Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Question Answers - Our Changing Earth
Q1. What are the two types of the earth’s forces?
Ans: The earth’s movements are divided based on the forces which cause them. The forces which act in the interior of the earth are called endogenic forces. The forces that work on the earth's surface are called exogenic forces.
Endogenic forces sometimes produce sudden movements. At other times they produce slow movements. Sudden movements are earthquakes and volcanoes. They cause mass destruction over the surface of the earth.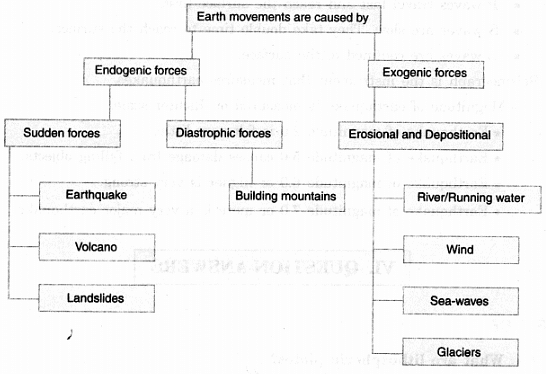
Q2. What are earthquakes? Define focus and epicentre.
Ans: When the lithosphere plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. The vibrations travel all around the earth. These vibrations are called earthquakes.
Focus: The place or point in the crust where the movement starts is called Focus.
Epicentre: The place or the surface above the focus is called Epicentre. Vibrations travel outwards from the epicentre as waves. The greatest damage occurs closest to the epicentre. The strength of the earthquake decreases, going away from the centre.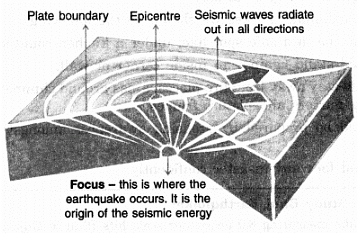 Origin of an Earthquake
Origin of an Earthquake
Q3. What is seismograph? How is the magnitude of earthquake measured?
Ans: An earthquake is measured with a machine. It is called a seismograph.
The magnitude of the earthquake is measured on Richter scale. An earthquake of 2.0 or less is felt only a little. An earthquake over 5.0 causes damage from things falling. A 6.0 or higher magnitude is considered very strong and 7.0 is classified as a major earthquake.
Q4. Explain Earthquake preparedness.
Ans: When an earthquake strikes we should do the following:
- We should be in a safe spot like: under a kitchen counter, table or desk.
- We should stand against an inside comer or wall.
- We should stay away from fire places, areas around chimneys, windows that shatter including mirrors and picture frames.
- We should be prepared by arousing awareness amongst our friends and family members.
- We should face any disaster confidently.
Notes: Case Study Bhuj Earthquake:
- An earthquake measuring 6.9 on richter scale hits Bhuj in Gujarat.
- Schools worst affected.
- Communication water power supply affected
- Hundreds of fire started
- Emergency declared and CM appeals for help.
Q5. What are the two processes which continuously wear away the landscape? Explain them.
Ans: The landscape is continuously worn away by two processes. They are as follows:
- Weathering and erosion.
- Weathering is the breaking up of rocks on the earth’s surface.
- Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice.
- The eroded material is carried away or transported by water, wind etc.
- They deposit material eventually.
- This process of erosion and deposition creates different landforms on the surface of the earth.
Q6. Describe the work of a river.
Ans: Running water in the river erodes the landscape. When the river tumbles at a steep angle over very hard rocks or down a steep valley side, it forms a waterfall. When the river enters the plain it twists, turns and forms large bends. These bends are known as meanders.
Due to continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the meander, the ends of the meander loop come closer and closer. At times the river overflows its banks. This leads to the flooding of the neighbouring areas. The flood water deposits layers of fine soil and other materials. They are called sediments, along its banks. This leads to the formation of a flat fertile land called a flood plain.
As the river approaches the sea, the speed of the running water decreases. The river begins to break up into several streams. They are called distributaries. Each distributary forms its mouth. The collection of sediments from all the mouths forms a delta, the triangular-shaped land mass.
Q7. Write a note on the work of sea-waves.
Ans: Erosion and deposition of the sea waves form coastal land forms. Sea waves continuously strike at the rocks. In course of time they become larger and wider. Hollow like caves are formed on the rocks. They are called sea caves. As caves become bigger and bigger only the roofs of the caves remain. This leads to formation of Sea arches. Continuous erosion breaks the roofs and only walls are left. These wall-like features are called stacks. The steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above sea water is called sea cliff. The sea waves deposit sediments along the shores. This leads to formation of sea beaches.
Q8. Give an account of the work of wind.
Ans: An active agent of erosion and deposition in the deserts is wind. In deserts there are numerous rocks with a shape of a mushroom. They are commonly called mushroom rocks. Winds erode the lower section of the rock more than the upper part. Such rocks have narrower base and wider top. When the wind blows, it lifts and transports sand from one place to another. When it stops blowing, the sand falls and gets deposited in low hill like structures. These are called sand dunes. When the grains of sand are very fine and light, the wind carries it over very long distances. When such a sand is deposited in large areas, they are called loess. Large deposits of loess are found in China.
Q9. Describe the work of ice.
Ans: Work of Ice are Glaciers are “rivers” of ice. They too erode the landscape by bulldozing soil and stones to expose the solid rock below. Glaciers carve out deep hollows. As the ice melts they get filled up with water and become beautiful lakes in the mountains. The material carried by the glacier like big and small rocks, sand, silt gets deposited. These deport from glacial moraines.
Q10. Give an account of some common earthquake prediction methods adopted locally by people.
Ans: Some of the common earthquake prediction methods adopted locally by people are:
- Wild animal behaviour.
- Agitated fish in the ponds.
- Snakes coming out to the surface from their holes.
- Animals trying to untie themselves and run away.
- Birds leaving their nests and beginning to chatter loudly.
- Aborigines beginning to run to higher grounds.
|
66 videos|336 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Question Answers - Our Changing Earth
| 1. What are the main factors contributing to the changes in our Earth's climate? |  |
| 2. How do geological processes affect the Earth's surface over time? |  |
| 3. What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity? |  |
| 4. How does human activity influence natural disasters? |  |
| 5. What are some effective strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|

















