Class 12 Political Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term I (2021-22)- 1 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions
1. The question paper has three sections as A, B & C.
2. Section A has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
3. Section B has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
4. Section C has 12 questions, attempt any 10 questions.
5. There is only one correct option for every question. Marks will not be awarded for marking more than one option.
6. All questions carry equal marks. There is no negative marking
Section A
Q.1: The US, Japan, Germany, France, the UK, Italy, Canada and Russia are the:
(a) G8 members
(b) D8 members
(c) Cold War countries
(d) Dominating members
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Group of Eight + Five (G8+5) was an international group that consisted of the leaders of the heads of government from the G8 nations (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States), plus the heads of government
Q.2: When did Cuban Missile Crisis occur?
(a) 1967
(b) 1962
(c) 1960
(d) 1970
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In 1962 the Soviet Union began to secretly install missiles in Cuba to launch attacks on U.S. cities. The confrontation that followed, known as the Cuban missile crisis, brought the two superpowers to the brink of war before an agreement was reached to withdraw the missiles.
Q.3: Which set of the countries belonged to the NATO Group?
(a) Poland, Britain, Romania
(b) USA, Czech Republic, France
(c) United Kingdom, France, West Germany
(d) Spain, France, East Germany
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Twelve countries took part in the founding of NATO: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1952, Greece and Turkey became members of the Alliance, joined later by West Germany (in 1955) and Spain (in 1982).
Q.4: Which of the following statements about the NIEO is false?
(a) Give the LDCs control over their natural resources.
(b) Obtain access to western markets.
(c) Reduce the cost of technology from western countries.
(d) Provide the developed countries with a greater role in international economic institutions.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The crucial aim of the NIEO is to promote economic development among the poor countries through self- help and South- South cooperation. The NIEO intends to deal with the major problems of the South, such as balance of payments disequilibrium, debt crisis, exchange scarcity etc.
Q.5: When did Mahatma Gandhi die?
(a) 30th January 1948
(b) 31st January 1948
(c) 30th December 1948
(d) 30th November 1948
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Gandhi was assassinated on 30 January 1948 in the compound of Birla House, New Delhi by Nathuram Godse.
Q.6: Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel faced key challenges of integration in which of the following state
(a) Hyderabad, Moradabad, Junagarh
(b) Hyderabad, Sikandrabad, Jammu
(c) Hyderabad, Junagarh, Kashmir
(d) Jammu, Junagarh, Kashmir
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Sardar Patel faced key challenges of integration from three states, viz., Hyderabad, Junagarh and Kashmir. It was under his leadership that Indian forces compelled Hyderabad and Junagarh to merge with India. Like Hyderabad, he also wanted Kashmir’s integration with India through military operations. But due to political decisions of some prominent leaders, Sardar could not succeed in integrating Kashmir fully with India which later turned into a major historical blunder for the country.
Q.7: Sri Lanka is a member of:
(a) SAARC
(b) UNESCO
(c) G7
(d) WHO
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an organization of eight countries (Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka) in South Asia established in 1985.
Q.8: It was in ........................ that full diplomatic relations were restored between India and Pakistan.
(a) 1976
(b) 1966
(c) 1956
(d) 1946
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.9: When did India and China signed Panchsheel agreement?
(a) 24 April, 1954
(b) 29 April, 1954
(c) 30 April, 1954
(d) 1 March, 1959
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Panchsheel Agreement signed on 29 April 1954 by the Indian Prime Minister Jawahar Lal Nehru and the Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai to make stronger relationship between the two countries.
Q.10: The first non-aligned summit was held in the year 1961 in ...................
(a) Venice
(b) Delhi
(c) Belgrade
(d) Dhaka
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.11: In which year NAM was established?
(a 1956
(b) 1960
(c) 1990
(d) 1957
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.12: Which of the following countries was not a member of NATO?
(a) France
(b) The U.S.A.
(c) England
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.13: ...................... witnessed a Civil War that went on for ten years till 2001.
