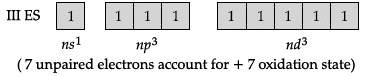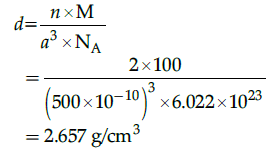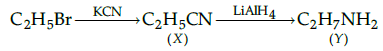Class 12 Chemistry: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term I (2021-22)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 90 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- The Question Paper contains three sections.
- Section A has 25 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section C has 6 questions. Attempt any 5 questions.
- All questions carry equal marks.
- There is no negative marking.
Section - A
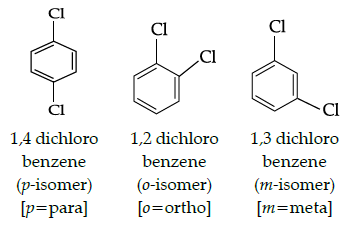
Q.1: Which of the following isomer has the highest melting point?
(a) 1,2-Dicholorbenzene
(b) 1,3 -Dichlorobenzene
(c) 1,4-Dicholorbenzene
(d) All isomers have same melting points
Correct Answer is Option (c)
From the above structure, it is clear that p-isomer is more symmetric than o-and m-isomers due to which p-isomers (1,4,- dichlorobenzene) fits closely in the crystal lattice. As a result, there are strong intermolecular forces of attraction in p-isomer and higher energy is required to break its lattice and it melts at higher temperature, Hence, p-isomer has the highest melting point.
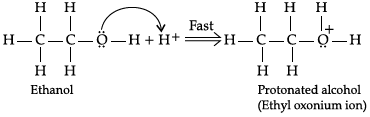
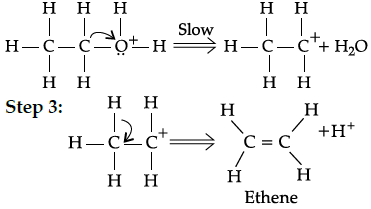
Q.2: During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with concentrated H2SO4, the initiation step is:
(a) Protonation of alcohol molecule
(b) Formation of carbocation
(c) Elimination of water
(d) Formation of an ester
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Step 1:
Step 2:
Q.3: Williamson’s synthesis of preparing dimethyl ether is an:
(a) SN1 reaction
(b) Elimination reaction
(c) SN2 reaction
(d) Nucleophilic addition reaction
Correct Answer is Option (c)
SN2 reaction (alkoxide ion reacts with primary alkyl halide in a single step to form ether)
Q.4: Which of the following is a correct statement for C2H5Br?
(a) It reacts with metallic Na to give ethane.
(b) It gives nitroethane on heating with aqueous solution of AgNO2.
(c) It gives C2H5OH on boiling with alcoholic potash.
(d) It forms diethyl thioether on heating with alcoholic KSH.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
C2H5Br reacts with metallic Na to give butane , gives ethene on boiling with alcoholic potash. and forms C2H5SH (thiol) on heating with alcoholic KSH.
Q.5: Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Melting point of Phosphorous is less than that of Nitrogen
(b) N2 is highly reactive while P4 is inert
(c) Nitrogen shows higher tendency of catenation than P
(d) N-N is weaker than P-P
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Other statements are incorrect as Phosphorus has a higher melting point due to its bigger size than Nitrogen. Also, Nitrogen is inert due to the formation of triple bonds and has a lower covalence due to non- availability of d –orbitals.
Q.6: Which of the following reactions is used to prepare salicylaldehyde?
(a) Kolbe’s reaction
(b) Étard’s reaction
(c) Reimer-Tieman reaction
(d) Stephen’s reduction.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Kolbe’s reaction is used to prepare salicylic acid, Etard reaction used for benzaldehyde preparation, Reimer- Tiema reaction for salicylaldehyde and Stephen’s reduction for aldehyde.
Q.7: Identify the law which is stated as: “For any solution, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction.”
(a) Henry’s law
(b) Raoult’s law
(c) Dalton’s law
(d) Gay-Lussac’s Law
Correct Answer is Option (b)
It establishes the relation between partial vapour pressure and mole fraction of the solution. On the other hand, Henry law gives the relation between the amount of gas dissolved and its partial pressure. Whereas Dalton’s law relates the contribution of partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases and Gay-Lussac’s law relate pressure of a gas with temperature at constant volume.
