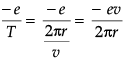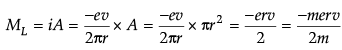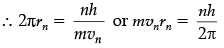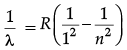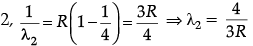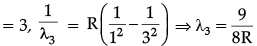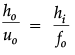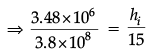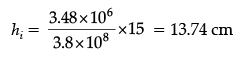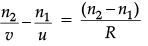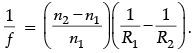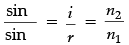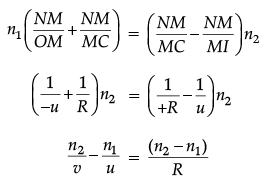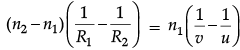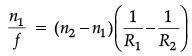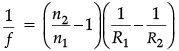Class 12 Physics: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 4 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- There are 12 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A contains three questions of two marks each, Section B contains eight questions of three marks each, Section C contains one case study-based question of five marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks and two questions of three marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- You may use log tables if necessary but use of calculator is not allowed.
Section - A
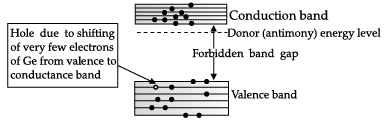
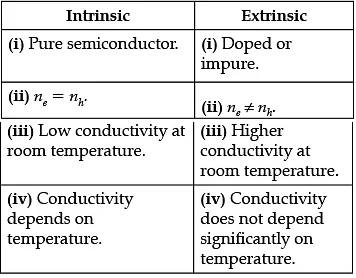
Q.1. Draw the energy band diagram when intrinsic semiconductor (Ge) is doped with impurity atoms of Antimony (Sb). Name the extrinsic semiconductor so obtained and majority charge carriers in it.
This is an n-type extrinsic semiconductor. Majority charge carriers are electrons.
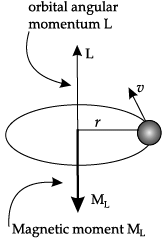
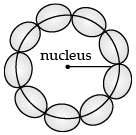
Q.2. Use Bohr ’s model of hydrogen atom to obtain the relationship between the angular momentum and the magnetic moment of revolving electron.
OR
The figure shows the stopping potential (V0) for the photoelectron versus 1/λ graph, for two metals A and B, λ being the wavelength of incident light.
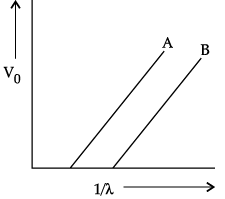
(a) Can the Planck's constant be determine by using given graph?
(b) What would be the effect on stopping potential if the distance between source of light and surface of metals A increases?
In Bohr model of Hydrogen atom, electron is modeled as a point negative charge rotating in a circular orbit about a fixed axis about a nucleus.
Let us consider,
r = Radius of the orbit, v = Velocity
e = Charge of electron, m = Mass of electron
Time period (T) = circumference/velocity = 2πr/v
Current (i)=
The magnetic moment due to a current loop enclosing an area A is given by:
L = Angular momentum = mvr
So, (ML = (-e)/2m)L
OR
(a) Planck’s constant can be determined from the gradient of the graph.
Gradient = hc/e
Here, h = Planck’s constant,
c = Velocity of light in vacuum,
e = Charge of electron
Gradient to be measured from graph. The values of c and e are known. Hence, h can be determined.
(b) If distance between source of light and surface of metal A is increased, the intensity of incident light decreases. Since, stopping potential does not depend on the intensity of the incident light. So, the stopping potential will not be affected.
Q.3. Write two points of difference between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Section - B
Q.4. (a) How is the stability of hydrogen atom in Bohr model explained by de-Broglie’s hypothesis?
(b) A hydrogen atom initially in the ground state absorbs a photon which excites it to n = 4 level. When it gets de-excited, find the maximum number of lines which are emitted by the atom. Identify the series to which these lines belong. Which of them has the shortest wavelength ?
(a) Explanation
(b) Identification of Series
(c) Identification of shortest wavelength
(a) Explanation: The quantised electron orbits and energy state are due to wave nature of the electron and only resonant standing waves can persist.
