Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Measurement of Time and Motion
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the advantage of a distance-time graph?
Ans: Distance-time graphs give information about the nature of the motion of an object, like uniform or non-uniform motion. Motion of an object can be represented by its distance-time graphs.
Q2: Differentiate between uniform speed and average speed.
Ans: An object is said to be moving with uniform speed if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. But when we travel in a vehicle, the speed of the vehicle changes from time to time depending upon the conditions existing on the road. In such a situation, the speed is calculated by taking the ratio of the total distance travelled by the vehicle to the total time taken for the journey. This is called the average speed.
Q3: What do you mean by non-uniform speed?
Ans: An object is said to be moving with variable speed or non-uniform speed if it covers equal distances in unequal intervals of time or vice versa.
Q4: What do you mean by instantaneous speed?
Ans: When we say that the car travels at an average speed of 60 km/h it does not mean that the car would be moving with the speed of 60 km/h throughout the journey. The actual speed of the car may be less than or greater than the average speed at a particular instant of time. The speed of a moving body at any particular instant of time is called instantaneous speed.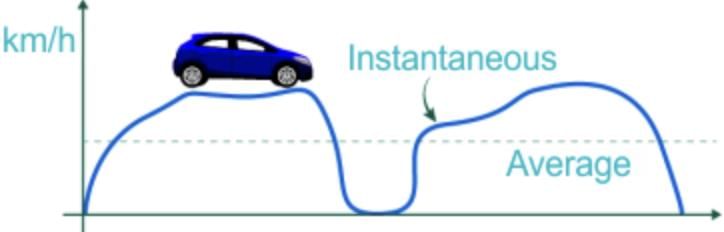
Q5: A child is on a see-saw. What kind of motion does he have, and why? Explain.
Ans: On a see-saw child goes up and comes down from the mean position and repeats itself. So there is oscillatory motion.
Q6: Explain how, in ancient times, a day, a month and a year were measured.
Ans: In ancient times, the time between one sunrise and the next was called a day. A month was measured from one new moon to the next and a year was fixed as the time taken by the earth to complete one revolution of the sun.
Q7: Define velocity along with its unit.
Ans: Velocity can be defined as the rate of change of displacement.SI unit of velocity is m/s (meter/second Velocity is a vector quantity.
Q8: What are quartz clocks?
Ans: It is a special type of clock or watch which have an electric circuit with one or more cells and is called a quartz clock.
Q9: How do we know an object is moving faster compared to the speed of another object?
Ans: By finding the distance travelled by a moving body in unit time, 1 hr. or 1 sec, we know the speed of an object, which helps us to know which one is moving faster, i.e. having greater speed.
Q10: If a car is moving with a speed of 5Km/h on highway, then find the distance travelled by the car in 4 hours?
Ans: We know distance travelled by a body = speed X time
So, distance travelled by the car =5x4=20 km
Q11: Sumit covers a distance of 2.4 Km from his house to reach her college on a scooter. If the scooter has a speed of 6m/sec, calculate the time taken by her to reach the college.
Ans:
Total distance travelled =2.4km=2.4x1000m=2400m. Speed is 6m/sec
as time = (Distance/speed) time=2400/6= 400sec.
Q11: How can you say that motion and rest are relative?
Ans: We have observed that the position of stars and planets changes while you remain stationary. In reality, the Earth is moving too. Thus, an object that appears to be at rest may actually be in motion. Therefore, motion and rest are relative terms.
Q12: Differentiate between circular motion and periodic motion.
Ans: Motion of an object in a circular path is called circular motion eg. the Motion of the hands of a clock. But when an object repeats its motion after some time. This type of motion is called periodic motion. E.g. Motion of a pendulum, motion of a child on a swing, motion of the strings of a guitar.
Q13: Give an example when objects undergo combinations of different types of motion.
Ans: The motion of a ball on the ground. Here, the ball is rolling on the ground and rotating as well as moving forward on the ground. Thus, the ball undergoes a rectilinear motion as well as rotational motion.
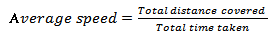
Q14: What is a simple pendulum?
Ans: A simple pendulum consists of a small metallic ball or a piece of stone suspended from a rigid stand by a thread. The metallic ball is called the bob of the pendulum.
Q15: What is the oscillation of a pendulum?
Ans: One complete to and fro motion of a pendulum from the rest position is called one oscillation. The time taken by the pendulum to complete one oscillation is called its time period. It only depends on the length of the string of pendulum.
Q16: What do you mean by time?
Ans: The interval between two events is called time. Example: The time between one sunrise and the next was called a day. Clocks or watches are the most common time-measuring devices. The basic unit of time is a second. Its symbol is s. Larger units of time are minutes (min) and hours (h).
Q17: A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Ans:
Time taken to complete 20 oscillations = 32 s
Time period of the pendulum = No of oscillations/Total Time taken = 32/20 s = 1.6s
Q18: Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Ans:
Distance between her school and house = speed of bicycle X Time taken
= 2m/s × 60s= 1800m
Q19: The distance between two stations is 300 km. A train takes 6 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Ans:
The distance between the two stations = 300 km
Time taken by the train to cover that distance = 6 hours
Speed of the train = 300/6 Km/h =50 km/h
Long Answer Questions
Q1: State different types of motion?
Ans: The Following are different types of motion:
- Translatory Motion: - In Translatory motion, the particle moves from one point in space to another. This motion may be along a straight line or along a curved path.
- Rectilinear motion: Motion along a straight line is called rectilinear motion. Example: A car moving on a straight road
- Curvilinear motion: Motion along a curved path is called curvilinear motion. Example: A car negotiating a curve
- Rotatory Motion: In rotatory motion, the particles of the body describe concentric circles about the axis of motion
- Vibratory Motion: In vibratory motion, the particles move to and fro about a fixed point.
Q2: A simple pendulum takes 15 seconds to complete 5 oscillations. What is the time period of pendulum?
Ans:
The time taken by the pendulum to complete 1 oscillation is called the time period
The time taken by the pendulum to complete 5 oscillations = 15sec
The time taken by the pendulum to complete 1 oscillation = 15/5= 3 sec
So time period = 3 sec
Q3: The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 08:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Ans:
Initial reading of car odometer = 57321.0 km
Final reading of car odometer = 57336.0 km
Time at the time of Initial reading = 08:30 AM
Time at the time of Initial reading = 08:50 AM
Distance travelled by the car = 57336.0 km - 57321.0 km
= 15 Km
Time taken by the car to cover the distance = 08:50 AM -08:30 AM
= 20 m
Speed of the car in Km/m = 15 km/20m
= .75 Km/m
Speed of the car in Km/h = 15 km/20m X 60
= 45 Km/h
Q5: A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
Ans:
Distance covered by the car with a speed of 40 km/h in 15 minutes = Speed * Time
= (40 Km/h /60 minutes) * 15 minutes
= 10 Km
Distance covered by the car with a speed of 40 km/h in 15 minutes = Speed * Time
= (60 Km/h /60 minutes) * 15 minutes
= 15 Km
Total distance covered by the car =(10 + 15 )km = 25 Km
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Measurement of Time and Motion
| 1. What are the different units of measurement for time in daily life? |  |
| 2. How do we measure motion in physics? |  |
| 3. Why is it important to understand time and motion in our daily lives? |  |
| 4. What tools can be used to measure time accurately? |  |
| 5. How does technology impact the measurement of time and motion? |  |
















