Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 4 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 34 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and carry 1 mark each. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-17 are very short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 18-28 are short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 29-34 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
Section - A
Q1. Which unit is used to measure the thickness of a coin? (1 Mark)
(a) Kilometre
(b) Metre
(c) Millimetre
(d) Centimetre
Ans: (c) Millimetre
The thickness of a coin is very small, and millimetres are the most appropriate unit for measuring small lengths like this.
Q2. Which material is non-lustrous? (1 Mark)
(a) Gold
(b) Aluminium foil
(c) Wood
(d) Copper
Ans: (c) Wood
Wood is a non-lustrous material, meaning it does not have a shiny appearance, unlike metals such as gold or copper.
Q3. What is the SI unit of mass? (1 Mark)
(a) Litre
(b) Kilogram
(c) Gram
(d) Newton
Ans: (b) Kilogram
The SI unit of mass is the kilogram, which is used to measure the amount of matter in an object.
Q4. Which process converts liquid water to vapour? (1 Mark)
(a) Condensation
(b) Freezing
(c) Evaporation
(d) Melting
Ans: (c) Evaporation
Explanation: Evaporation is the process where liquid water changes into water vapour due to heat, like water drying from a surface.
Q5. Which planet is called the "Red Planet"? (1 Mark)
(a) Venus
(b) Mars
(c) Jupiter
(d) Saturn
Ans: (b) Mars
Mars is known as the "Red Planet" because of its reddish appearance, which is due to iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
Q6. Which method separates oil from water? (1 Mark)
(a) Filtration
(b) Decantation
(c) Sieving
(d) Magnetic separation
Ans: (b) Decantation
Decantation is the process of separating a liquid (oil) from another liquid (water) by gently pouring off the top layer.
Q7. What is the main source of energy in the Solar System? (1 Mark)
(a) Moon
(b) Stars
(c) Sun
(d) Asteroids
Ans: (c) Sun
The Sun is the primary source of energy in the Solar System, providing light and heat that sustain life on Earth.
Section - B
Q8. How can studying Science help in solving bigger problems and mysteries of the universe? (2 Marks)
Ans: Solving Bigger Problems with Science: Studying Science equip us with the skills to solve larger and more complex problems by enhancing our ability to observe, analyze, and experiment. It encourages critical thinking and systematic problem-solving, which are essential for addressing global challenges, such as environmental issues, medical advancements, and technological innovations. Science provides the tools and methodologies needed to explore and understand complex phenomena and find effective solutions.
Q9.Identify the seeds a and b. How many cotyledons do these seeds have? In which category (dicot or monocot) would you keep their plants? (2 Marks)
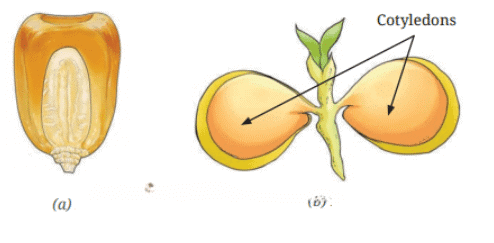
Ans: Fig. a is maize seed which has only one cotyledon. This is a monocot seed.
Fig. b is a gram seed which has two cotyledons. This is a dicot seed.
Q10. What is threshing, and where is it used? (2 marks)
Ans: Threshing is the process used to separate grains from the stalks.
- This is usually done by beating or mechanically separating the grain from the plant parts.
- Threshing is commonly used in fields to harvest crops like wheat, where the grain is separated from the straw.
Q11. Why is Venus called the Morning Star? (2 marks)
Ans: Venus is called the Morning Star because it is brightly visible in the eastern sky at dawn before sunrise.
Venus is one of the most luminous planets, and its visibility during early morning hours gives it this nickname, even though it is a planet, not a star.
Q12. How does a soop aid in winnowing? (2 marks)
Ans: A soop (a traditional bamboo tray) is used to separate husk from grains in the winnowing process.
- The grain-husk mixture is placed on the soop, and when tossed in the air, the wind blows away the lighter husk while the heavier grains fall back into the tray.
- This method is widely used in regions like Haryana for separating grains after harvesting.