Q.8: Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
(a) H2O
(b) H2S
(c) H2Se
(d) H2Te
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Boiling point increases down the group but water forms strong hydrogen bonds so has higher boiling point than H2S
Q.9: Major product obtained on reaction of 3-Phenyl propene with HBr in presence of organic peroxide:
(a) 3- Phenyl 1- bromopropane
(b) 1 –Phenyl -3- bromopropane
(c) 1-Phenyl -2-bromopropane
(d) 3-Phenyl -2- bromopropane
Correct Answer is Option (b)
((C6H5)CH2CH=CH2 + HBr (organic peroxide) → (C6H5)CH2CH2CH2Br following anti-Markovnikov addition rule
Q.10: Maximum oxidation state exhibited by Chlorine is:
(a) +1
(b) +3
(c) +5
(d) +7
Correct Answer is Option (d)
+7 (Cl : 1s22s22p63s23p5)
Q.11: Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Fibrous proteins are generally soluble in water.
(b) Albumin is an example of fibrous proteins.
(c) In fibrous proteins, the structure is stabilised due to formation of hydrogen bonds and disulphide bonds.
(d) pH does not affect the primary structure of protein.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
pH does not affect the primary structure of protein (but pH a effects the tertiary structure).
Q.12: Which of the following is a non-stoichiometric defect?
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Metal deficiency defect
(d) Interstitial defect
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In Frenkel defect, the smaller ion occupies the interstitial sites whereas in Schottky defect equal number of cations in and anions are missing. In Interstitial defect, an atom or molecule occupies interstitial sites so in these three defects the ratio of positive and negative ions (Stoichiometric) of a solid is not disturbed in these three.
Q.13: Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with rise in temperature because dissolution is an:
(a) Endothermic and reversible process
(b) Exothermic and reversible process
(c) Endothermic and irreversible process
(d) Exothermic and irreversible process
Correct Answer is Option (b)
According to Le-Chatelier principle Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with rise in temperature.
Q.14: Which one of the following reactions is not explained by the open chain Structure of glucose:
(a) Formation of pentaacetate of glucose with acetic anhydride.
(b) Formation of addition product with 2,4 DNP reagent
(c) Silver mirror formation with Tollen’s reagent
(d) Existence of alpha and beta forms of glucose.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The existence of alpha(α) and beta (β) forms of glucose could not be explained by the open chain structure for glucose. However, these forms prove that glucose exists as a cycle structure.
Q.15: Amorphous solids are:
(a) Isotropic
(b) Anisotropic
(c) Isotopic
(d) Isomeric
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Amorphous solids are isotropic that is the value of any physical property is same along any direction.
Q.16: Substance having the lowest boiling point:
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Helium
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Helium (He is monoatomic and has low atomic mass).
Q.17: Pink colour of LiCl crystals is due to:
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) Metal excess defect
(d) Metal deficiency defect
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Metal excess defect is caused due to anionic vacancies in LiCl crystal. Lithium loses an electron which diffuses the crystal and occupies the anionic vacancy site and produces F-centre inside the crystal due to which LiCl crystal gives pink colour.
Q.18: The boiling points of alcohols is higher than those of hydrocarbons of comparable masses due to presence of:
(a) Hydrogen bonding
(b) Ion – dipole interaction
(c) Dipole- dipole interaction
(d) Van der Waal’s forces.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Hydrogen bonding (alcohols form intermolecular hydrogen bonds).
Q.19: Chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing because:
(a) HCl gas is produced, due to the action of sunlight.
(b) A mixture of HOCl and HCl is produced in the presence of light
(c) HOCl and hydrogen gas is produced
(d) A mixture of HCl and ClO3 is produced, due to the action of sunlight
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Cl2(g) +H2O (l) → HCl (g) +HOCl(aq)
Q.20: Which of the following is an example of a solid solution?
(a) Sea water
(b) Sugar solution
(c) Smoke
(d) 22 carat gold
Correct Answer is Option (d)
22 carat gold (it is an alloy so solid in solid solution).
Q.21: In which of the following cases blood cells will shrink:
(a) When placed in water containing more than 0.9% (mass/ volume) NaCl solution.
(b) When placed in water containing less than 0.9% (mass /volume) NaCl solution. (c) When placed in water containing 0.9% (mass/volume) NaCl solution.
