Class 7 Social Science Chapter 10 Question Answers - The Constitution of India — An Introduction
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Why was the Constitution of India adopted in 1949 but implemented in 1950?
Ans: The Constitution was adopted on 26 November 1949 but came into effect on 26 January 1950 to give time for the country to prepare for the transition from British rule. This also marked India’s Republic Day, symbolizing the country’s self-governance.
 Constitution of India
Constitution of India
Q2: What was the role of the Constituent Assembly in shaping India’s Constitution?
Ans: The Constituent Assembly was responsible for drafting the Constitution of India. It included representatives from diverse regions and communities, ensuring the Constitution reflected India’s values of democracy, equality, and justice.
Q3: What are the main components of the government structure as per the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Indian Constitution establishes three main branches of government: the legislature (which makes laws), the executive (which implements laws), and the judiciary (which ensures laws are followed and settles disputes).
Q4: How did the Indian Freedom Movement influence the Constitution?
Ans: The Indian Freedom Movement emphasized values like equality, justice, and freedom, which were incorporated into the Constitution. Leaders of the movement brought their experiences into the Constituent Assembly to create a fair and democratic system.
Q5: How is the Constitution a "living document"?
Ans: The Constitution is a "living document" because it can be amended to meet the changing needs of the country. Amendments help adapt the Constitution to new challenges and evolving societal norms, keeping it relevant over time.
Q6: What is the significance of the Preamble to the Constitution of India?
Ans: The Preamble sets out the fundamental values and objectives of the Constitution, including justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity. It guides the government and citizens in ensuring a fair and just society.
Q7: What is the role of the President, Prime Minister, and judges in the Constitution?
Ans: The President is the ceremonial head of state, the Prime Minister leads the executive, and judges in the judiciary ensure laws are in line with the Constitution. These officials take an oath to uphold the Constitution.
Q8: How does the Indian Constitution protect individual rights?
Ans: The Constitution provides Fundamental Rights that guarantee individual freedoms like equality, freedom of speech, and protection from exploitation. These rights are enforceable in court if violated by the government or others.
 Constituent Assembly
Constituent Assembly
Q9: What are Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) and how do they guide the government?
Ans: DPSPs are guidelines for the government to create laws and policies aimed at improving the standard of living, ensuring justice, and protecting the environment. They are not legally enforceable but guide government actions.
Q10: What changes have been made to the Constitution since its adoption?
Ans: The Constitution has been amended several times to address evolving issues. Notable changes include the addition of Fundamental Duties in 1976, the recognition of the Panchayati Raj System in 1992, and rights like the freedom to fly the national flag.
Q11: How does the Indian Constitution ensure a separation of powers?
Ans: The Constitution ensures the separation of powers by clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of the legislature, executive, and judiciary. This system prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful and ensures fairness in governance.
Q12: How does the Constitution promote equality in India?
Ans: The Constitution promotes equality by ensuring that all citizens are treated equally before the law, regardless of religion, caste, gender, or race. It guarantees equal opportunities and prohibits discrimination, upholding the values of justice and fairness.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: What was the role of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar in the drafting of the Indian Constitution?
Ans:
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar played a pivotal role as the Chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Indian Constitution.
- He ensured that the Constitution upheld the values of equality, justice, and social rights, particularly for marginalized groups.
- His leadership and vision shaped key sections of the Constitution, particularly those related to fundamental rights, social justice, and the protection of individual liberties.
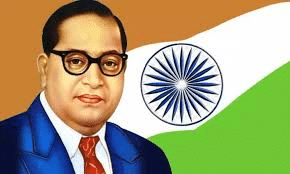
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Q2: How did the freedom struggle influence the inclusion of Fundamental Rights in the Constitution?
Ans:
- The freedom struggle was focused on the protection of citizens' rights against colonial oppression.
- Leaders from the movement, including Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and others, ensured that the Constitution included Fundamental Rights to protect individual freedoms.
- These rights guarantee equality, freedom of speech, and protection from exploitation, ensuring the spirit of democracy and justice.
Q3: Why was it necessary to include the concept of "Separation of Powers" in the Constitution?
Ans:
- The separation of powers ensures that no one branch of government becomes too powerful.
- By dividing authority among the legislature, executive, and judiciary, the Constitution maintains a system of checks and balances.
- This system allows each branch to act independently, preventing misuse of power and safeguarding democratic principles.
Q4: Explain the significance of the Preamble and how it reflects the values of the Constitution.
Ans:
- The Preamble serves as the introduction to the Constitution, outlining its core values and objectives.
- It reflects the ideals of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity.
- The Preamble emphasizes India’s commitment to a sovereign, secular, democratic republic, guiding the government in ensuring fairness and respect for all citizens, regardless of their background.
Q5: What role did the Constituent Assembly play in shaping the Indian Constitution?
Ans:
- The Constituent Assembly was tasked with framing the Constitution of India after independence.
- It consisted of elected representatives who debated key issues such as governance, fundamental rights, and the structure of the government.
- The assembly's decisions shaped India’s democratic framework and ensured the inclusion of values like equality, justice, and social welfare.
Q6: How does the Indian Constitution ensure the protection of minority rights?
Ans:
- The Indian Constitution guarantees the protection of minority rights through provisions like the Right to Equality and the Right to Freedom of Religion.
- It ensures that no individual or community is discriminated against based on religion, caste, or language.
- Additionally, the Constitution encourages the protection of minority languages and cultures, promoting an inclusive society.
Q7: What is the significance of the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) in the Indian Constitution?
Ans:
- The DPSP provides guidelines to the government for achieving social and economic justice.
- While they are not legally enforceable, they guide government policies on issues like healthcare, education, and the environment.
- The DPSPs reflect the Constitution’s commitment to improving the quality of life for all citizens, particularly the disadvantaged.
Q8: How does the Constitution accommodate India's diversity in terms of religion, language, and culture?
Ans:
- The Indian Constitution accommodates India’s diversity by recognizing multiple languages, religions, and cultures.
- It guarantees the freedom to practice any religion and promotes the idea of "unity in diversity."
- The Constitution allows for the protection of cultural heritage and the promotion of multiple languages through the recognition of various regional languages in the Eighth Schedule.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 10 Question Answers - The Constitution of India — An Introduction
| 1. What is the Constitution of India and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. How does the Constitution of India protect the rights of citizens? |  |
| 4. What is the process of amending the Constitution of India? |  |
| 5. Why is the Preamble to the Constitution significant? |  |
