(a) Dagestan
(b) Tajikistan
(c) Chechnya
(d) Moscow
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Economic hardship, communal lifestyle of Tajiki people and their high religiosity caused the Civil War in Tajikistan.
Q.14: The real GDP of Russia in 1999 was below what it was in:
(a) 1959
(b) 1969
(c) 1979
(d) 1989
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.15: The post-Soviet countries underwent a process of transition from an authoritarian socialist system to ...................... capitalism system.
(a) democratic
(b) authoritative
(c) aristocratic
(d) systematic
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Democratic capitalism system is a political and economic system that combines capitalism and strong social policies.
Q.16: Arrange the following in the chronological order:
(i) Establishment of Human Rights Council
(ii) Yalta Conference
(iii) Atlantic Charter
(iv) India join the UN
(a) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(i) The Atlantic Charter issued on 14 August 1941. (ii) Yalta Conference held on 11 February 1945. (iii) On 26 June 1945, India join the UN. (iv) Human Rights Council established on 15 March 2006.
Q.17: What was India’s partition plan called?
(a) Gandhi Plan
(b) Nehru Plan
(c) Mountbatten Plan
(d) Jinnah Plan
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Lord Mountbatten, the last Viceroy of India, came up with a plan under which he proposed that the provinces be declared independent successor states. The plan was the last plan for Indian independence and included the principles of partition, autonomy, sovereignty, and the right to make the Indian constitution.
Q.18: The ............................ laid foundation for Non Alignment Movement established in 1961 with Nehru as the co-founder.
(a) Bandung Conference
(b) Foreign Policy
(c) US Aid
(d) Peace Treaty
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Bandung Conference and its final resolution laid the foundation for the non- aligned movement during the Cold War. Leaders of developing countries banded together to avoid being forced to take sides in the Cold War contest. The initial motivation for the movement was the promotion of peace.
Q.19: The high point of Cold War was ....................... .
(a) Cuban Missile Crisis
(b) Atomic bomb attack on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
(c) Establishment of SEATO and CENTO
(d) Establishment of NATO
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a dangerous confrontation between the US and the USSR in which both of them came closest to nuclear conflict.
Q.20: The ‘Two-Nation Theory’ was based upon:
(a) expansion of India
(b) bifurcation of the states
(c) partition of India
(d) All of the Above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Two Nation Theory is based on the hypothesis that India should be divided into two: Pakistan and Hindustan, the Muslim nation to occupy Pakistan and the Hindu nation to occupy Hindustan.
Q.21: In post WW2 era, why the tensions were erupted between India and US?
(a) US feared that India would join USSR.
(b) US wanted to colonize India.
(c) The NAM pursued by India was not liked by USA.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
While India was trying to convince the other developing countries about the policy of non-alignment, the US was not happy about India’s these independent initiatives. The US also disliked India’s growing partnership with the Soviet Union. Therefore, there was a considerable unease in Indo- US relations during the 1950s.
Q.22: Which U.N. agency concerned with the safety and peaceful use of nuclear technology?
(a) The UN Committee on Disarmament
(b) International Atomic Energy Agency
(c) UN International Safeguard Committee
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The main functions of the IAEA are to: encourage and assist research, development and practical application of atomic energy for peaceful uses throughout the world; establish and administer safeguards designed to ensure that such activity assisted by the Agency is not used to further any military purpose.
Q.23: The Secretary-General - Ban Ki-Moon from South Korea is the ................... Secretary-General of the UN.
(a) Fifth
(b) Sixth
(c) Seventh
(d) Eighth
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Ban Ki-moon is a South Korean politician and diplomat who served as the eighth Secretary-General of the United Nations from January 2007 to December 2016.
Q.24: Who was India’s Deputy Prime Minister at the time of integration of princely states?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar
(c) Narsimha Rao Reddy
(d) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Section B
Q.25: What was the first among the three challenges to India while building a nation-state?
(a) building a united nation
(b) poverty
(c) communal tensions
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The first and the immediate challenge was to shape a nation that was united, yet accommodative of the diversity in our society.