Q13. What is periodic motion? Give an example. (2 marks)
Ans: Periodic motion is the type of motion that repeats at regular intervals.
An example of periodic motion is a fan rotating. It spins continuously, completing a circular path repeatedly in fixed intervals, which is characteristic of periodic motion.
Q14. Why does ice not flow like water? (2 marks)
Ans: Ice does not flow like water because it is a solid and has a fixed structure.
- The molecules in ice are closely packed and do not move freely like in water, where the molecules are more spaced out and can flow.
- This rigidity in ice keeps it in a solid form, preventing it from flowing as liquid water does.
Q15. What are comets made of? (2 marks)
Ans: Comets are composed of a mixture of dust, gases, rocks, and ice.
- When comets approach the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, forming a glowing tail that points away from the Sun.
- These tails are visible from Earth and are one of the most distinctive features of comets.
Q16. How does soil form over time? (2 marks)
Ans: Soil forms over thousands of years as rocks break down due to the actions of sunlight, water, and living organisms.
- Weathering and erosion cause rocks to break into smaller pieces, eventually becoming soil.
- The process involves the interaction of biological, chemical, and physical forces, with plants and microorganisms contributing to soil formation over time.
Q17. How do leaves help plants excrete? (2 marks)
Ans:
- Leaves help plants excrete excess water through a process called transpiration.
- Through stomata, tiny pores on the leaf surface, plants release excess water vapor into the atmosphere.
- This helps in maintaining a balance of water within the plant, as seen in plants like grasses and roses, where water vapor is expelled through the leaves.
Section - C
Q18. How does condensation form dew drops on plants? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Condensation occurs when water vapour in the air cools down upon contact with cooler surfaces, such as plant leaves, especially during the night when temperatures drop.
- As the warm air cools, the water vapour condenses and forms small droplets of water on surfaces like leaves, grass, and other plants. This is commonly seen as dew in the early morning.
- The formation of dew helps in maintaining moisture around the plant, providing essential hydration, especially in the morning when the air is cooler.
Q19. Why do planets not twinkle like stars? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Planets do not twinkle because they are much closer to Earth compared to stars. The light from planets is steady and does not get affected much by the Earth's atmosphere.
- The light that reflects off planets such as Venus or Mars appears consistent because of their larger size in the sky and their relatively stable light reflection.
- In contrast, stars are far away, and their light has to pass through many layers of the Earth's atmosphere, which distorts the light, causing the twinkling effect. This atmospheric interference makes the stars appear to flicker.
Q20. How does a threshing machine improve farming? (3 marks)
Ans:
- A threshing machine is a mechanical device used to separate grains from the stalks and husks in an efficient manner. It improves farming by reducing labor and time compared to traditional manual methods, such as using a sickle or beating by hand.
- This machine can separate grains much faster and more efficiently, helping farmers process larger quantities of crops, such as wheat or rice, in a short amount of time.
- Additionally, threshing machines are equipped with mechanisms that ensure the grains are separated cleanly, minimizing the loss of crops and improving the overall yield for the farmer.
Q21. What are the benefits of rainwater harvesting? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Rainwater harvesting involves the collection and storage of rainwater for various purposes. The primary benefit is that it helps in reducing water scarcity, particularly in areas where fresh water is limited.
- The harvested rainwater can be used for drinking, irrigation, and washing, which helps in conserving groundwater resources. By diverting rainwater to underground reservoirs, it also recharges groundwater levels, ensuring a sustainable water supply.
- This method also helps in reducing the dependence on conventional water sources, which are often polluted or over-exploited, and promotes environmental sustainability by reducing surface runoff and preventing flooding.
Q22. How do insectivorous plants show movement? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Insectivorous plants are plants that capture and digest insects to obtain essential nutrients like nitrogen. These plants show movement by modifying their leaves to trap their prey.
- For example, the Venus flytrap has modified leaves that snap shut when triggered by the movement of an insect. The trap then closes tightly, trapping the insect inside.
- Similarly, plants like Drosera (sundew) have sticky hairs on their leaves that move inward when they come into contact with insects, trapping them for digestion. These movements help the plants survive in nutrient-poor soil by supplementing their nutrition with insects.
