Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
Q31: What is the difference between noise and music, can music become noise sometimes?
Ans: The sound that is pleasing to the ear is called music, such as sounds produced by a guitar or piano. In contrast, sounds that are unpleasant are referred to as noise, like those from factories or traffic. Music can indeed become noise if it is played at a high volume.
Here are some key points:
- Music is generally harmonious and enjoyable.
- Noise is often disruptive and irritating.
- Volume can transform music into noise.
Q32: Define:
a. Reverberation of sound
b. Echo
Ans: The persistence of sound due to repeated reflection and its gradual fading away is known as reverberation of sound.
Echo: Echo is defined as a repetition of sound due to the reflection of original sound by a large and hard obstacle.
Q33: What is the intensity of sound?
Ans: The intensity of sound refers to the amount of sound energy that passes through a unit area each second. It is a measure of how much sound is present in a given space.
Q34. How is sound produced?
Ans: Sound is produced by vibrating objects. When an object vibrates, it creates sound waves.
- If the vibrations stop, the sound ceases.
- In humans, sound originates from the vibration of the vocal cords.
- Sound requires a medium (gas, liquid, or solid) to travel; it cannot move through a vacuum.
Q35. Explain the importance of sound in our daily life.
Ans: Sound plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It is essential for various actions and interactions, including:
- Enabling communication between individuals.
- Helping us understand messages conveyed by others.
- Allowing us to perceive our surroundings through different sounds.
Without sound, our ability to connect and interact would be severely limited.
Q35. What are musical instruments? How do they produce sound?
Ans: Musical instruments are devices that create sounds that are pleasing to our ears, known as music. They can produce sound through various methods:
- Instruments often have strings or membranes that vibrate.
- Some instruments contain air columns that also vibrate.
- When these parts vibrate, they generate sound.
Overall, the vibrations of these components are what allow us to hear music.
Q36. Explain with the help of an activity that vibrating bodies produce sound.
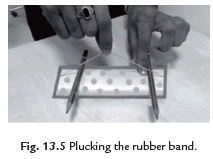
Ans: To demonstrate how vibrating bodies produce sound, follow these steps:
- Take a rubber band and stretch it around the longer side of a pencil box.
- Insert two pencils between the box and the stretched rubber band.
- Pluck the rubber band in the middle.
- You will hear a sound and see the rubber band vibrating.
This activity clearly shows that when objects vibrate, they produce sound.
Q37. Do you see the vibrations in all the cases?
Ans: The objects that vibrate create sound. Here’s what you need to know:
- In some instances, vibrations are clearly visible.
- In most cases, the vibrations are too small to see.
- Regardless of visibility, vibrations can always be felt.
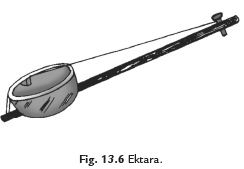
Q38. What is ektara? Identify its vibrating part.
Ans: The ektara is a simple musical instrument made from a hollow coconut shell or an earthen pot. To create sound, the following components are used:
- A hollow coconut shell or an earthen pot serves as the body.
- A stretched rubber band or wire acts as the vibrating part.
When you pluck the rubber band or wire, it vibrates, producing sound.
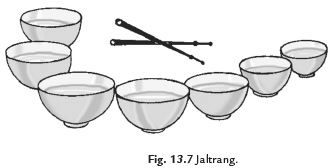
Q39. Explain the principle on which Jaltrang works.
Ans: Jaltrang operates on the principle that the quality of sound changes with frequency. It involves:
- Using metal tumblers filled with water at varying heights.
- Each height produces different vibrations.
- These vibrations generate distinct sounds.
Q40. Name the organ in human that produces sound. How does it work?
Ans: In humans, sound is produced by the voice box, also known as the larynx. Here’s how it works:
- The voice box contains two vocal cords that are stretched across it.
- These vocal cords create a narrow slit for air to pass through.
- When air from the lungs is forced through this slit, the vocal cords vibrate.
- This vibration produces sound.
The tension of the vocal cords can change, affecting the pitch and quality of the sound.
Q41. Prove that sound needs a medium for propagation.
Ans: To demonstrate that sound requires a medium for propagation, follow these steps:
- Take a dry metal or glass tumbler.
- Place a cellphone inside it and ask a friend to call.
- Listen carefully to the ringtone.
- Now, cover the rim of the tumbler with your hands and put your mouth over the opening.
- Ask your friend to ring the phone again while you suck air from the tumbler.
- Notice how the sound becomes much fainter.
