Class 7 Social Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - From Barter to Money
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What problems did the barter system have that led to the need for money?
Ans: The barter system had issues like double coincidence of wants, where both parties needed to have what the other wanted. It also lacked a common standard of value, and goods like cattle were not portable or divisible, making trade slow and inefficient.
 Barter System
Barter System
Q2: How did the introduction of money simplify trade compared to the barter system?
Ans: Money simplified trade by providing a portable, divisible, and universally accepted medium of exchange. It allowed for easier transactions, and people could store value and make future payments, overcoming the limitations of the barter system.
Q3: What is the role of money as a store of value?
Ans: Money acts as a store of value by allowing individuals to save it for future use. Unlike perishable goods like wheat, money does not lose its value quickly, making it easy to save for future purchases or investments.
Q4: How does the common denomination function of money help in trade?
Ans: The common denomination function of money helps by allowing goods of different values to be compared and priced in a standard way. This makes it easier for people to understand the worth of various items and conduct transactions efficiently.
Q5: Why did early societies use items like cowrie shells and Rai stones as money?
Ans: Early societies used items like cowrie shells and Rai stones as money because they were valuable, durable, and could be easily traded. These items were widely accepted in their respective regions as a form of exchange.
Q6: How did the advent of coins change trade in ancient India?
Ans: The advent of coins in ancient India made trade more efficient by providing a standardized, portable, and durable form of money. Coins made from metals like gold, silver, and copper were easy to carry and were accepted across regions, promoting wider trade networks.
Q7: What was the significance of the introduction of paper currency in India?
Ans: The introduction of paper currency in India provided a more convenient way to handle large sums of money, especially for higher denominations. It made trade easier and reduced the need to carry heavy coins, facilitating smoother transactions.
Q8: How did the design of modern Indian currency notes evolve?
Ans: Modern Indian currency notes feature cultural motifs, symbols, and security features like raised marks for the visually impaired. These notes are made of durable cotton paper and are designed to prevent counterfeiting and to reflect India’s heritage.
 Paper Currency
Paper Currency
Q9: How does digital money work, and how has it impacted modern transactions?
Ans: Digital money works through electronic systems like mobile payments, bank transfers, and online banking. It has made transactions faster, easier, and more accessible, reducing the need for physical money and increasing convenience for users.
Q10: What is UPI, and how does it simplify payments?
Ans: UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a digital payment system that allows users to transfer money instantly between bank accounts using their mobile phones. It simplifies payments by linking multiple bank accounts to a single app and facilitates easy transactions.
Q11: How do QR codes facilitate digital payments in modern commerce?
Ans: QR codes facilitate digital payments by providing a quick and secure way to transfer money from one person’s bank account to another. By scanning the code with a smartphone, payments can be made instantly, making transactions more efficient.
Q12: What were the limitations of the barter system that money helped overcome?
Ans: The barter system had limitations such as the double coincidence of wants, where both parties needed to have what the other wanted, and issues with portability, divisibility, and durability. Money solved these problems by offering a universally accepted, portable, divisible, and durable means of trade.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: What were the main challenges of the barter system, and how did money address these issues?
Ans:
- The barter system faced challenges such as the double coincidence of wants, where both parties needed to have what the other wanted.
- There were also issues with measuring value, dividing goods, and portability.
- Money addressed these by providing a universally accepted, portable, divisible, and durable medium of exchange.
- It allowed for easy transactions, saving, and future payments, making trade more efficient.
Q2: How did the introduction of coins benefit ancient India’s economy and trade?
Ans:
- Coins helped facilitate trade by offering a standardized, easily portable, and widely accepted form of money.
- In ancient India, coins made from precious metals like gold, silver, and copper were used for transactions.
- The use of coins allowed for easier trade within the region and with foreign countries, such as during the Roman trade. The presence of coins helped stimulate economic activity and provided a stable basis for conducting business.