(d) When placed in distilled water.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
When placed in water containing more than 0.9% (mass/ volume) NaCl solution. This is because fluid inside blood cells is isotonic with 0.9% NaCl solution.
Q.22: All elements of Group 15 show allotropy except:
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Arsenic
(c) Antimony
(d) Bismuth
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.23: Covalency of nitrogen is restricted to:
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Co-valency of nitrogen is restricted to 4 due to non availability of d-orbitals.
Q.24: Which of the following is a polysaccharide?
(a) Glucose
(b) Maltose
(c) Glycogen
(d) Lactose
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Glycogen in a polymer of glucose.
Q.25: Lower molecular mass of alcohols are:
(a) Miscible in limited amount of water
(b) Miscible in excess of water
(c) Miscible in water in all proportions
(d) Immiscible in water
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Lower molecular mass alcohols are able to form hydrogen bonds with water.
Section - B
Q.26: Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction ?
(a) 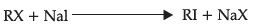
(b) 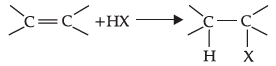
(c) 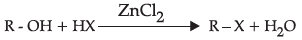
(d) 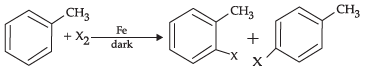
Correct Answer is Option (a)
It is halogen exchange reaction as in this reaction both R and Na exchanges halogens.
Q.27: An element having bcc structure has unit cell edge 500 pm. The density of element is: (atomic mass of element = 100 g/mol)
(a) 2.657 g/cm3
(b) 5.189 g/cm3
(c) 7.971 g/cm3
(d) 3.985 g/cm3
Correct Answer is Option (a)
M=100 g/mol
For bcc unit cell m=2
Na=6.022 x 1023
a = 500 pm
= 500 x 10-10 cm
Density of element (unit cell),
Q.28: When crystallisation occurs at fast rate:
(a) Single crystals are formed
(b) Crystals with no defects are formed.
(c) Small crystals with defects are formed.
(d) Huge size crystals with no defects are formed
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Single crystals are formed when the process of crystallisation occurs at extremely slow rate. These crystals are formed with defects. There are basically irregularities in the arrangement of constituent particles.
Q.29: Identify the products X and Y in the following sequence: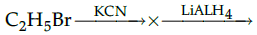
(a) X =C2H4, Y=C2H6
(b) X=C2H5CN, Y=C2H5NH2
(c) X=C2H5CN, Y=C3H7NH2
(d) X=C2H5NH2, Y=C2H6
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.30: What is the correct order of dissociation energy of C-X bond:
(a) C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
(b) C– Br > C-I > C-Cl
(c) C–Cl > C-I > C-Br
(d) C-I > C-Br > C-Cl
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Higher the bond dissociation energy of C-X bond, lesser is the reactivity
Q.31: 2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction:
(a) 2-Bromopentane
(b) 1- Bromopentane
(c) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.32: Close packed structures have:
(a) Tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(b) Only tetrahedral voids
(c) Only octahedral voids
(d) None of octahedral or tetrahedral voids.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In ccp structure there is one octahedral void at the centre and 12 octahedral voids on the edge. Two tetrahedral voids are located at each body diagonal.
Q.33: In carbohydrates, the Letter ‘D’ represents:
(a) Configuration
(b) dextrorotating
(c) Conformation
(d) Laevorotating
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Letter ‘D’ represents configuration on the basis of D-L nomenclature.
Q.34: The anhydride of nitrous acid is:
(a) NO
(b) NO2
(c) N2O3
(d) N2O4
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Let Oxidation number of N in HNO2 = x
1+x+2(-2)=0
1+x-4=0
x-3=0
x=+3
The anhydride of nitrous acid her also +3 oxidation number of nitrogen.
Oxidation number of N in NO =+2
Oxidation number of N in NO2 =+4
Oxidation number of N in N2O3 =+3
Oxidation number of N in N2O4=+4
The anhydride of nitrons acid (HNO2) is N2O3.
Q.35: Which of the following solutions has the highest boiling point at one atmospheric pressure ?
(a) 0.1 M NaCl
(b) 0.1 M Sucrose
(c) 0.1 M CaCl2
(d) 0.1 M Glucose
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Since,
Δ Tb = imKb
ΔTb = Tb – Tb0
So, ΔTb ∝ i
For NaCl, i = 2; For sucrose, i = 1
For CaCl2, i = 3; For glucose, i = 1
Hence, 0.1 M CaCl2 has highest boiling point at 1 atm.
