding due to large size of Cl-atom.
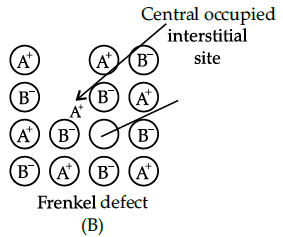
Q.24: Alkali metal halide do not represent Frenkel defect. It is due to:
(a) Large difference in size of atoms and anions
(b) Almost same size of atoms and anions
(c) low coordination number of atoms and anions
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The crystals showing Frenkel defect do not posses almost same size of atom and anions so alkali metal halides viz. NaCl etc. do not represent Frenkel defect.
Q.25: Glycosidic linkage belongs to which functional group ?
(a) Amide
(b) Ether
(c) Ester
(d) Alcohol
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Glyosidic linkage in a carbohydrate belongs to ether (-C-O-C-) functional group.
Section - B
Q.26: Ethanol is treated with sulphuric acid at 443K:
(a) ethene
(b) ethoxy ethane
(c) ethanoic acid
(d) ethylene
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Inter molecular dehydration takes place and ethoxy ethane is formed.
Q.27: Alkyl halides are immiscible in water though they are polar because:
(a) they react with water give alcohol.
(b) they cannot form hydrogen bonds with water.
(c) C-X bond cannot be broken easily.
(d) they are stable compounds and are not reactive.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The molecules of water held together by hydrogen bonds. The new force of attraction are weaker than the force that existing between alkyl halide -alkyl halide molecules and water molecules. So they can not form hydrogen bonds with water
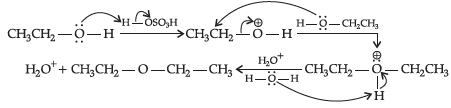
Q.28: Choose the correct 2nd step taking place after the reaction shown below:
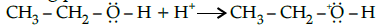
(a) 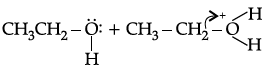
(b) 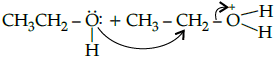
(c) 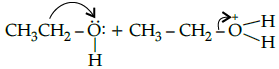
(d) 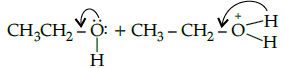
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.29: In dehydration of alcohols, name the product formed if instead of primary alcohol , tertiary alcohol is used ?
(a) ether
(b) alkene
(c) no change in product
(d) either alkene or ether
Correct Answer is Option (b)
To form ether alkyl group should be unhindered. As in tertiary alcohol, alkyl group is hindered the reaction favours formation of ethene.
Q.30: Bimolecular dehydration does not involve:
(a) Preparation of diethyl ether from dehydrating action of conc. H2SO4 on ethanol.
(b) Sulphuric acid grabs a mole of water
(c) This method works only for symmetrical ethers.
(d) Preparation of ethyl methyl ether using conc.H2SO4.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Ethyl methyl ether is better prepared by Sodium ethoxide and methanol or Sodium methoxide and ethanol.
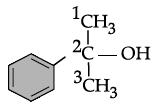
Q.31: Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
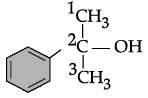 (a) 2-methyl, 2-phenyl ethanol
(a) 2-methyl, 2-phenyl ethanol
(b) 2-phenyl butanol
(c) 2-Phenylopropan-2-ol
(d) 1-methyl, 1-phenyl ethanol
Correct Answer is Option (c)
IUPAC name = 2-Phenylpropan-2-ol
Q.32: Protein loses its biological activity on heating due to:
(a) decrease in entropy
(b) disturbances in hydrogen bonding
(c) folding
(d) Van der weaal’s interactions
Correct Answer is Option (c)
When a protein in its native form, is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and protein loses its biological activity.
Q.33: It is necessary to use a silent electrical discharge in the preparation of ozone from oxygen to prevent its decomposition because the process is:
(a) exothermic
(b) endothermic
(c) reversible
(d) irreversible
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Formation of ozone from oxygen is an endothermic process thus it is necessary to use a silent electrical discharge in the preparation of ozone to prevent its decomposition.
Q.34: Electrophilic substitution reactions in haloarenes occur slowly due to:
(a) alumatic nature of haloarenes
(b) +I effect of halogen atom
(c) resonance
(d) -I effect of halogen atom
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Due to -I effect, the halogen atom has some tendency to withdraw electrons from the benzene ring. Due to strong inductive effect electrophilic substitution reactions in haloarenes occur slowly.