This experiment shows that without air (the medium), the sound diminishes significantly, proving that sound cannot travel in a vacuum.

Q42. What do you mean by vacuum? What happens to the loudness of sound in vacuum?
Ans: A vacuum is a space where there is no air or matter. When air is completely removed from a vessel, it creates a vacuum. In a vacuum:
- Sound cannot travel because it needs a medium, like air, to propagate.
- If all the air is sucked out, any sound produced will stop completely.
Thus, the loudness of sound decreases as the amount of air decreases.
Q43. Prove that sound can travel through the liquids.
Ans: To demonstrate that sound can travel through liquids, follow these steps:
- Fill a bucket or bathtub with clean water.
- Hold a small bell and shake it inside the water to create sound.
- Gently place your ear on the water surface (be careful not to let water enter your ear).
- If you can hear the bell, it shows that sound travels through liquids.

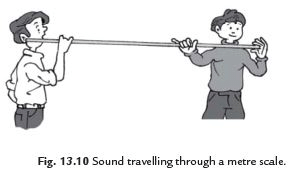
Q44. Prove that sound can travel through solids also.
Ans: To demonstrate that sound can travel through solids, follow these steps:
- Take a metre scale or a long metal rod.
- Hold one end to your ear.
- Ask a friend to gently scratch or tap the other end.
- You will hear the sound through the solid rod.
- Others nearby may not hear it, as the sound is faint.
This simple activity shows that sound can indeed travel through solids.
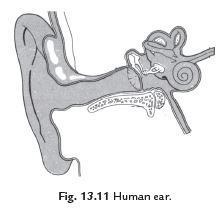
Q45. How do human being hear the sounds?
Ans: The human ears are the organs responsible for hearing. They consist of a structure called the eardrum, which is a thin, stretched membrane. Here’s how we hear sounds:
- Sound waves enter the ear through the ear canal.
- These waves cause the eardrum to vibrate.
- The vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear.
- From the inner ear, the signals are sent to the brain for interpretation.
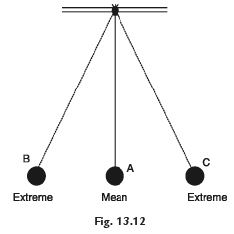
Q46. What do you mean by an oscillatory motion?
Ans: The to and fro motion of an object is known as vibration. This movement, occurring on either side of the object's mean position, is also referred to as oscillatory motion.
Q47. What is frequency? How does it affect the quality of sound?
Ans: Frequency refers to the number of oscillations or vibrations that occur in one second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz equals one oscillation per second. The frequency of a sound affects its pitch:
- A higher frequency results in a higher pitch, making the sound shrill.
- A lower frequency leads to a lower pitch, resulting in a deeper sound.
For example:
- A whistle has a high frequency, producing a high-pitched sound.
- A drum has a low frequency, resulting in a low-pitched sound.
Q48. What are the two important properties of sound?
Ans: Amplitude: This is the maximum distance a vibrating object moves from its resting position. It determines the loudness of a sound. A larger amplitude means a louder sound.
Frequency: This refers to the number of vibrations or oscillations per second. It affects the pitch of the sound. A higher frequency results in a higher pitch, while a lower frequency produces a lower pitch. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz).
Q49. What do you mean by noise and musical sound?
Ans: Noise: Unpleasant sounds that are considered unwanted and can be harmful to our ears. Musical sound: Sounds that produce pleasant sensations, typically created by various musical instruments.
Q50. What is noise pollution?
Ans: The presence of unwanted and excessive sounds in the environment is known as noise pollution. It can cause discomfort and various health issues. Common sources include:
- Honking of horns
- Loudspeakers
- Fireworks
- Machinery
In homes, noise can come from:
- Television and radio at high volumes
- Kitchen appliances
- Air conditioners
Excessive noise may lead to health problems such as:
- Lack of sleep
- Hypertension
- Anxiety
- Hearing impairment
Q51. How can noise pollution be controlled?
Ans: The control of noise pollution involves reducing its sources. Here are some effective measures:
- Avoid using horns in residential areas, especially near schools and hospitals.
- Minimise the use of loudspeakers.
- Keep the volume of TVs and radios low.
- Plant trees along roads and around buildings to absorb excess sound.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
| 1. What is sound and how is it produced? |  |
| 2. How does sound travel through different mediums? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between pitch and loudness of sound? |  |
| 4. How does sound travel in outer space? |  |
| 5. How does the speed of sound change with temperature? |  |
















