Connecting People | Social Science Olympiad for Class 3 PDF Download
Means of Transport
India has a diverse and extensive network of transportation, ranging from traditional modes to modern systems. Here are some common means of transport in India:
Road Transport
- Buses: Public and private buses connect cities, towns, and villages, providing a widely used mode of transport.
- Cars and Taxis: Private cars, taxis, and rideshare services are prevalent in urban and suburban areas.
- Auto-rickshaws: Three-wheeled vehicles are common for short-distance travel in cities and towns.
Rail Transport
- Indian Railways: One of the world's largest railway networks, connecting cities and remote areas. It includes various classes of trains, such as express, local, and luxury trains like the Palace on Wheels.
Air Transport
- Commercial Airlines: Major airports across the country facilitate domestic and international air travel. Airlines offer a range of flights, from low-cost carriers to full-service airlines.
Water Transport
- Ferries and Boats: Waterways are used for transport in coastal areas, rivers, and backwaters. Ferries operate in regions like Kerala and Goa.
- Inland Water Transport: Cargo and passenger boats navigate rivers and inland water bodies.
Metro and Rapid Transit Systems
- Metro Rail: Several cities, including Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Bengaluru, have metro rail systems to ease urban congestion.
- Monorail and Trams: Some cities have monorail systems, while trams operate in places like Kolkata.
Cycles and Cycle-Rickshaws
- Cycles: Common for short-distance travel, especially in smaller towns and villages.
- Cycle-Rickshaws: Human-powered rickshaws are used for short distances, particularly in congested areas.
Cable Cars and Funiculars
- Cable Cars: In hilly regions like Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir, cable cars provide scenic transportation.
- Funiculars: Some areas use inclined planes for transportation, such as the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway.
Goods Transport
- Trucks and Lorries: Road transport is crucial for the movement of goods, and trucks play a significant role in transporting cargo across the country.
- Goods Trains: Indian Railways operates freight trains for transporting goods over long distances.
India's transportation infrastructure is continually evolving, with ongoing efforts to enhance connectivity, improve efficiency, and accommodate the diverse needs of its population.
What are Road Signs?
Road signs are visual indicators placed along roadways to convey important information, guide drivers, and ensure road safety. These signs use symbols, colors, and text to communicate various messages and warnings. Road signs play a crucial role in regulating traffic, providing directions, and alerting drivers to potential hazards. Here are some common types of road signs:
Regulatory Signs
- Stop Sign: Indicates that a driver must come to a complete stop before proceeding.
- Yield Sign: Instructs drivers to give the right of way to other vehicles.
Warning Signs
- Cautionary (Triangular) Signs: Warn drivers about potential hazards, such as curves, intersections, or pedestrian crossings.
- Railroad Crossing Sign: Indicates the presence of a railroad crossing ahead.
Informational Signs
- Guide Signs: Provide information about routes, destinations, and distances.
- Service Signs: Indicate the location of services such as gas stations, rest areas, and food establishments.
Directional Signs
- Arrow Signs: Guide drivers on the direction to follow, especially at intersections and turns.
- Route Marker Signs: Display route numbers and help drivers navigate through highways and roads.
Traffic Regulatory Signs:
- Speed Limit Signs: Specify the maximum allowed speed on a particular stretch of road.
- No Entry Sign: Prohibits vehicles from entering a specific area or road.
Construction and Work Zone Signs:
- Construction Zone Signs: Inform drivers about ongoing roadwork or construction activities.
- Detour Signs: Redirect traffic to an alternative route due to road closures or construction.
School Zone Signs:
- School Crossing Sign: Alerts drivers to the presence of a school zone and the possibility of pedestrians.
Pedestrian Signs:
- Pedestrian Crossing Sign: Indicates a designated area for pedestrians to cross the road.
- Walk/Don't Walk Signals: Used at crosswalks to guide pedestrians when to proceed or wait.
Emergency and Information Signs:
- Hospital Signs: Indicate the direction to nearby medical facilities.
- Emergency Evacuation Route Signs: Provide information on evacuation routes during emergencies.
Parking Signs:
- No Parking Sign: Prohibits parking in a specific area.
- Parking Lot Signs: Provide information about parking rules and regulations in designated lots.
Understanding and following road signs is essential for safe and efficient driving. Different countries may have variations in the design and meaning of road signs, so it's important for drivers to be familiar with the specific signs in their region.
