Class 7 Social Science Chapter 9 HOTS Questions - From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
Q1: How does the separation of powers in a democracy ensure fairness and protect citizens' rights?
Ans:
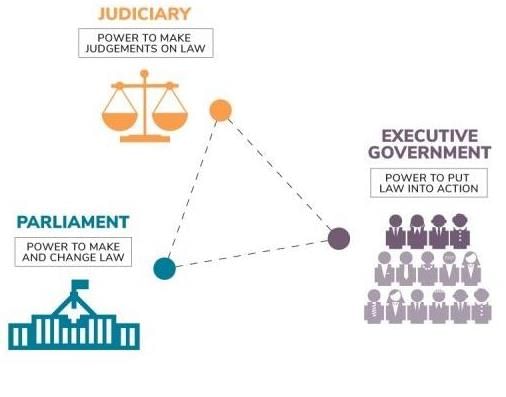
- The separation of powers in a democracy ensures fairness by dividing the responsibilities of governance into three distinct branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial.
- The legislative branch makes the laws, the executive implements them, and the judiciary ensures that the laws are followed and that no one, including government officials, is above the law.
- This system prevents any one branch from gaining too much power and acts as a safeguard against abuse of power, protecting citizens' rights by ensuring that laws are made fairly, enforced properly, and impartially judged.
 Q2: Compare the role of the king in a monarchy to that of a representative in a democracy. How do their powers differ?
Q2: Compare the role of the king in a monarchy to that of a representative in a democracy. How do their powers differ?
Ans:
- In a monarchy, the king holds supreme power and usually rules for life, with his position often passed down through generations.
- The king has the authority to make decisions for the kingdom, and his power may be absolute or ceremonial depending on the type of monarchy.
- In contrast, a representative in a democracy is elected by the people for a fixed term and is accountable to them.
- The powers of a representative are limited by the constitution and laws, and they work with other elected officials in the legislature.
- While a monarch’s power is personal and hereditary, a representative’s power is based on the will of the people and subject to checks and balances.
Q3: How would you apply the principles of democracy to improve student participation in school decisions?
Ans:
- To apply the principles of democracy to improve student participation, I would encourage the formation of a student body that elects representatives from each class or grade.
- These representatives would be tasked with voicing student concerns, such as issues related to the timetable, extracurricular activities, and school facilities.
- Similar to the legislative function in a democracy, the student representatives would debate and vote on decisions that affect the whole school.
- The executive function could be handled by a student council that implements the decisions made, and the judicial function could involve a review system to ensure fairness and that rules are being followed.
- This would make the school environment more inclusive and ensure that students feel their opinions matter.
Q4: Suppose you are tasked with creating a new form of government for a small community. How would you balance the need for effective leadership with the principles of fairness and equality?
Ans:
- To balance effective leadership with fairness and equality, I would establish a system where a small group of elected leaders manage day-to-day decisions, but the overall power remains with the people.
- The leadership would be chosen through regular elections, ensuring that everyone in the community has a voice, similar to a representative democracy.
- I would also introduce checks and balances by giving citizens the power to vote on major decisions, such as changes to laws or the community's budget.
- A council could be established to review actions taken by the leadership, ensuring transparency and fairness.
- This would allow for efficient leadership while maintaining fairness and accountability to all community members.
Q5: Justify why universal adult franchise is considered an essential feature of democracy.
Ans:
- Universal adult franchise is essential to democracy because it ensures that every citizen, regardless of their background, has an equal say in how the country is governed.
- By allowing all adults to vote, democracy guarantees that political power is not concentrated in the hands of a few, but is distributed among the people.
- This ensures that the government is accountable to the public, reflecting the will of the majority while safeguarding minority rights.
- Without universal adult franchise, a democracy would be incomplete, as it would exclude a significant portion of the population from participating in decision-making processes, undermining the core principle of equality.
Q6: How might the challenges faced by democracies, such as corruption or inequality, be addressed by citizens?
Ans:
- The challenges of corruption and inequality in democracies can be addressed by active citizen participation.
- Citizens must hold their representatives accountable by voting regularly, raising concerns, and demanding transparency in government actions.
- Establishing independent bodies like anti-corruption commissions and ensuring the media can freely report on government activities also helps.
- Additionally, citizens can engage in grassroots movements and protests to bring attention to social injustices, advocating for policies that promote equality and fairness.
- In a democracy, it is the responsibility of the citizens to remain vigilant, ensuring their leaders act in the public interest and that the rights of all are upheld.
Q7: Design a campaign to educate the public about the importance of voting in a democracy. What key elements would you include?
Ans: A campaign to educate the public about the importance of voting would include several key elements:
- Awareness Programs: Organizing workshops and social media campaigns to explain how voting influences government decisions and the importance of each person’s vote in shaping the future.
- Simplified Voting Process: Providing information on how to register to vote, the voting process, and how votes are counted, ensuring it is accessible and easy to understand for everyone.
- Highlighting the Impact: Using real-life examples of how voting has led to changes in policies, such as improvements in education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Incentives: Offering incentives such as voting registration drives in schools, universities, and workplaces, or recognition for first-time voters.
- Appeals to Civic Duty: Creating messages that appeal to the sense of responsibility and empowerment that comes with participating in the democratic process, emphasizing that voting is both a right and a duty that impacts everyone’s future.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 9 HOTS Questions - From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
| 1. What are the different types of government discussed in the article "From the Rulers to the Ruled"? |  |
| 2. How does a democracy differ from a monarchy according to the article? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a dictatorship as mentioned in the article? |  |
| 4. What role do citizens play in an oligarchy compared to a democracy? |  |
| 5. How does the article describe the evolution of governments from rulers to the ruled? |  |
