Q.35: 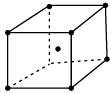 The structure represents:
The structure represents:
(a) Simple cubic unit cell
(b) Body centred cubic unit cell
(c) Face centred cubic unit cell
(d) End centred cubic unit cell
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Since, the structure of a unit cell shows a lattice point at the centre of the body in addition to the lattice point at the corners, so it is called body centred. cubic unit cell.
Q.36: Which of the following is not a colligative property ?
(a) Osmotic pressure
(b) Vapour pressure
(c) Elevation of boiling point
(d) Depression of freezing point
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property
Q.37: Which one of the following in monoatomic ?
(a) Fluorine
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Argon
(d) Hydrogen
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Argon is a noble gas which is unreactive due to its complete octet. So, it in monoatomic.
Q.38: Anti-Markownikoff addition of HBr is not shown in:
(a) 2-Butene
(b) 1-Hexene
(c) Propene
(d) 1-Butene
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Unsymmetrical alkenes add HBr by means of Anti-Markownikoff’s rule in the presence of peroxide, 2-Butene in symmetrical alkene (CH3CH=CH-CH3), so it does not exhibit Anti-Markownikoff ’s addition of HBr.
Q.39: The IUPAC name of 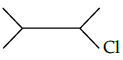 is
is
(a) 3-chloro -2- methyl butane
(b) 2-chloro pentane
(c) 2-chloro -3 methyl butane
(d) 2-chloro -3 methyl butane
Correct Answer is Option (c)
IUPAC name= 2-chloro -3 -methyl butane
Q.40: A primary alcohol undergoes dehydrogenation to give a/an:
(a) alkene
(b) aldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) carboxylic acid
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A primary alcohol undergoes dehydrogenation of heating with Cu at 575 K to give an aldehyde.
Q.41: A nucleotide consist of:
(a) sugar molecule and phosphoric acid
(b) sugar molecule and nitrogenous base
(c) nitrogenous base and phosphoric acid
(d) sugar molecule, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Nucleotide = Sugar molecule + phosphoric acid +nitrogenous base
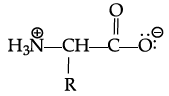
Q.42: Zwitter ion is represented as:
(a) 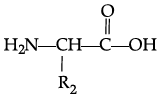
(b) 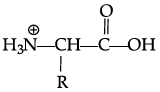
(c) 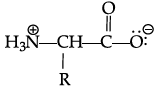
(d) 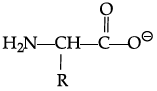
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In the formation of Zwitter ion, a proton from –COOH part of the molecule is released and attaches itself to – NH2 Past to constitute a dipolar ion Zwitter ion is shown as below:
Q.43: Which of the following reasons is not responsible for abnormal behaviour of fluorine ?
(a) small size
(b) high electronegativity
(c) Non-availability of d-orbitals in valence shell
(d) high ionization enthalpy of F-F bond
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Small size, high electronegativity, non-availability of d orbitals and low ionisation enthalpy of F-F bond in valence shell is responsible for abnormal behaviour of fluorine.
Q.44: In the following sequence of reaction
The product ‘B’ in the reaction is –
(a) Phenol
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Benzyl alcohol
(d) 2-phenyl ethanol
Correct Answer is Option (c)
From Q. 45 to Q. 49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
Q.45:
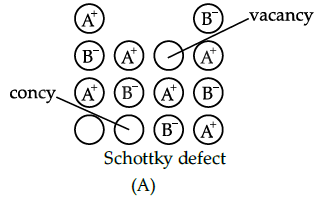
Assertion (A): All ionic compounds show Frenkel and Schottky defects.
Reason (R): Vacancy and interstitial defects can also be shown by ionic compounds.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Non-ionic compounds show vacancy and interstitial defects.
Q.46:
Assertion (A): Alkali halides like NaCl show non-stoichiometric defects.
Reason (R): When some of the lattice sites are vacant, the crystal is said to have vacancy defect.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Alkali halides like NaCl show non-stoichiometric defects. The defect is due to anionic vacancies.
Q.47:
Assertion (A): It is not possible to separate the components of azeotropes by fractional distillation.
Reason (R): The solutions which show a large positive deviation from Raoult’s law form minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
It is not possible to separate the components of azeotropes by fractional distillation because they boil at constant temperature.
Q.48:
Assertion (A): Two strands of DNA are complementary to each other.