Q.36: When there are deviations from ideal arrangement around a point or an atom in a crystalline substance, it is known as:
(a) point defect
(b) vacancy defect
(c) line defect
(d) interstitial defect
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The two defects are point defects and line defects.
Q.37: The correct axial angle for tetragonal crystal system is:
(a) α = β = γ = 90°
(b) α = β≠γ = 90°
(c) α = β = γ ≠ 90°
(d) α≠β = γ≠ 90°
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Though axial angles are equal and are equal to 90˚ ,the axial distance a = b ≠ c.
Q.38: Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows _______.
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
(d) Saytzeff rule.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
is stable cation so favours the progress of reaction by SN1 mechanism.
Q.39: Complete the reaction: H3C-Br + AgF →
(a) H3C-Br + AgF → H3C-F + AgBr
(b) H3C-Br + AgF → Br-CH2-F + AgH
(c) H3C-Br + AgF → [Ag(CH3)]F + Br
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
H3C -Br + AgF → H3C-F + AgBr
Q.40: A unit cell is characterised by ___________parametres:
(a) two
(b) four
(c) Six
(d) One
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Six parameters are:
- Its dimension along the three edges (3),
- angles between the edges (3)
Q.41: Name the major monohalo product of the following reaction: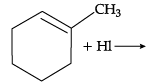
(a) 1-Iodo-1-methyl cyclohexane
(b) 1-Iodomethyl cyclohexane
(c) 1-Chloro cyclohexane
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
According to Markovnikov’s rule, iodine will add to the carbon atom having less number of hydrogen atoms.
Q.42: Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
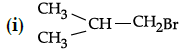
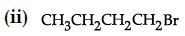
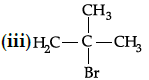
(a) (ii) < (iii) < (i)
(b) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(c) (iii) < (i) < (ii)
(d) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Boiling point of (i) is 364 K, boiling point of (ii) is 375 K. boiling point of (iii) is 346 K As the branching increases in the isomeric alkyl halides, the boiling point decreases.
Q.43: Which one of the following alcohol does not react with Lucas reagent ?
(a) 2-methyle propom-2-ol
(b) Propanol
(c) Propan-2-ol
(d) Sec. butyl alcohol
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH) is a primary alcohol which does not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature.
Q.44: Glucose forms glucose penta acetate when reacts with acetyl chloride. This reaction represents:
(a) Cyclic structure of glucose
(b) Open chain structure of glucose
(c) Presence of five –OH groups in glucose
(d) Presence of –CHO group in glucose
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Formation of glucose penta acetate shows the presence of five -OH groups in glucose.
From Q. 45 to Q. 49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below:
Q.45: Assertion (A): Osmosis is the process used in desalination of sea water.
Reason (R): The direction of osmosis can be reversed if a pressure smaller than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
On moving from top to bottom in group 15 elements, the ionization enthalpy decreases while the atomic size increases.
Q.46: Assertion (A): Formation of sulphuric acid is exothermic and reversible process.
Reason (R): Low temperature and high pressure are the favourable conditions for the maximum yield.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
As the formation of sulphuric acid is exothermic and reversible process, forward reaction leads to decrease in volume. Thus, low temperature and high pressure are the favourable conditions for the maximum yield.
Q.47: Assertion (A): Ionization enthalpy in group 15 elements decreases down the group.
Reason (R): Atomic size of group 15 elements gradually increases down the group
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
On moving from top to bottom in group 15 elements, the ionization enthalpy decreases while the atomic size increases.
Q.48: Assertion (A): Pressure does not have any significant effect on solubility of solids in liquids.
Reason (R): Dinitrogen is a toxic gas.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Due to high bond enthalpy of N ≡ N, dinitrogen is inert at room temperature.
Q.49: Assertion (A): The vapour pressure of some solutions is higher and show positive deviation.
Reason (R): The intermolecular attractive forces between the solute-solvent molecules are weaker than those between the solute-solute and solvent-solvent molecules.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
As the formation of sulphuric acid is exothermic and reversible process, forward reaction leads to decrease in volume. Thus, low temperature and high pressure are the favourable conditions for the maximum yield.
