Class 12 Political Science: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 4 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions
1. The question paper has three sections as A, B & C.
2. Section A has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
3. Section B has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
4. Section C has 12 questions, attempt any 10 questions.
5. There is only one correct option for every question. Marks will not be awarded for marking more than one option.
6. All questions carry equal marks. There is no negative marking
Section A
Q.1: A system in which the affairs at the international level cannot be dominated by only one superpower but by a group of countries is known as:
(a) unipolar world
(b) capitalise world
(c) multi-polar world
(d) collective world
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Multi-polarity is a distribution of power in which more than two nation-states have nearly equal amounts of military, cultural, and economic influence.
Q.2: The Secretary-General - Ban Ki-Moon from South Korea is the ................... Secretary-General of the UN.
(a) Fifth
(b) Sixth
(c) Seventh
(d) Eighth
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Ban Ki-moon is a South Korean politician and diplomat who served as the eighth Secretary-General of the United Nations from January 2007 to December 2016.
Q.3: Which one of the following leaders played an important role in the integration of princely states with India?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) SardarVallabhbhai Patel
(c) C. Rajagopalchari
(d) Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
Correct Answer is Option (b)
At the time of independence, the problem of integration of princely states was a big challenge for the national unity and integrity of India. Under such difficult times, Sardar Patel undertook the daunting tasks of uniting all 565 princely states of India. Known as an ‘Iron Man’ of India, Patel’s approach to the question of the merger of princely states into independent India was very clear. He was not in favour of any compromise with the territorial integrity of India.
Q.4: Nehru was our first Prime Minister as well as:
(a) Health Minister
(b) Foreign Minister
(c) Education Minister
(d) Finance Minister
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.5: Which of the following statement is true for the Cold War?
(a) The two superpowers were poised for direct confrontations in India (1950 - 53), Gulf (1958 - 62).
(b) The two superpowers were poised for direct confrontations in Berlin only (1958 - 62).
(c) The two superpowers were poised for direct confrontations in Korea (1950 - 53), Berlin (1958 - 62).
(d) The two superpowers were poised for direct confrontations in Korea only (1950 - 53).
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Cold War also led to several shooting wars, but it is important to note that these crisis and wars did not lead to another World War. The two superpowers were poised for direct confrontations in Korea (1950 - 53), Berlin (1958 - 62), the Congo (the early 1960s), and in several other places.
Q.6: The ‘Two-Nation Theory’ was based upon:
(a) expansion of India
(b) bifurcation of the states
(c) partition of India
(d) All of the Above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Two Nation Theory is based on the hypothesis that India should be divided into two: Pakistan and Hindustan, the Muslim nation to occupy Pakistan and the Hindu nation to occupy Hindustan.
Q.7: The foreign policy of independent India vigorously pursued the dream of a peaceful world by advocating the policy of:
(a) non-alignment
(b) no nuclear weapons
(c) military expansion
(d) no Cold War
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India didn’t join US & USSR during cold war. India advocating the policy of non alignment by reducing the Cold war alliance and led the protest against Neocolonialism.
Q.8: Where is the head quarter of UNICEF?
(a) Tokyo
(b) Chicago
(c) Los Angeles
(d) New York
Correct Answer is Option (d)
UNICEF founded on 11 December, 1946 at New York, an agency responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to children worldwide
Q.9: In 1992, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution related to:
(a) UN Security Council
(b) UNESCO
(c) UNICEF
(d) World Bank
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.10: Which one of the following leaders played an important role in the integration of princely states with India?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
(c) C. Rajagopalchari
(d) Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
Correct Answer is Option (b)
At the time of independence, the problem of integration of princely states was a big challenge for the national unity and integrity of India. Under such difficult times, Sardar Patel undertook the daunting tasks of uniting all 565 princely states of India. Known as an ‘Iron Man’ of India, Patel’s approach to the question of the merger of princely states into independent India was very clear. He was not in favour of any compromise with the territorial integrity of India.
