Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion
Very Short Answer Questions
Ques 1: The phenomenon of motion was placed on a sound scientific footing by two scientists. Write their names.
Ans: Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton.
Ques 2: Are rest and motion absolute or relative terms?
Ans: They are relative terms.
Ques 3: Suppose a ball is thrown vertically upwards from a position P above the ground. It rises to the highest point Q and returns to the same point P. What is the net displacement and distance travelled by the ball?
Ans: Displacement is zero. Distance is twice the distance between position P and Q.
Ques 4: Which speed is greater: 30 m/s or 30 km/h?
Ans: 30 m/s
Ques 5: What do you mean by 2 m/s2?
Ans: The velocity of the body increases by 2 m/s after every second.
Ques 6: Can uniform linear motion be accelerated?
Ans: No
Ques 7: Define one radian.
Ans: It is the angle that is subtended at the center by an arc having a length equal to the radius of the circle.
Ques 8: What is the relation between linear velocity and angular velocity
Ans: Linear velocity = Angular velocity x Radius of circular path.
Short Answer Questions
Ques 1: Give an example of a body that may appear to be moving for one person and stationary for the other.
Ans: The passengers in a moving bus observe that the trees, buildings, as well as people on the roadside, appear to be moving backward. Similarly, a person standing on the roadside observes that the bus (along with its passengers) is moving in a forward direction. But, at the same time, each passenger in a moving bus or train observes his fellow passengers sitting and not moving. Thus, we can tell that motion is relative.
Ques 2: How can we describe the location of an object?
Ans: To describe the position of an object, we need to specify a reference point called the origin. For example, suppose that a library in a city is 2 km north of the railway station. We have specified the position of the library with respect to the railway station i.e., in this case, the railway station acts as the reference point.
Ques 3: What do you mean by average speed? What are its units?
Ans: Average speed is defined as the average distance travelled per unit time and is obtained by dividing the total distance travelled by the total time taken. The unit of average speed is the same as that of the speed, that is, ms-1.
Ques 4: What is the difference between uniform velocity and non-uniform velocity?
Ans: Uniform velocity: An object with uniform velocity covers equal distances in equal intervals of time in a specified direction, e.g., an object moving with speed of 40km h-1 towards west has uniform velocity.
Non-uniform velocity: When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time in a specified direction, or if the direction of motion changes, it is said to be moving with a non-uniform or variable velocity, e.g., a revolving fan at a constant speed has variable velocity.
Ques 5: Differentiate between distance and displacement.
Ans:
Distance | Displacement |
| It is the length of the actual path covered by an object, irrespective of its direction of motion. | Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object in a given direction. |
| Distance is a scalar quantity | Displacement is a vector quantity. Displacement may be positive negative or zero. |
| Distance between two given points may be the same or different for different paths chosen. | Displacement between two given points is always the same. |
| Distance covered can never be negative. It is always positive or zero. | Displacement between two given points is always the same. |
Ques 6: What are the uses of a distance-time graph?
Ans: The various uses of a distance-time graph are as follows:
(a) It tells us about the position of the body at any instant of time.
(b) From the graph, we can see the distance covered by the body during a particular interval of time.
(c) It also gives us information about the velocity of the body at any instant in time.
Long Answer Questions
Ques 1: With the help of a graph, derive the relation v = u + at.
Ans: Consider the velocity-time graph of an object that moves under uniform acceleration as shown in the figure (u≠0).
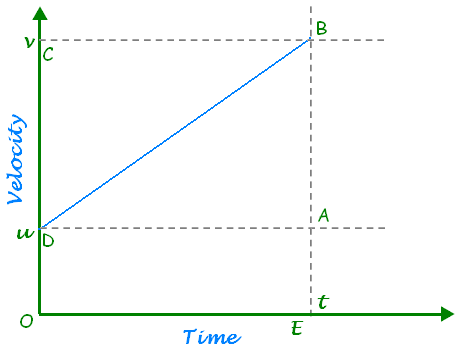
From this graph, we can see that initial velocity of the object (at point D) is u and then it increases to v (at point B) in time t. The velocity changes at uniform rate a. As shown in the figure, the lines BC and BE are drawn from point B on the time and the velocity axes respectively.
The initial velocity is represented by OD.
The final velocity is represented by BE.
The time interval t is represented by OE.
BA = BE - EA, represents the change in velocity in time interval t.
If we draw DA parallel to OE, we observe that BE = BA + DE = BA + OD
Substituting, BE with v and OD with u, we get
v = BA + u
or, BA = v - u --- (i)
Thus, from the given velocity-time graph, the acceleration of the object is given by Change in velocity
a = (Change in velocity)/(Time Taken)= BA/DA= BA/OE
Substituting OC with t, we get
a = BA/t ⇒ BA = at --- (ii2)
From equations (1) and (2), we have
v-u = at or v =u + at
Ques 2: Obtain a relation for the distance travelled by an object moving with a uniform acceleration in the interval between 4th and 5th seconds.
Ans: Using the equation of motion, s = ut+ 1/2 at2
Distance travelled in 5 seconds, s = u ∗ 5 + 1/2 a ∗ 52
⇒ s = 5u +25/2 a
Similarly, distance travelled in 4 seconds,sι = 4u + 16/2 a
Distance travelled in the interval between 4th and 5th seconds
= (s-sι) = (u + 9/2 a)m
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion
| 1. What is motion in physics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of motion? |  |
| 3. How is speed different from velocity in motion? |  |
| 4. What is the equation for calculating average speed? |  |
| 5. How does acceleration affect motion? |  |






