According to de-Broglie Hypothesis,
2πr = nλ
= nh/mv
mvr = (nh/2π)
(b) Lyman series:
transition from n = 4 to n = 1 will have shortest wavelength.
Detailed Answer:
(a) Bohr combined classical and early quantum concepts and gave his theory in the form of three postulates. The second postulates is: Electron revolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which angular momentum in integral multiple h/2π.
de-Broglie had proposed that material particle such as electrons also have a wave nature. He argued that the electron in its circular orbit, as proposed by Bohr, must be seen as a particle wave. Drawing an analogy with waves travelling on the string, particle waves too can lead to formation of standing waves. In a string, standing waves are formed, when the total distance travelled by a wave back and forth is one wavelength, two wavelength or integral multiple of wavelengths. Other waves interfere with themselves after reflection and their amplitude falls to zero. For an electron moving in nth orbit with radius rn, its circumference is 2πrn.
∴ 2πrn = nλ, n = 1, 2, 3
From de-Broglie’s hypothesis,
Wavelength of the election (λ) is given as, λ = h/p = h/mv
For nth orbit, λ = h/mvn
This is the second postulate of Bohr that gives the discrete orbits and energy levels in hydrogen atom.
Thus de-Broglie explained the postulate of quantisation angular momentum.
(b) For ground state n = 1, For de-excitation from n = 4 to n = 1, we get spectral lines constituting Lyman series whose wavelength is given by the formula,
Here R = Rydberg constant number n = 2, 3, 4
For n =
For n
For n[Here, 1/R = 912Å]
There would be maximum three lines emitted by the atom. λ4 is the shortest wavelength.
Q.5. (a) Can a slab of p-type semiconductor be physically joined to another n-type semi-conductor slab to form p-n junction ? Justify your answer.
(b) In the case of n-type semiconductor, the donor energy level is slightly below the bottom of conduction band whereas in p-type semiconductor, then acceptor energy level is slightly above the top of the valance band. Explain what role these energy levels play in conduction and valence bands?
(a) No, a p-type semi-conductor slab cannot be physically joined with a n-type semiconductor slab to produce a p-n junction.
If we physically join the two semiconductor blocks, there will always be little microscopic gap between the slabs due to roughness of the surfaces.
(b) In case of n-type semiconductor, electrons from donor impurity atoms move into conduction band with very small supply of energy. Hence, the conduction band have electrons as majority carrier.
In case of p-type semiconductor, very small supply of energy cause an electron to jump from its valance band to the acceptor energy level. Hence, the valence band will have dominant density of holes which shows that holes are the majority charge carriers in p-type semiconductor.
Q.6. (a) State two distinguishing features of nuclear force.
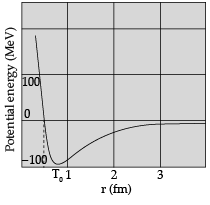
(b) Draw a plot showing the variation of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separation. Mark the regions on the graph where the force is (i) attractive, and (ii) repulsive.
(a) Stating distinguishing feature of nuclear force.
(b) Draw a plot showing variation of potential energy.
(i) and (ii) Marking the regions.
(a) Distinguishing feature:
- Short range force
- Strongest force
- Attractive in nature
- Does not depend on charge (any two)
(b) Plot showing variation of potential energy:
Marking the regions:
(i) r > r0 : attractive force
(ii) r < r0 : repulsive force
Q.7. (a) What is the phase difference between two points on the same wavefront?
(b) Define secondary wavelets and how can we construct new wavefront with them?
(a) Phase difference between two points on the same wavefront is zero.
(b) According to the Huygens’ principle, every particle of the medium, situated on the wavefront, acts as a new source of light wave from which new similar waves originates. These waves are called secondary wavelets.
The envelop of the secondary wavelets in the forward direction at any instant gives the new wavefront at that instant.
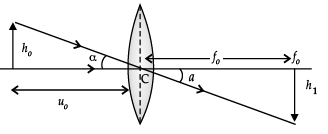
Q.8. (a) A giant refracting telescope has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eye piece of focal length 1.0 cm is used, what is the angular magnification of the telescope?
(b) If above telescope is used to view the Moon, what is the diameter of the image of the Moon formed by the objective lens? The diameter of the Moon is 3.48 × 106 m and the radius of lunar orbit is 3.8 × 108 m.