Q.11: With the disappearance of the Soviet Union, the US stands as the only:
(a) Major power
(b) Master power
(c) Superpower
(d) Inner power
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.12: Who was the Secretary of UN in 1997?
(a) Bill Clinton
(b) General Kofi Annan
(c) George W Bush
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.13: Which set of the countries belonged to the NATO Group?
(a) Poland, Britain, Romania
(b) USA, Czech Republic, France
(c) United Kingdom, France, West Germany
(d) Spain, France, East Germany
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Twelve countries took part in the founding of NATO: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1952, Greece and Turkey became members of the Alliance, joined later by West Germany (in 1955) and Spain (in 1982).
Q.14: Who was the President of USA during Cuban Missile Crisis?
(a) Abraham Lincoln
(b) John F Kennedy
(c) Bill Clinton
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.15: Reorganisation of the North-East was completed in:
(a) 1962
(b) 1972
(c) 1982
(d) 1992
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.16: What was India’s partition plan called?
(a) Gandhi Plan
(b) Nehru Plan
(c) Mountbatten Plan
(d) Jinnah Plan
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.17: Select the correct option for the leader and the country that helped to reach the Tashkent agreement between India and Pakistan:
(a) India, Nehru
(b) USSR, Kosygin
(c) Egypt, Nasser
(d) Indonesia, Sukarno
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Tashkent Declaration was a peace agreement between India and Pakistan signed on 10 January 1966 to resolve the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. The meeting was held in Tashkent in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Union represented by Premier Aleksey Kosygin.
Q.18: Why stronger countries’ foreign policies were supported by many countries after WW2?
(a) Because stronger countries supported them and aided them financially.
(b) Because they were afraid of being colonized again.
(c) Because most countries in the world did so.
(d) Because they were poor.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Most of the newly independent countries feared of the war between the two blocs. They never wanted to face any financial as well as political consequences. Hence, they supported the stronger nations for financial as well as military aid.
Q.19: The period when the nuclear test was conducted was a difficult period in:
(a) Domestic politics
(b) Foreign politics
(c) Military dominance
(d) Financial world
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The 1973–1975 was a period of economic stagnation where high unemployment and high inflation existed simultaneously.
Q.20: When did India intervened the Bangladesh Liberation War?
(a) November 1971
(b) February 1971
(c) December 1971
(d) December 1972
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.21: Which among the following is not among the objectives of NAM?
(a) Enabling newly decolonized countries to pursue independent policies
(b) Not to joining any military alliances
(c) Following a policy of neutrality on global issues
(d) Focus on elimination of global economic inequalities
Correct Answer is Option (c)
NAM has sought to “create an independent path in world politics that would not result in member states becoming pawns in the struggles between the major powers.” It identifies the right of independent judgment.
Q.22: In which year NAM was established?
(a) 1956
(b) 1960
(c) 1990
(d) 1957
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.23: The real GDP of Russia in 1999 was below what it was in:
(a) 1959
(b) 1969
(c) 1979
(d) 1989
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.24: After which event in 1917 Soviet Union came into existence?
(a) French Revolution
(b) First World War
(c) November Revolution
(d) Socialist Revolution
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The Soviet Union had its roots in the Socialist Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks overthrew the Russian Provisional Government that had replaced Tsar Nicholas II.
Section B
Q.25: What was the first among the three challenges to India while building a nation-state?
(a) building a united nation
(b) poverty
(c) communal tensions
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The first and the immediate challenge was to shape a nation that was united, yet accommodative of the diversity in our society.
Q.26: How many states signed United Nations Charter in 1945?
(a) 55
(b) 39
(c) 67
(d) 50
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The Charter was signed on 26 June 1945 by 50 countries; Poland signed on 15 October 1945.
Q.27: Which one of the following statements is ‘not correct’ about the ‘Non-Aligned Movement’?
(a) It suggested to the newly independent countries ways to stay out of alliances.
(b) India’s policy of non-alignment was neither negative nor passive.
(c) The non-aligned posture of India served its interests.