Q.26: In 1992, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution related to:
(a) UN Security Council
(b) UNESCO
(c) UNICEF
(d) World Bank
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.27: When did Cuban Missile Crisis occur?
(a) 1967
(b) 1962
(c) 1960
(d) 1970
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In 1962 the Soviet Union began to secretly install missiles in Cuba to launch attacks on U.S. cities. The confrontation that followed, known as the Cuban missile crisis, brought the two superpowers to the brink of war before an agreement was reached to withdraw the missiles.
Q.28: The first nuclear explosion undertaken by India was in May:
(a) 1964
(b) 1974
(c) 1984
(d) 1994
Correct Answer is Option (a)
During the tenure of Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, first underground nuclear explosion occurred at Pokhran in Rajasthan on May 18, 1974.
Q.29: Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, the undisputed leader of the North Western Frontier Province was known as:
(a) Frontier Gandhi
(b) Father of Pakistan
(c) Staunch Muslim
(d) Patriot of Pakistan
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Ghaffar Khan was a Pashtun who greatly admired Mahatma Gandhi and his nonviolence principles and saw support for the Congress as a way of pressing his grievances against the British frontier regime. Hence, he was called the Frontier Gandhi
Q.30: Arrange the following in the chronological order:
(i) Establishment of Human Rights Council
(ii) Yalta Conference
(iii) Atlantic Charter
(iv) India join the UN
(a) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(i) The Atlantic Charter issued on 14 August 1941.
(ii) Yalta Conference held on 11 February 1945.
(iii) On 26 June 1945, India join the UN.
(iv) Human Rights Council established on 15 March 2006.
Q.31: Which one of the following is the permanent member of UN?
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Sweden
(d) Ireland
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The UN Security Council has five permanent members i.e. China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States.
Q.32: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: International organizations only solve the disputes among the countries.
Reason: International organizations are helpful in another way. Nations can usually see that there are some things they must do together. There are issues that are so challenging that they can only be dealt with when everyone works together. Disease is an example.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
International organizations, apart from resolving disputes, can play an important role to deal with the other issues like poverty, pandemic or any natural disaster which needs international attention.
Q.33: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The fact that the UN is physically located within the US territory gives Washington additional sources of influence.
Reason: Within the UN, the influence of the US is considerable.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The history of United States of America (USA) and the United Nations (UN) is long and complex. The United Nations owes a lot of what it is today to the US. It was the US that breathed life into the UN with its power and resources. ... Despite that, the UN does hold an important position in US foreign policy.
Q.34: The WHO has played a leading role in ................... .
(a) public health achievement
(b) economic development
(c) children’s health
(d) resolving disputes among the nations
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays an essential role in the global governance of health and disease; due to its core global functions of establishing, monitoring and enforcing international norms and standards, and coordinating multiple actors toward common goals.
Q.35: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The UN is an imperfect body, but without it the world would be worse off.
Reason: Given the growing connections and links between societies and issues—what we often call ‘interdependence’—it is hard to imagine how more than seven billion people would live together without an organization such as the UN.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The UN accomplishes this by working to prevent conflict, helping parties in conflict make peace, deploying peacekeepers, and creating the conditions to allow peace to hold and flourish. The UN Security Council has the primary responsibility for international peace and security.
Q.36: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The installation of these weapons put the US, for the first time, under fire from close range and nearly doubled the number of bases or cities in the American mainland which could be threatened by the USSR.
Reason: Nikita Khrushchev, the leader of the Soviet Union, decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.37: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Development was now envisaged through more trade, and thus a sudden and complete switch to free trade was considered essential. A
Reason: Shock therapy also involved a drastic change in the external orientation of these economies.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
They needed a change in all the aspects of the post-soviet nations. Hence, Shock Therapy demanded the changes which in turn anticipated a united contribution of the nations.
Q.38: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralized control.