Section - C
Q.50: Match the following :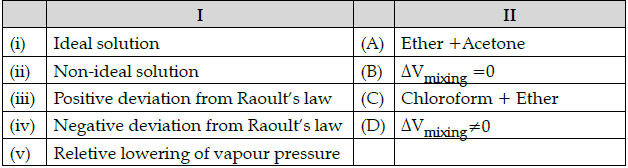
Which of the following is the best matched options ?
(a) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
(b) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
(c) i-B, ii- D, iii-A, v-C
(d) i-D, iii-D, iv-A, iv-C
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Ideal solution: ΔVmixing = 0
For an ideal solution, volume of solution on adding to components should be equal to volume of two component.
Non-ideal solution : ΔVmixing ≠ 0
For a non-ideal solution, volume of solution on adding two components should not be equal to volume of two component.
Positive deviation from Raoult’s law: Ether + Acetone Ether + Acetone are the two components forming non-ideal solution which represents positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Negative deviation from Raoult’s low: Chloroform + Ether Chloroform + ether are the two components forming non-ideal solution which represents negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Q.51: Which of the following analogies is correct:
(a) Group 16 : Chalcogens : Group 17 : Halogens
(b) Oxygen : 1s2, 2s2 2p4 : Fluorine : 1s2, 2s2 2p6
(c) Galena : PbS : Gypsum : CaSO4 ½H2O
(d) NH3 : sp3 : SF6 : sp3d
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Group 16 elements are called chalcogens (Ore forming elements) group 17 elements are called halogens (salt forming elements).
Fluorine: 1s22s22p5
Gypsum: CaSO4, 2H2O
SF6 : sp3d2 hybridization
Q.52: Complete the following analogy :
Iodoform test : A :: Lucas : B
(a) 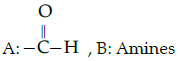
(b) 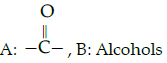
(c) 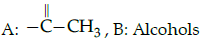
(d) 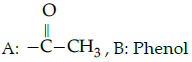
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Iodofrom test is used for the identification of functional group
Lucas test is used to differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55.
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They act both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O-H is broken when alcohols act as nucleophiles.
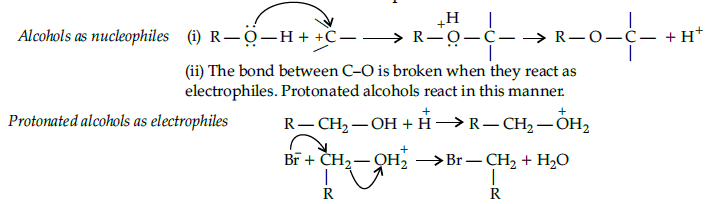
Based on the cleavage of O-H and C-O bonds, the reaction of alcohols and phenols may be divided into two groups :
(a) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond
(b) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond
Acidity of alcohols and phenols
(i) Reaction with metals :Alcohols and phenols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium and aluminium to yield corresponding alkoxide/phenoxides and hydrogen.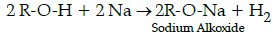
Q.53: Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols:
(a) 1ºalc<2ºalc<3ºalc
(b) 1ºalc>2ºalc>3ºalc
(c) 3ºalc<1ºalc<2ºalc
(d) 3ºalc>1ºalc < 2ºalco
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Na metal is basic and alcohols are acidic in nature. Hence, reactivity of Na metal towards alcohols decreases as the acidic strength of alcohols decreases due to steric hinderance of alkyl groups in tertiary alcohol and increase in electron density on an oxygen atom in the hydroxyl bond.
Q.54: Name the following reaction: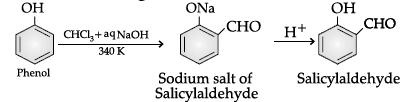
(a) Williamson’s synthesis
(b) Kolbe’s reaction
(c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(d) Sandmeyer’s reaction
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.55: Given the descending order of acid strength of alcohols:
(a) RCH2OH > RR’CHOH >> RR’R”COH
(b) RCH2OH > RR’R”COH > RR’CHOH
(c) RCH2OH < RR’CHOH << RR’R”COH
(d) RCH2OH < RR’R”COH < RR’CHOH
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The more stable the alkoxide ion, the more acidic is the alcohol. Electron releasing effect (+I effect ) of alkyl group in secondary and tertiary alcohols makes the alkoxide ion less stable.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|