Reason (R): In DNA, between specific pairs of bases there are sulphide bonds
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In DNA, between specific pairs of bases there are hydrogen bonds.
Q.49:
Assertion (A): Elements of group 16 generally show lower value of first ionisation enthalpy as compared to the group 15 elements.
Reason (R): Larger amount of energy is required to remove electrons from group 16.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Group-16 elements show lower value of first ionistion enthalpy than group 15, due to extra stability of half filled orbitals in 15-group elements. But in group 16 the p-orbital is not symmetrical. So it required less amount of energy to remove the electron.
Section - C
Q.50: Match the following:
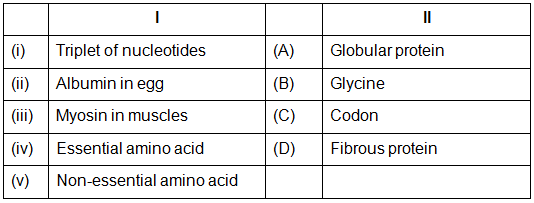
Which of the following is the best matched options ?
(a) i-A, v- B, iii- D, iv-C
(b) i-D, ii-B, iii- A, iv-C
(c) i-C, v- A, iii- D, iv-B
(d) i-C, ii- A, iii- D, iv-B
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Triplet of nucleotides - Codon Each triplet of nucleotides having a spectic sequence of basic is called codon.
Albumin in egg : Globular protein.
Globular proteins are cross - linked condensation polymers of acidic and basic amino acids.
Myosin in muscles - Fibrous protein. Fibrous proteins are linear condensation products.
Non- essential amino acid -Glycine Glycine is non-essential amino acid which can be synthesized in the body.
Q.51: Which of the following analogies is correct:
(a) Chlorobenzene : Aromatic : : Phenol : Aliphatic
(b) Alcohol : Basic : : Phenol : Acidic
(c) Ethanol : Soluble in Water : : Methanol : insoluble in water
(d) Electron releasing group : decreases the acidic strength : : Electron withdrawing group : increases the acidic strength
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Electron releasing group decrease the acidic strength by destabilization the corresponding ion of acid.
Electron withdrawing group increases the acidic strength by stabilizing the corresponding ion of acid.
Q.52: Complete the following analogy:
Point defect by missing of equal number of cations and anions from lattice site : A : : Point defect by missing of one of an ion from lattice site and occupies interstitial site : B
(a) A : Frenkel defect B : Shottky defect
(b) A : Schottky defect B : Frenkel defect
(c) A : Metal excess defect B : Frenkel defect
(d) A : Metal deficiency defect B : Schottky defect
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55
Nucleophiles are electron rich species. Therefore, they attack at that part of the substrate molecule which is electron deficient. The reaction in which a nucleophile replaces already existing nucleophile in a molecule is called nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction has been found to proceed by two different mechanisms which are described below:
In SN2 the incoming nucleophile interacts with alkyl halide causing the carbon-halide bond to break and a new bond is formed between carbon and attacking nucleophile
SN1 occurs in two steps. In step I, the polarised C—Br bond undergoes slow cleavage to produce a carbocation and a bromide ion. The carbocation thus formed is then attacked by nucleophile in step II to complete the substitution reaction.
Q.53: The preferred solvents for SN1 reactions are:
(a) Polar in nature
(b) Protic in nature
(c) Both polar and protic
(d) Non-polar and non protic
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Eg. Water, alcohol
Polar and protic solvents stabilize the charged carbocation that results from loss of the leaving group.
Q.54: The stereochemistry in SN1 is ______________ while that in SN2 is______________ :
(a) Racemization, inversion
(b) Inversion, racemization
(c) Inversion, retention
(d) Retention, inversion
Correct Answer is Option (a)
SN2 proceeds with backside attack (inversion) while in SN1 the nucleophile can attack from either side of carbocation (racemization).
Q.55: In SN1, the rate law depends only on:
(a) Conc. of nucleophile
(b) Conc. of the substrate
(c) Conc. of solvent
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The slow step which is the rate determining step involves only the substrate.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Chemistry: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term I (2021-22)- 3 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical
| 1. What is the duration of Class XII Chemistry exam? |  |
| 2. What is the maximum marks for the Class XII Chemistry exam? |  |
| 3. How many sections are there in the Class XII Chemistry exam? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between Section A, Section B, and Section C in the Class XII Chemistry exam? |  |
| 5. What is the complexity level of the questions in the Class XII Chemistry exam? |  |