Reason: A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The 1991 Soviet coup d’état attempt, also known as the August Coup, was a failed attempt made by Communist leaders of the Soviet Union to take control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was Soviet President and General Secretary of the party.
Q.39: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Central Asian countries were already in control of US.
Reason: Central Asia has also become a zone of competition between outside powers and oil companies.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Central Asia is a major focus of competition for the world’s political and economic powers because of its strategic position and rich oil and gas resources.
Q.40: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: It was decided to follow the principle of religious majorities for the partition. A
Reason: The process of partition was smooth and none of the violence took place.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
During the Partition of India, violence against women was an extensive issue. It is estimated that during the partition between 75,000 and 100,000 women were kidnapped and raped. India and Pakistan later worked to repatriate the abducted women. Muslim women were to be sent to Pakistan and Hindu and Sikh women to India.
Q.41: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The problem was that two of the Muslim majority provinces of British India, Punjab and Bengal, had very large areas where the non- Muslims were in majority.
Reason: It was decided that these two provinces would be bifurcated according to the religious majority at the district or even lower level
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Since there was no possibility of large-scale migration of the people, the decision was taken to divide it according to the religious majority.
Q.42: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The draft of the First Five Year Plan and then the actual Plan Document, released in December 1951, generated a lot of excitement in the country. AE
Reason: This draft failed to meet the expectations of the country as it did not have anything for common men.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The first year plan was Harrod – Domar model of development economics. Five Year Plan had a target of 2.1% PA growth in national income. Top priority was given to the development of agricultural sector. The idea was agricultural development would lead to higher rate of economic growth.
Q.43: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The nationalist leaders were clear that the economic concerns of the government of free India would have to be different from the narrowly defined commercial functions of the colonial government.
Reason: It was further clear that the eradication of the poverty was not the responsibility of the government, but the people.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The task of poverty alleviation and social and economic redistribution was being seen primarily as the responsibility of the government because for some people industrialisation was priority while for others, the development of agriculture and alleviation of rural poverty was the priority.
Q.44: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Indian air crafts attacked parts of Pakistan and the army moved into POK and Swat Valley.
Reason: After months of diplomatic tension and military build-up, a full-scale war between India and Pakistan broke out in December 1971.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
India indeed had given the answer to Pakistan’s mischievous acts on the border. But, the attack was never initiated by Indian side, nor did Indian army entered Swat Valley.
Q.45: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Huge stocks of arms were considered necessary to prevent wars from taking place.
Reason: Since the Cold War did not eliminate rivalries between the two alliances, mutual suspicions led them to arm themselves to the teeth and to constantly prepare for war.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In time, therefore, the US and USSR decided to collaborate in limiting or eliminating certain kinds of nuclear and nonnuclear weapons. A stable balance of weapons, they decided, could be maintained through ‘arms control’.
Q.46: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: ‘Development’ was about becoming more ‘modern’ and modern was about becoming more like the industrialized countries of the West.
Reason: It was believed that every country would go through the process of modernization as in the West, which involved the breakdown of traditional social structures and the rise of capitalism and liberalism.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q.47:
Assertion: The British Government took the view that all these 565 states were free to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent if they so wished.
Reason: This was a very serious problem and could threaten the very existence of a united India.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The official policy statement of the Government of India made by Sardar Patel on July 5, 1947 made no such threats. It reassured the princely states about the Congress’ intentions, and invited them to join independent India.
Q.48: Assertion: The Indian national movement was not an isolated process. It was a part of the worldwide struggle against colonialism and imperialism.
Reason: It influenced the liberation movements of many Asian and African countries.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Indian national movement encouraged many colonies to stand against their oppressors. Taking India’s example, many African and Asian countries stood against imperialism.
Section C
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the following question (49-50)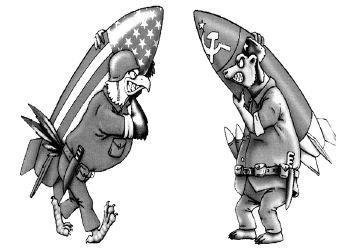
Q.49: Name two allied countries each of these superpowers.