(d) India was praised for signing the treaty of friendship with USSR to strengthen NAM.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The name Non-Alignment was coined by Jawahar Lal Nehru in his 1954 speech in Colombo, Sri Lanka. After independence, India did not want to be part of these blocs led by the USSR or the USA. It chose to follow a non-compliance policy.
Q.28: It was in ........................ that full diplomatic relations were restored between India and Pakistan.
(a) 1976
(b) 1966
(c) 1956
(d) 1946
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India was attacked by China in October 1962. It took more than a decade for India and China to resume normal relations.
Q.29: Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, the undisputed leader of the North Western Frontier Province was known as:
(a) Frontier Gandhi
(b) Father of Pakistan
(c) Staunch Muslim
(d) Patriot of Pakistan
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Ghaffar Khan was a Pashtun who greatly admired Mahatma Gandhi and his nonviolence principles and saw support for the Congress as a way of pressing his grievances against the British frontier regime. Hence, he was called the Frontier Gandhi.
Q.30: On the reforms of structures and processes, the biggest discussions has been on the functioning of the
(a) Security Council.
(b) Health of the infants
(c) Child mortality rate
(d) Nuclear weapon possession
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Security Council has primary responsibility, under the United Nations Charter, for the maintenance of international peace and security. It is for the Security Council to determine when and where a UN peace operation should be deployed.
Q.31: The UN is an ................... body.
(a) indigenous
(b) imperfect
(c) impressive
(d) imperative
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In UN, the power of the US and its veto within the organisation split the rest of the world and to reduce opposition to its policies.
Q.32: Who is the single largest contributor to UN?
(a) China
(b) India
(c) US
(d) Europe
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The United States is the largest provider of financial contributions to the United Nations, providing 22 percent of the entire UN budget in 2020.
Q.33: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The UN is not a great balance to the US.
Reason: The UN can and has served to bring the US and the rest of the world into discussions over various issues.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.34: The WHO has played a leading role in ................... .
(a) public health achievement
(b) economic development
(c) children’s health
(d) resolving disputes among the nations
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q.35:
Assertion: Amnesty International is an NGO that campaigns for the protection of human rights all over the world.
Reason: It promotes respect for all the human rights in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Amnesty has grown from seeking the release of political prisoners to upholding the whole spectrum of human rights. Our work protects and empowers people - from abolishing the death penalty to protecting sexual and reproductive rights, and from combating discrimination to defending refugees and migrants’ rights.
Q.36:
Assertion: The Cold War was not simply a matter of power rivalries, of military alliances, and of the balance of power.
Reason: These were accompanied by a real ideological conflict as well, a difference over the best and the most appropriate way of organizing political, economic, and social life all over the world.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.37:
Assertion: After the Second World War, the east European countries that the Soviet Army had liberated from the fascist forces came under the control of the USSR.
Reason: The Soviet System, however, became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
USSR emerged as two of the most powerful blocs. Many countries after Second World War adopted Soviet system. Russia was in control of this bloc.
Q.38:
Assertion: In Georgia, the demand for independence has come from two provinces, resulting in a Civil War.
Reason: In Central Asia, Tajikistan witnessed a Civil War that went on for ten years till 2001.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Post cold war era was not free of the uproars. Former soviet republics witnessed violent conflicts over many issues. Many new countries were born after the disintegration of Soviet Union. But, their inception was not free from bloodshed.
Q.39:
Assertion: Gorbachev did nothing to save the disintegration of soviet system.
Reason: These developments were accompanied by a rapidly escalating crisis within the USSR that hastened its disintegration.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Gorbachev passed many reforms to revitalize the disintegrating Soviet system. But the bureaucrats never supported the reforms. Moreover, corruption and distrust of the people contributed in the decline of USSR.
Q.40:
Assertion: The interim government took a firm stance against the possible division of India into small principalities of different sizes.
Reason: Before 15 August 1947, peaceful negotiations had brought almost all states whose territories were contiguous to the new boundaries of India, into the Indian Union.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The interim government took a firm stance against the possible division of India into smaller principalities of different sizes. The Muslim League opposed the Indian National Congress and took the view that the States should be free to adopt any course they liked.