OR
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
(a) Angular magnification of telescope.
m = (-f0)/fe ; ignoring –ve sign as it only shown that image is inverted.
fo = 1500 cm
fe = 1 cm
m = 1500/1 = 1500
(b) Angular size of the Moon,
tanα = h0/u0
Let ho and hi be the diameters of the Moon and its image respectively.Angular size of the Moon’s image by objective lens is also, tan b = hi/f0
If,
Here, ho = 3.48 × 106 m
uo = 3.8 × 108 m.
fo = 15 m
OR
Conditions required for Total Interval Reflection
(i) Light travels from denser to rarer medium.
(ii) Angle of incidence is more than the critical angle.
Relation between refractive index and critical angle
By Shell's law, we have, 2n1 = sin i/sin r
For Total Internal Reflection, i = c and r = 90°
Hence, 2n1 = sin c/sin 90°
1n2 = 1/sin c [∵ sin90° = 1]
where, c = critical angle.
Q.9. State the main implications of observations obtained from various photoelectric experiments. Can these implications be explained by wave nature of light? Justify your answer.
Main implications:
Kinetic energy of emitted electrons depends upon frequency, but not on intensity of radiation.
There exist a frequency of radiation below which no photoemission takes place, however high intensity of radiation may be.
Wave nature of radiation fails to explain photoelectric effect.
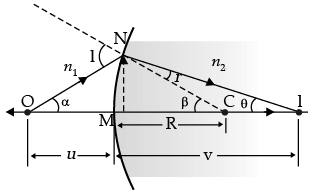
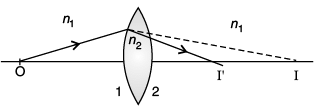
Q.10. Derive the mathematical relation between refractive indices n1 and n2 of two lenses and radii of curvature R for refraction at a convex spherical surface. Consider the object to be a point since lying on the principle axis in rarer medium of refractive index n1 and a real image formed in the denser medium of refractive index n2. Hence, derive lens maker’s formula.
Derivation of
For paraxial rays, θ1 and θ2 are small
Therefore, n2 sin θ1 = n1 sin θ2 (Snell’s law)
Reduces to
or, i × n1 = r × n2
(α + β)n1 = (β – γ)n2
Applying above relations to refraction through a lens:For surface 1,
...(i)
For surface 2,...(ii)
Adding eqn. (i) and (ii),
For u = ∞, v = f,∴
⇒
Q.11. (a) We feel the warmth of the sunlight but not the pressure on our hands. Explain.
(b) Which out of wavelength, frequency and speed of an electromagnetic wave does not change on passing from one medium to another?
(c) A thin ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is crucial for humans’ survival on Earth, why?
OR
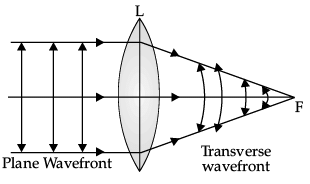
(a) State Huygens' principle.
(b) Based on Huygens construction, draw the shape of a plane wavefront as it gets refracted on passing through a convex lens.
(a) The Sun outputs about 1300 watts per square metre (W/m2) in space near the Earth, which gets reduced to around 650 W/m2 after through the atmosphere. So, the amount of heat is quite realisable.
The forces generated by solar radiation is generally too small to be noticed under everyday life. The radiation pressure of sunlight on Earth is equivalent to that exerted by about a thousandth of a gram on an area of 1 square metre. It is approximatel 10μN/m2. Hence, it is negligible.
(b) Frequency of electromagnetic wave does not change from one medium to another medium.
(c) Ozone layer absorbs biologically harmful ultraviolet radiation coming from the Sun. Hence, it is crucial for humans’ survival on Earth.
OR
(a) Huygens' Principle : Each point of a wavefront is the source of a secondary disturbance and the wavelets emanating from these points spread out in all directions. These travel with the same velocity as that of the original wavefront.
(b) Refracted wavefront will be spherical in nature.
Section - C
Q.12. Case Study: Fresnel Biprism
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
In one of his experiments on interference, August Jean Fresnel used a biprism to induce interference between two beams. He split a diverging beam of light into two parts by using the biprism to refract them. This resulted in two split beams which acted as if they were from two coherent sources and which therefore interfered with each other.
