Concept of Product & Its Classification | Marketing and Sales for Class 10 PDF Download
As stated earlier, product refers to the goods and services offered by the organisation for sale. Here the marketers have to recognise that consumers are not simply interested in the physical features of a product but a set of tangible and intangible attributes that satisfy their wants. For example, when a consumer buys a washing machine he is not buying simply a machine but a gadget that helps him in washing clothes. It also needs to be noted that the term product refers to anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, or use. Thus, the term product is defined as “anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want”. It normally includes physical objects and services. In a broader sense, however, it not only includes physical objects and services but also the supporting services like brand name, packaging accessories, installation, after sales service etc. Look at the definitions by Stanton and McCarthy as given in the box.
Product
William J. Stanton
- “Product is a set of tangible and intangible attributes including packaging, colour, price, manufacturer’s prestige, retailer’s prestige and manufacturer’s and retailer’s services which buyer may accept as offering satisfaction of wants and services”.
Jerome McCarthy
- “A product is more than just a physical product with its related functional and aesthetic features. It includes accessories, installation, instructions on use, the package, perhaps a brand name, which fulfills some psychological needs and the assurances that service facilities will be available to meet the customer needs after the purchase”.
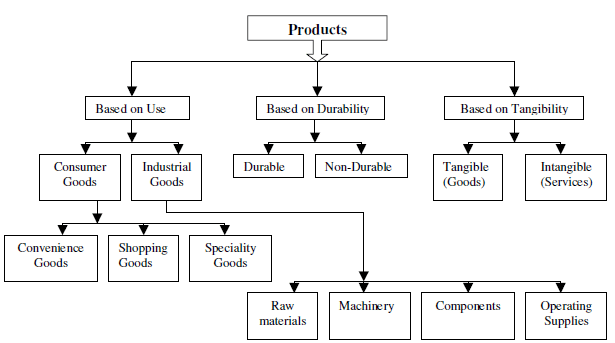
Product Classification
Product can be broadly classified on the basis of (1) use, (2) durability, and (3) tangibility. Let us have a brief idea about the various categories and their exact nature under each head, noting at the same time that in marketing the terms ‘product’ and ‘goods’ are often used interchangeably.
1. Based on use, the product can be classified as:
- Consumer Goods; and
- Industrial Goods.
(a) Consumer goods: Goods meant for personal consumption by the households or ultimate consumers are called consumer goods. This includes items like toiletries, groceries, clothes etc. Based on consumers’ buying behaviour the consumer goods can be further classified as :
(i) Convenience Goods;
(ii) Shopping Goods; and
(iii) Speciality Goods.
(i) Convenience Goods: Do you remember, the last time when did you buy a packet of butter or a soft drink or a grocery item? Perhaps you don’t remember, or you will say last week or yesterday. Reason is, these goods belong to the categories of convenience goods which are bought frequently without much planning or shopping effort and are also consumed quickly. Buying decision in case of these goods does not involve much pre-planning. Such goods are usually sold at convenient retail outlets.
(ii) Shopping Goods: These are goods which are purchased less frequently and are used very slowly like clothes, shoes, household appliances. In case of these goods, consumers make choice of a product considering its suitability, price, style, quality and products of competitors and substitutes, if any. In other words, the consumers usually spend a considerable amount of time and effort to finalise their purchase decision as they lack complete information prior to their shopping trip. It may be noted that shopping goods involve much more expenses than convenience goods.
(iii) Speciality Goods: Because of some special characteristics of certain categories of goods people generally put special efforts to buy them. They are ready to buy these goods at prices at which they are offered and also put in extra time to locate the seller to make the purchase. The nearest car dealer may be ten kilometres away but the buyer will go there to inspect and purchase it. In fact, prior to making a trip to buy the product he/she will collect complete information about the various brands. Examples of speciality goods are cameras, TV sets, new automobiles etc.
(b) Industrial Goods: Goods meant for consumption or use as inputs in production of other products or provision of some service are termed as ‘industrial goods’. These are meant for non-personal and commercial use and include (i) raw materials, (ii) machinery, (iii) components, and (iv) operating supplies (such as lubricants, stationery etc). The buyers of industrial goods are supposed to be knowledgeable, cost conscious and rational in their purchase and therefore, the marketeers follow different pricing, distribution and promotional strategies for their sale.
It may be noted that the same product may be classified as consumer goods as well as industrial goods depending upon its end use. Take for example the case of coconut oil. When it is used as hair oil or cooking oil, it is treated as consumer goods and when used for manufacturing a bath soap it is termed as industrial goods. However, the way these products are marketed to these two groups are very different because purchase by industrial buyer is usually large in quantity and bought either directly from the manufacturer or the local distributor.
2. Based on Durability, the products can be classified as :
- Durable Goods; and
- Non-durable Goods.
(a) Durable Goods: Durable goods are products which are used for a long period i.e., for months or years together. Examples of such goods are refrigerator, car, washing machine etc. Such goods generally require more of personal selling efforts and have high profit margins. In case of these goods, seller’s reputation and presale and after-sale service are important determinants of purchase decision.
(b) Non-durable Goods: Non-durable goods are products that are normally consumed in one go or last for a few uses. Examples of such products are soap, salt, pickles, sauce etc. These items are consumed quickly and we purchase these goods more often. Such items are generally made available by the producer through large number of convenient retail outlets. Profit margins on such items are usually kept low and heavy advertising is done to attract people towards their trial and use.
3. Based on tangibility, the products can be classified as:
- Tangible Goods; and
- Intangible Goods.
(a) Tangible Goods: Most goods, whether these are consumer goods or industrial goods and whether these are durable or non-durable, fall in this category as they have a physical form, that can be touched and seen. Thus, all items like groceries, cars, raw-materials, machinery etc. fall in the category of tangible goods.
(b) Intangible Goods: Intangible goods refer to services provided to the individual consumers or to the organisational buyers (industrial, commercial, institutional, government etc.). Services are essentially intangible activities which provide want or need satisfaction. Medical treatment, postal, banking and insurance services etc., all fall in this category.
|
25 videos|14 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
