 Digital Currency
Digital Currency
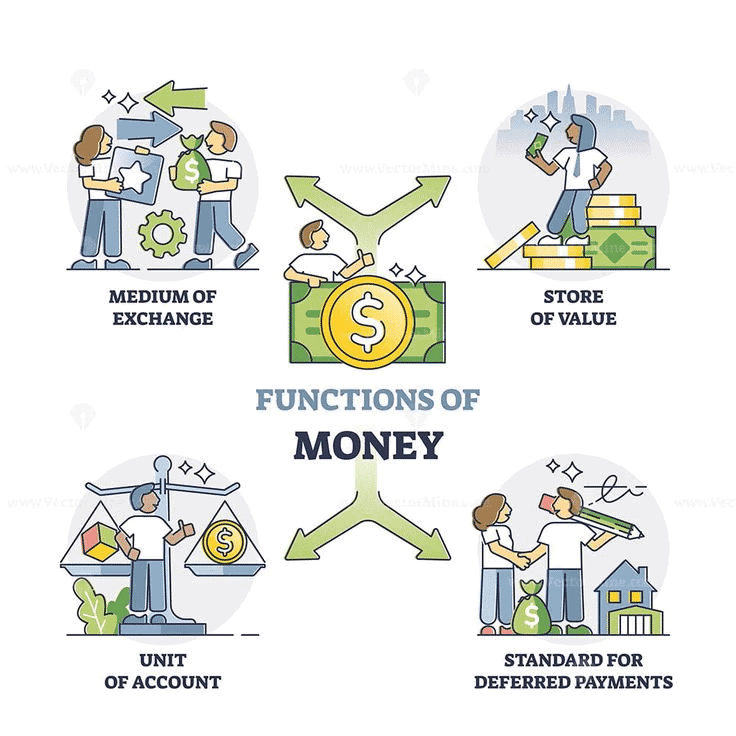
Q3: What are the functions of money, and how do they help the economy?
Ans:
- Money serves as a medium of exchange, a store of value, a common denomination for measuring the value of goods, and a standard of deferred payment.
- These functions help simplify trade by providing a common tool for transactions, enabling people to save wealth for future use, compare prices, and make payments over time.
- The functions of money contribute to economic stability by making transactions smoother and more predictable.
Q4: How did the transition from barter to money impact social and cultural life?
Ans:
- The transition from barter to money made trade more efficient, allowing for greater social interaction and the expansion of economies.
- With the ability to store wealth and trade more easily, people could engage in more diverse economic activities, from farming to craftsmanship.
- This shift also led to greater cultural exchanges, as people could now trade goods across longer distances, influencing art, philosophy, and other cultural aspects.
Q5: Why is the standard of deferred payment an important function of money?
Ans:
- The standard of deferred payment allows people to make transactions over time by agreeing to pay at a later date.
- This function is important because it enables businesses and individuals to engage in long-term contracts and investments, providing flexibility in financial planning.
- It allows for purchases that may be too expensive to pay upfront, such as education, real estate, or larger goods, supporting both economic growth and personal financial management.
Q6: How did paper currency evolve, and what role did it play in modern economies?
Ans:
- Paper currency evolved in ancient China and was introduced to India in the 18th century by banks. It was used for higher denominations, making large-scale transactions easier.
- Paper currency facilitated economic growth by providing a more convenient alternative to heavy coins, promoting trade and commerce.
- Today, it plays a crucial role in modern economies by being the main medium for most transactions, controlled by central banks to ensure stability.
Q7: How has the rise of digital money impacted traditional systems of payment?
Ans:
- The rise of digital money has transformed traditional payment systems by providing faster, more convenient alternatives like mobile payments, credit and debit cards, and online banking.
- Digital money has made transactions quicker and more accessible, especially for online shopping, reducing the need for physical currency. It has also expanded financial inclusion by allowing people in remote areas to access banking services through smartphones and the internet.
Q8: How did the development of trade routes impact the evolution of money and currency?
Ans:
- The development of trade routes, such as those connecting India to the Roman Empire, encouraged the need for a standardized form of money.
- Trade across long distances required a universal medium of exchange that could be easily carried and recognized. This led to the invention of coins, which facilitated smoother and more secure transactions.
- Over time, the growth of trade networks and the increasing complexity of economies led to the evolution of paper money and, later, digital currency.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - From Barter to Money
| 1. What is barter and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the limitations of the barter system? |  |
| 3. How did money evolve from the barter system? |  |
| 4. What are the different forms of money? |  |
| 5. Why is money considered more efficient than barter? |  |
