Q23. Why is a 15-cm scale divided into millimetres? (3 marks)
Ans:
- A 15-cm scale is divided into millimetres to allow for precise measurements of small lengths, which are crucial for tasks that require accuracy, such as measuring the length of a pencil, the width of an object, or the thickness of paper.
- 1 centimetre (cm) is equal to 10 millimetres (mm), so dividing the scale into millimetres helps in measuring smaller distances that may not be accurately captured using just centimetres.
- This division provides more accuracy when measuring small items, especially in science experiments or other activities that require fine precision.
Q24. How do larvae and pupae differ in mosquitoes? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Larvae are the immature stage of mosquitoes. They live in water and feed on tiny microorganisms. Mosquito larvae are worm-like and have a tail that allows them to swim. They are active and grow during this stage.
- In contrast, pupae are a later stage where mosquitoes do not feed. The pupa is a resting stage where the mosquito undergoes its transformation into an adult. The pupal stage is characterized by the mosquito being enclosed in a protective case and remaining relatively still.
- After the pupal stage, the mosquito matures into an adult, leaving the water to begin the cycle again, as seen in the mosquito life cycle.
Q25. What role does sand play in a pot-in-pot cooler? (3 marks)
Ans:
- The sand in a pot-in-pot cooler plays a crucial role in the cooling process. It acts as a medium to retain water.
- Water is poured onto the sand, and it gradually evaporates through the outer pot. As the water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air and cools the inner pot. This process is known as evaporative cooling, and it helps in lowering the temperature inside the inner pot, making it cooler than the surrounding environment.
- This method is effective in hot climates and is a traditional cooling method used to preserve food and keep water cool without using electricity.
Q26. How does the Sun drive the water cycle? (3 marks)
Ans:
- The Sun is the primary energy source that drives the water cycle. It provides the heat necessary to evaporate water from oceans, lakes, and other water bodies.
- As the Sun heats the surface of water, it changes the liquid water into water vapour, which rises into the atmosphere. Once the water vapour cools down, it condenses to form clouds.
- When the clouds become heavy, they release the water as precipitation in the form of rain, snow, or hail. This continuous cycle of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation is essential for maintaining the Earth’s water supply.
Q27. Why is coal a non-renewable resource? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Coal is formed from the remains of plants that lived millions of years ago. Through geological processes, these plant remains are compressed and transformed into coal over a long period.
- The process of coal formation takes millions of years, and since it is consumed much faster than it can be replenished, coal is considered a non-renewable resource.
- Once coal is extracted and burned for energy, it cannot be replenished within a human lifetime, making it a limited resource that is not sustainable in the long run.
Q28. How do animals respond to stimuli? Give an example. (3 marks)
Ans:
- Animals respond to stimuli in their environment to ensure survival. Stimuli can be changes in light, sound, temperature, or touch, and animals react to them in various ways.
- For example, a dog barks when it hears an unfamiliar sound, such as a doorbell ringing or a stranger approaching. This is a response to an auditory stimulus, and it helps alert the dog to potential danger.
- These responses are part of the animal's instinctual behavior, helping it to react to environmental changes and increase its chances of survival.
Section - D
Q29. (i) How can you test presence of proteins in a given food item?
(ii) Write test for detecting the presence of starch (5 marks)
Ans: (i) Test to detect presence of Protein
- Take a small quantity of the food item. If the sample is solid, grind it.
- Put some part of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops, of water to it and shake the test tube.
- Now, with the help of a dropper, add 2 drops of solution of copper sulphate and 10 drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube.
- Shake well and place the test tube in test tube stand for a few minutes.
- Observe colour of the contents of test tube. If colour of the contents turns violet, the food item contains protein.
- Food + Water + Copper sulphate + Caustic soda → Violet colour → Protein is present. (Note: Copper sulphate and caustic soda solutions are harmful. Handle them with care.)
(ii) Test to detect presence of Starch
- Take a piece of the food item. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. If the colour of the food item becomes blue-black, then it indicates the presence of starch in the food item.