Q.41:
Assertion: India adopted representative democracy based on the parliamentary form of government.
Reason: These features ensure that the political competition would take place in a democratic framework.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India is a parliamentary Democratic Republic in which the President of India is the head of state and the Prime Minister of India is the head of government. It is based on the federal structure of government, although the word is not used in the Constitution itself. It assures a healthy and democratic political competition.
Q.42:
Assertion: The excitement with planning reached its peak with the launching of the Second Five Year Plan in 1956 and continued somewhat till the Third Five Year Plan in 1961.
Reason: Though many criticisms emerged both about the process and the priorities of these plans, the foundation of India’s economic development was firmly in place by then.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.43:
Assertion: ‘Development’ was about becoming more ‘modern’ and modern was about becoming more like the industrialized countries of the West.
Reason: It was believed that every country would go through the process of modernization as in the West, which involved the breakdown of traditional social structures and the rise of capitalism and liberalism.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.44:
Assertion: Indian air crafts attacked parts of Pakistan and the army moved into POK and Swat Valley.
Reason: After months of diplomatic tension and military build-up, a full-scale war between India and Pakistan broke out in December 1971.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.45: Assertion: The two sides understood that war might occur in spite of restraint.
Reason: Because they wanted to confront each other with weapons.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Both of the superpowers had nuclear weapons, and the enormous possibility that any kind of escalation could potentially lead to their use and the end of human life. A stable balance of weapons, they decided, could be maintained through ‘arms control’.
Q.46:
Assertion: The example of Orissa shows us that it is not enough to say that everyone wants development.
Reason: For ‘development’ has same or similar meanings for different sections of the people.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Development has different meanings for different sections of the people. People do not have the same notion of development. This is because people have different occupations and different lifestyles. Since people have the different quality of life, so notions of development are not similar to each other.
Q.47:
Assertion: The British Government took the view that all these 565 states were free to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent if they so wished.
Reason: This was a very serious problem and could threaten the very existence of a united India.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The official policy statement of the Government of India made by Sardar Patel on July 5, 1947 made no such threats. It reassured the princely states about the Congress’ intentions, and invited them to join independent India.
Q.48:
Assertion: Communist China conducted nuclear tests in October 1964.
Reason: The five nuclear weapon powers, the US, USSR, UK, France, and China – also the five Permanent Members of the UN Security Council – tried to impose the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968 on the rest of the world.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
It has always been a tendency of the powerful nations not to let any other nation be in their competence.
Hence, soon after China tested her nuclear weapons, they have come up with NPT.
Section C
Q.49: Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow:
Which two countries relationship were strained after Suppression of Tibetan culture?
(a) India and Nepal
(b) India and Bangladesh
(c) India and China
(d) India and Myanmar
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.50: Study the cartoon given below and answer the following questions: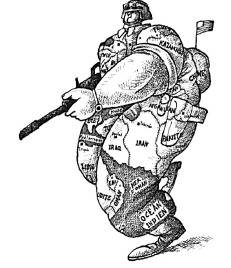
Which of the countries listed below was never invaded by USA?
(a) Japan
(b) England
(c) Iraq
(d) Afghanistan
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Study the cartoon given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Q.51: How has US dominated the world?
(a) By its trade and commerce
(b) By its technology
(c) By its advancement in space research.
(d) By dominating military, economy and cultural aspects of the other nations.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.52: What have been the reasons for immense influence of US on UN?
(a) USA’s economic superiority
(b) USA’s weapon capacity
(c) UN’s head quarter is in USA and USA’s financial contribution to UN.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Although the United States continues to play a leadership role at the UN, it has also accumulated massive arrears in its payments to the UN, owing the world organization approximately $1 billion, far more than any other member state.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The Western alliance was formalized into an organization, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which came into existence in April 1949. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them. Each of these states would be obliged to help the other. The eastern alliance, known as the Warsaw Pact, was led by the Soviet Union. It was created in 1955 and its principal function was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe. International alliances during the Cold War era were determined by the requirements of the superpowers and the calculations of the smaller states. As noted above, Europe became the main arena of conflict between the superpowers. In some cases, the superpowers used their military power to bring countries into their respective alliances. Soviet intervention in east Europe provides an example. The Soviet Union used its influence in eastern Europe, backed by the very large presence of its armies in the countries of the region, to ensure that the eastern half of Europe remained within its sphere of influence. In East and Southeast Asia and in West Asia (Middle East), the United States built an alliance system called — the Southeast Asian Treaty Organization (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organization 1 (CENTO). The Soviet Union and communist China responded by having close relations with regional countries such as North Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.
