Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Heat
Q1: Define temperature.
Ans: The measure of hotness or coldness of an object is called temperature. It is usually measured in "degrees".
Q2: Name the device used to measure temperature.
Ans: A thermometer is a device used to measure temperature.
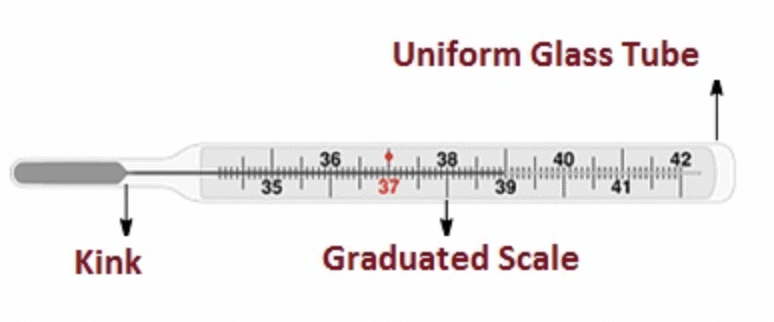 Thermometer
Thermometer
Q3: Name the two types of thermometers.
Ans: Clinical thermometer and laboratory thermometer.
Q4: What do you mean by clinical thermometer?
Ans: The thermometer used to measure our body temperature is called a clinical thermometer.
Q5: The bulb in the thermometer contains _____________.
Ans: Mercury
Q6: Thermometer should be washed before and after use with, preferably with an _________ solution.
Ans: Antiseptic solution
Q7: Before use, the mercury level of the thermometer should be below __________.
Ans: 35°C
Q8: We should hold the thermometer by the bulb while holding it. True/False.
Ans: False
Q9: What is the unit of temperature as adopted by India?
Ans: Degree Celsius (°C)
Q10: What is the average body temperature of a healthy person?
Ans: 37°C
Q11: What is the range of laboratory thermometers?
Ans: - 10°C to 110°C
Q12: Laboratory thermometer should be kept upright and not tilted. True/False.
Ans: True.
Q13: The bulb of the laboratory thermometer should not touch the surface of the ________________.
Ans: Container.
Q14: What is the use of kink in a clinical thermometer?
Ans: Kink prevents mercury levels from falling on their own.
Q15: Give an example to show the transfer of heat from one body to another.
Ans: Any utensil kept on flame becomes hot because heat transfers from flame to the utensil.
Q16: Heat always flows from a hotter object to ________________.
Ans: Colder object
Q17: In solid heat is transferred by the process of
a. Conduction
b. convection
c. Radiation
d. None of these
Ans: Conduction.
Q18: Give examples of conductors.
Ans: Aluminium, copper, iron etc.
Q19: Give examples of insulators.
Ans: Wood, plastic, rubber
Q20: Insulators are ________ conductors of heat.
Ans: Poor
Q21: Conductors are _____________ conductors of heat.
Ans: Good
Q22: Name the process by which heat transfers in air.
Ans: Convection.
Q23: From the sun, the heat comes to us by the process called __________________.
Ans: Radiation.
Q24: Which of the two absorbs more radiation- a dark-coloured object or a light-coloured object?
Ans: A dark-coloured object.
Q25: The temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a ________________________.
Ans: Clinical thermometer
Q26: Land breeze blows at the time of __________.
Ans: Night
Q27: Sea breeze blows at the time of _________.
Ans: Day
Q28: Which type of clothing should be preferred for the month of June?
Ans: Light-coloured clothes
Q29: Which type of clothing should be preferred in January?
Ans: Dark coloured clothes.
Q30: A cold steel spoon is dipped into a cup of hot coffee. Will it transfer heat to its other end or not? If yes, then by which process?
Ans: Yes, by conduction.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Heat
| 1. What is heat? |  |
| 2. How is heat transferred? |  |
| 3. What are the units used to measure heat? |  |
| 4. How does heat affect different materials? |  |
| 5. How can heat be controlled or managed? |  |

