- Food + Iodine → Blue-black colour (starch present)
- Food + Iodine → No blue-black colour (no starch present)
Q30. Name the three scales of measuring temperatures known to you. Write down the correct ways to write the names and units of these scales. (5 Marks)
Ans: The three scales of measuring temperature are the Celsius scale, the Fahrenheit scale and the Kelvin scale.
- The names of temperature scales Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale and Kelvin scale, start with a capital letter.
- For the units for temperature, degree Celsius and degree Fahrenheit, the word degree starts with a lower-case letter while Celsius and Fahrenheit start with a capital letter.
- The unit kelvin starts with a lower-case letter.
- The symbols of all units (°C, °F, K) are capital letters. The degree sign (°) is not written with K.
- A full stop is not written after the symbol, except at the end of a sentence.
- While writing the temperature, a space is left between the number and the unit.
- For temperatures more than one degree, we use the plural of ‘degree’, that is, ‘degrees’, while writing the full form of the unit.
Q31. How can you show that some solids like sugar and salt are soluble in water whereas solids like chalk powder and sand are not soluble in water?
Ans: Collect samples of sugar, salt, chalk powder and sand. Take four beakers. Fill each one of them about two-third with water. Add a teaspoonful of sugar to the first beaker, salt to the second, chalk powder to the third and sand to the fourth. Stir the contents of each beaker with a spoon/stirrer.
Wait for a few minutes and observe what happens to the substances added to the water.
(a) The solid substance is visible in water and hence insoluble (chalk powder and san(d),((b) The solid is not visible in water and hence soluble (sugar and salt). Note down your observations in the following table.
Table: Mixing different solid materials in water
Substance Disappears in water/does not disappear in water 1. Sugar Disappears completely in water 2. Salt Disappears completely in water 3. Chalk powder Does not disappear in water 4. Sand Does not disappear in water Inference:
(i) Sugar and salt are soluble in water.
(i) Chalk powder and sand are insoluble in water.
Q32.
(i)Why is Jupiter called the Stormy Planet?
(ii) What are artificial satellites used for?
(iii) What is the other name of inner planets and name them?
(iv) What is the other name of outer planets and name them?
(v) Why is Venus called the Twin Planet? (5 Marks)
Ans: (i) Jupiter revolves around itself with a great speed; hence Jupiter is called the Stormy planet.
(ii) Artificial satellites are used for weather forecasting, long distance communication and remote sensing.
(iii) Inner planets are also called Terrestrial planets, They are – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
(iv) Outer planets are also called Jovian planets. They are- Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
(v) Venus is considered as ‘Earth’s-twin’ because its size and shape are very much similar to that of the earth.
Q33. Define the following terms.(5 Marks)
(i) Nutrition
(II) Respiration
(iii) Excretion
(iv) Stimulus
(v) Reproduction
Ans: (i) Nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain and utilize nutrients from food for growth development and energy.
(ii) Respiration is the process by which organisms take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide to obtain energy from food.
(iii) Excretion is the process by which waste is removed from body. Urine, sweat and salts are called excretion.
(iv) Anything or any event that prompt living beings to respond is called a stimulus.
(v) Reproduction is the process of producing new ones of one’s own kind.
Q34. Prepare a chart to show various vitamins and minerals and the disorders caused by their deficiency. (5 marks)
Ans:
Vitamin/mineral Deficiency disease/disorder Symptoms Vitamin A Loss of vision Poor vision, loss of vision in darkness, sometimes complete loss of vision. Vitamin B1 Beriberi Swelling, tingling or burning sensation in feet and hands. Vitamin C Scurvy Bleeding gums, wounds take longer time to heal. Vitamin D Rickets Bones become soft and bend easily. Calcium Bone and tooth decay Weak bones, tooth decay. Iodine Goitre Glands in the neck appear swollen, mental disability in children. Iron Anaemia Weakness
FAQs on Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 4 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What are the main topics covered in Class 6 Science? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are typically asked in Class 6 Science exams? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific tips for answering science exam questions? |  |
| 5. How important is practical work in Class 6 Science? |  |




