(a) Albania and Romania
(b) New Zealand and China
(c) India and Nepal
(d) France and Canada
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.50: What was the result of the Cold War?
(a) Disintegration of USSR and US emerging as the sole superpower.
(b) Beginning of Russian dominance over the world.
(c) Fall down of US as a capitalist economy and its adoption of Communist model.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
During 1989 and 1990, the Berlin Wall came down, borders opened, and free elections ousted Communist regimes everywhere in eastern Europe. In late 1991 the Soviet Union itself dissolved into its component republics. With stunning speed, the Iron Curtain was lifted and the Cold War came to an end.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
Q.51: Who opposed the coup of 1991?
(a) Mikhail Gorbachev
(b) Post-Soviet republics
(c) Communist party
(d) Boris Yeltsin
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Boris Yeltsin denounced the coup and asked the world to help maintain the Soviet Union’s movement towards democracy. Within two days the coup collapsed. One of the largest public demonstrations in Russian history celebrated the failure of the coup in Moscow.
Q.52: Which were the three major republics of USSR
(a) Poland, Cuba, Russia
(b) Sweden, Germany, France
(c) Russia, Ukraine, Belarus
(d) Ukraine, Poland, Sweden
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Soviet Union was created by the treaty between the Soviet Socialist Republics of Belarus, Ukraine, Russia, and the Trans Caucasian Federation, by which they became its constituent republics.
Q.53: Which type of government was adopted by the post-soviet countries?
(a) Socialist
(b) Capitalist and Democratic
(c) Communist Democratic
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.54: Which country became the successor state of the Soviet Union?
(a) Belarus
(b) Ukraine
(c) Central Asian Republics
(d) Russia
Correct Answer is Option (d)
With the dissolution of the USSR in 1991, the United States considered the Russian Federation as the successor state of the USSR.
Study the cartoon given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
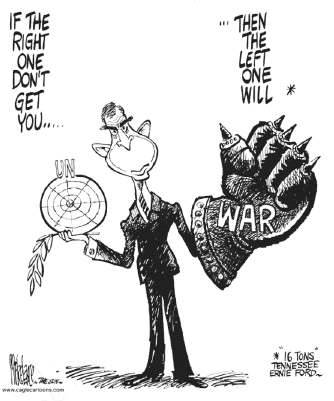
Q.55: What does this cartoon depict?
(a) UN’s influence on the world
(b) USA’s influence on UN
(c) US Hegemony
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.56: What have been the reasons for immense influence of US on UN?
(a) USA’s economic superiority
(b) USA’s weapon capacity
(c) UN’s head quarter is in USA and USA’s financial contribution to UN.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Although the United States continues to play a leadership role at the UN, it has also accumulated massive arrears in its payments to the UN, owing the world organization approximately $1 billion, far more than any other member state.
Q.57: Why this cartoon is not relevant today?
(a) Because all the countries have their powerful organizations.
(b) US is now not as powerful as it used to, as the new centres of power emerged.
(c) Iraq and Afghanistan war has affected US economy.
(d) UN has become more powerful.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.58: How has US dominated the world?
(a) By its trade and commerce
(b) By its technology
(c) By its advancement in space research.
(d) By dominating military, economy and cultural aspects of the other nations.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.59: Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow:

What is represented by the cartoon?
(a) Poverty in the third world countries
(b) Poverty in South African countries
(c) Humanitarian crisis in Darfur, Sudan.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Darfur, the western region of Sudan, has been in a state of humanitarian crisis since 2003. The current conflict in Darfur is complex, caused by a host of political, social, economic and environmental problems. Hundreds of thousands of people have died and more than 8.5 million people are affected by the crisis.
Q.60: Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
Who propounded the ‘two nation theory’?
(a) Sardar Patel and Congress
(b) Muslim League
(c) Khan Abdul Ghaffar
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
|
145 docs|4 tests
|





