Q.53: When was NATO formed?
(a) June 1949
(b) March 1949
(c) February 1949
(d) April 1949
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was created in 1949 to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
Q.54: How many states were associated with NATO?
(a) eleven states
(b) twelve states
(c) ten states
(d) nine states
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.55: When Warsaw Pact was created?
(a) 1955
(b) 1957
(c) 1954
(d) 1956
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Warsaw Pact was created in reaction to the integration of West Germany into NATO in 1955 per the London and Paris Conferences of 1954. The Warsaw Pact was established as a balance of power or counterweight to NATO.
Q.56: What was the primary aim of Warsaw Pact?
(a) To counter USA’s forces only
(b) To counter SEATO’s forces
(c) To achieve economic development in the countries of Soviet Union
(d) To counter NATO’s forces in Europe
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The primary aims of the Warsaw Pact were to safeguard the security of its member states and to increase military cooperation amongst its members.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow:
India has opposed the international treaties aimed at non-proliferation since they were selectively applicable to the non-nuclear powers and legitimised the monopoly of the five nuclear weapons powers. Thus, India opposed the indefinite extension of the NPT in 1995 and also refused to sign the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT). India conducted a series of nuclear tests in May 1998, demonstrating its capacity to use nuclear energy for military purposes. Pakistan soon followed, thereby increasing the vulnerability of the region to a nuclear exchange. The international community was extremely critical of the nuclear tests in the subcontinent and sanctions were imposed on both India and Pakistan, which were subsequently waived. India’s nuclear doctrine of credible minimum nuclear deterrence professes “no first use” and reiterates India’s commitment to global, verifiable and non-discriminatory nuclear disarmament leading to a nuclear weapons free world. Foreign policy is always dictated by ideas of national interest. In the period after 1990, Russia, though it continues to be an important friend of India, has lost its global pre-eminence. Therefore, India’s foreign policy has shifted to a more pro-US strategy.
Q.57: Which of the following nuclear treaties were rejected by India?
(a) NPT, CTBT
(b) Kyoto Protocol
(c) Panchsheel Agreement
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India has refused to sign the Treaty on the grounds of CTBT, like the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), is discriminatory. Even before coming into force, the CTBT has helped the cause of test-ban and nuclear disarmament by discouraging member-states from testing for and developing nuclear weapons.
Q.58: When did India conduct series of nuclear tests?
(a) June 1998
(b) May 1998
(c) April 1998
(d) March 1998
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.59: Why India’s foreign policy shifted to become more pro-US?
(a) Because Russia betrayed India.
(b) Because Russia attacked India.
(c) Because US derived more profit to India.
(d) Because Russia lost its global pre-eminence.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The absolute increase in its military and economic resources began to compel India to think less like a developing, non-aligned country and more like an emerging and responsible power. India is also struggling to address the tension between the concepts of ‘strategic autonomy’ and ‘strategic influence’. This was the reason for India’s foreign policy shifted to become more pro-US.
Q.60: Which one of the following is India’s stand for the use of nuclear weapon?
(a) No use of nuclear weapon at all.
(b) No first use of nuclear weapon.
(c) Use nuclear weapon in case of war.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
India’s adherence to a no-first use principle is long-standing. Ever since 1998, when the country went nuclear, New Delhi has rejected the idea of initiating the use of such weapons in any conflict scenario. Nukes, in Indian strategy, are purely retaliatory. And that stance has made good military and diplomatic sense.
|
145 docs|4 tests
|





