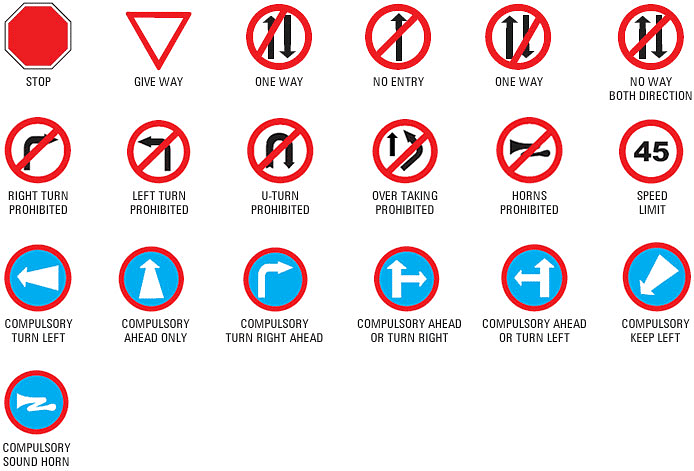
Mandatory Signs
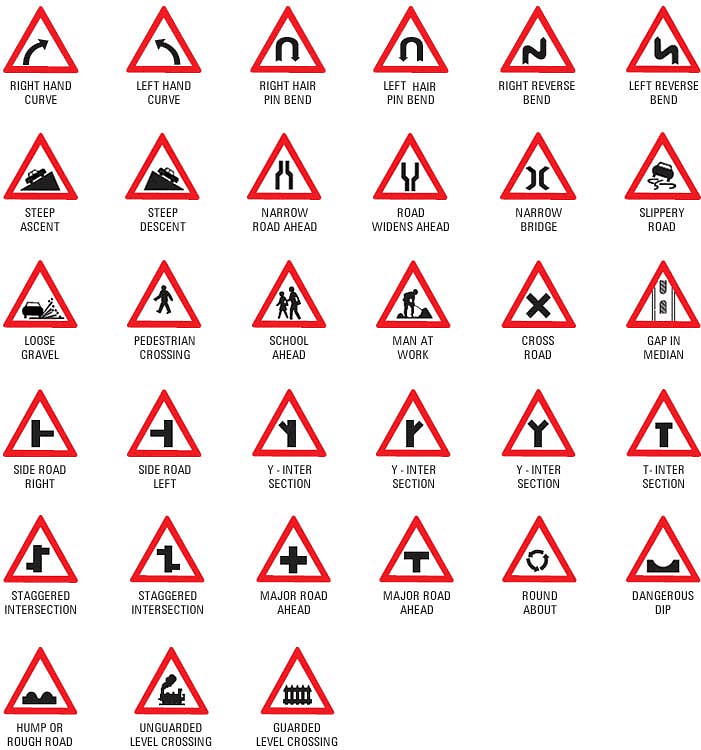
Cautionary Signs
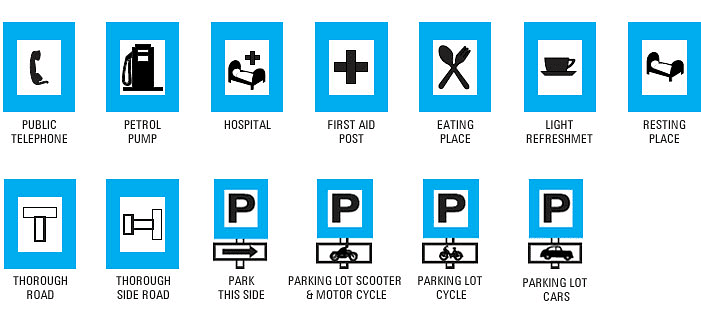
Informatory Signs
 What is Communication?
What is Communication?
Communication is the process of exchanging information, ideas, thoughts, or feelings between individuals or groups using verbal and non-verbal methods. It is a fundamental aspect of human interaction and plays a crucial role in conveying messages, building relationships, and facilitating understanding.
Means of Communication
Verbal Communication:
- Talking: When we talk to each other, we use words to share information or feelings.
- Phone Calls: Speaking to someone over the phone, even if they are far away.
Written Communication:
- Writing Letters: Sending messages to friends or family by writing on paper.
- Drawing Notes: Sometimes, we use pictures and colors to share our thoughts.
Non-Verbal Communication:
- Expressing Feelings: Using our face and body to show if we are happy, sad, or excited.
- Using Pictures: Drawing or pointing at pictures to share ideas without speaking.
Digital Communication:
- Using Computers: Playing games or talking to friends online.
- Video Calls: Seeing and talking to someone on a computer or tablet screen.
Print Media:
- Books: Reading stories and learning from books with words and pictures.
- Magazines: Looking at colorful magazines for fun pictures and short stories.
Broadcast Media:
- Watching TV Shows: Seeing and hearing stories on the television.
- Listening to Radio: Hearing music and stories on the radio.
Visual Communication:
- Drawing Pictures: Sharing ideas by drawing things on paper.
- Using Colors: Using different colors to make drawings more interesting.
Electronic Communication:
- Sending Messages on Phones: Using phones to send text messages or emojis.
- Playing Games on Tablets: Having fun and learning on tablets.
Interpersonal Communication:
- Talking in Groups: Sharing thoughts and ideas when we are in a group.
- Talking to Teachers: Asking questions or sharing things with our teachers.
Mobile Communication:
- Sending Short Messages: Using phones to send quick messages to friends or family.
- Using Apps for Learning: Playing educational games on phones or tablets.
|
15 videos|16 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Connecting People - Social Science Olympiad for Class 3
| 1. What is the difference between cable cars and funiculars? |  |
| 2. How do cable cars work? |  |
| 3. What are some popular destinations that have cable cars or funiculars? |  |
| 4. Are cable cars and funiculars safe for transportation? |  |
| 5. How can one differentiate between a cable car and a funicular when visiting a new destination? |  |
