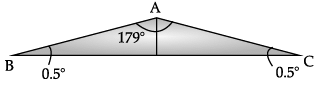
A Fresnel Biprism is a thin double prism placed base to base and have very small refracting angle (0.5°). This is equivalent to a single prism with one of its angle nearly 179° and other two of 0.5° each.
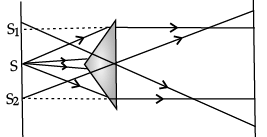
In Young’s double Slits experiment, a single source is split in two coherent sources. For the Young’s slits experiment, we must approximate that the slits act as point sources. This however is not the case, since the slits have finite width. In this way, it gives rise to unwanted diffraction effects that causes errors.
The Fresnel biprism experiment overcomes this problem.
A Fresnel biprism is a variation of Young’s Slits experiment. When monochromatic light through a narrow slit falls on biprism that divides it into two components. One of these component is refracted from upper portion of biprism and the other one refracted through lower portion. Two virtual coherent sources formed from the original source. In this case, two virtual coherent sources are point sources and replace slits in Young’s experiment.
(a) The Fresnel biprism is:
(i) a combination of two prisms with their bases in contact.
(ii) a combination of two prisms with their refracting surfaces in contact.
(iii) single prism
(iv) not a prism actually.
(b) Base angles of Fresnel biprism are:
(i) 179°
(ii) 90°
(iii) 0.50°
(iv) None of these
(c) Fresnel biprism produces:
(i) two real coherent sources.
(ii) two virtual coherent sources.
(iii) a number of real coherent sources.
(iv) a number of virtual coherent sources.
(d) What is the difference between the coherent sources produced by Young’s double slit arrangement and Fresnel biprism?
(i) Young’s double slit arrangement produces virtual coherent sources whereas Fresnel biprism produces real coherent sources.
(ii) Young’s double slit arrangement produces coherent point sources whereas Fresnel biprism produces coherent sources which are not point sources.
(iii) Both Young’s double slit arrangement and Fresnel biprism produce similar coherent sources.
(iv) Fresnel birism produces virtual coherent point sources whereas Young’s double slit arrangement produces real coherent sources which are not point sources.
(e) Which problem of Young’s double slit experiment is overcome by Fresnel biprism?
(i) Young’s double slit arrangement gives rise to irregular interference fringe pattern which is overcome by Fresnel biprism which produces coherent sources by refraction in a prism.
(ii) Finite width of slits in Young’s double slit experiment gives rise to unwanted diffraction effects that causes errors. This is overcome by Fresnel biprism by producing virtual coherent point sources.
(iii) Young’s double slit arrangement produces interference fringe pattern of low intensity which is overcome by Fresnel biprism.
(iv) All of the above.
(a) Option (i) is correct.
Explanation: A Fresnel Biprism is a thin double prism placed base to base.
(b) Option (iii) is correct.
Explanation: A Fresnel Biprism is a thin double prism placed base to base and have very small refracting angle (0.5°).
(c) Option (ii) is correct.
Explanation: When monochromatic light through a narrow slit falls on Fresnel biprism that divides it into two components. One of these component is refracted from upper portion of biprism and the other one refracted through lower portion. Thus, two virtual coherent sources formed from the original source.
(d) Option (iv) is correct.
Explanation: In Young’s double Slits experiment, a single source is split in two coherent sources which are real. Both the slits have finite width.
Fresnel biprism divides the beam of monochromatic light incident on it into two components. One of these component is refracted from upper portion of biprism and the other one refracted through lower portion. Thus two virtual coherent sources are formed from the original source.
(e) Option (ii) is correct.
Explanation: In Young’s double Slits experiment, a single source is split in two real coherent sources. For the Young’s slits experiment, we must assume that the slits act as point sources. This however is not the case, since the slits have finite width. In this way, it gives rise to unwanted diffraction effects that causes errors.
The Fresnel biprism experiment overcomes this problem.
When monochromatic light through a narrow slit falls on biprism that divides it into two components. One of these component is refracted from upper portion of biprism and the other one refracted through lower portion. Two virtual coherent point sources are formed from the original source.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|