Constitution: Why and How? Class 11 Political Science
Introduction
A constitution is essential as it sets up the basic rules for governance, ensuring coordination, protecting rights, and guiding societal goals. Many constitutions from the twentieth century, with the Indian Constitution being a prime example, also create a framework that allows the government to undertake positive actions that reflect the aspirations and goals of society. The Indian Constitution was particularly groundbreaking, emerging from India's struggle for independence. By agreeing on fundamental norms about governance and the governed, a shared identity is formed.
Why Do We Need a Constitution?
A constitution is needed for the following purposes:

Constitution Allows Coordination and Assurance
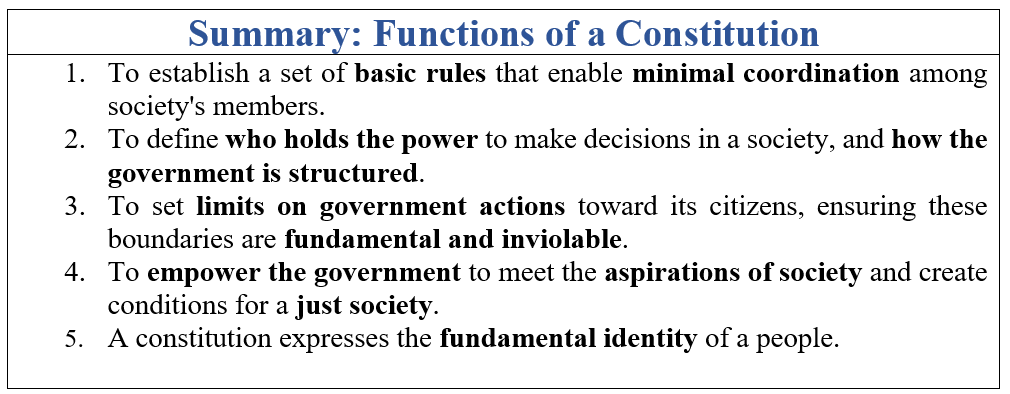
- The primary role of a constitution is to set out a framework of basic rules that facilitate minimal coordination among members of a society.
- It ensures that individuals feel secure about their rights and responsibilities within the community.
- For any group to function effectively, it requires clear rules that are known to all members to maintain a basic level of coordination.
- Rules must be publicly accessible and enforceable to foster trust and compliance.
- Without clear rules, individuals would feel insecure, unsure of how members might interact or who has rights over certain matters.
- The constitution makes sure that everyone knows the rules are followed, and if someone breaks them, they will be punished, helping people feel safe in their dealings with each other.
Specification of Decision-Making Powers
- The constitution specifies the basic allocation of power within society, determining who has the authority to make decisions regarding laws and policies.
- Outlines the process of decision-making, such as direct voting or elected representatives.
- In democratic constitutions, power usually belongs to the people.
- The constitution decides who has the right to make rules for society, helping to avoid conflicts when people have different ideas about what the rules should be.
- For example, in India, the Constitution gives Parliament the authority to make laws and policies. This setup creates the foundation for government and ensures that the decision-making process is clear and organized.
Limitations on Powers of Government
- The constitution establishes limits on the actions that government can take against its citizens.
- The constitution establishes basic rights that the government cannot violate, like protection against unfair arrests and guarantees of freedoms such as speech and association.
- However, these rights can be limited during national emergencies. By setting these fundamental rights, the constitution keeps government actions in check, protecting citizens' freedoms.
- Even a legally elected government might create laws that seem unfair, so limits on its power are important. Fundamental rights act as a shield for citizens, ensuring their freedoms are safe from government overreach.
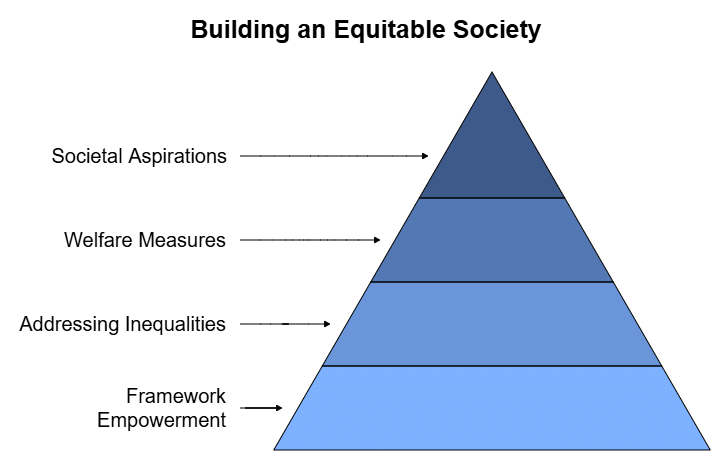
Aspirations and Goals of Society
- The constitution outlines a structure for the government to achieve the positive goals and aspirations of society.
- In societies with deep-rooted inequalities, there must be limits on government power, while also allowing the government to take constructive steps to address these inequalities or deprivations.
- These principles are included in the section on Fundamental Rights. The Directive Principles of State Policy also urge the government to realise certain aspirations of the people.
- The Indian Constitution was notably innovative in this regard. Modern constitutions like India’s aim to create conditions for a just and equitable society, reflecting societal aspirations. They are not just rules controlling government powers; they also empower the government to work for the common good.
- The framers of the Indian Constitution believed that every individual should have what is necessary to lead a life of basic dignity and social self-respect.
Fundamental Identity of People
- The constitution shows the fundamental identity of a people by establishing norms and principles that define their core political identity.
- It reflects the distinct historical traditions and various groups within a nation, while also promoting democratic governance and safeguarding basic rights.
- While constitutions differ in their types of government and procedures, they often include common elements like democratic governance.
- The Indian Constitution does not focus on ethnic identity for citizenship, representing a different idea of national identity compared to countries like Germany.
- A collective identity of the people is formed through the basic constitution, which is based on a shared agreement about governance and who is governed.
- Constitutional norms provide the main framework within which individuals pursue their aspirations, goals, and freedoms.
- The relationship between various regions of a nation and its central government shapes the national identity of the country.
 Functions of a Constitution
Functions of a Constitution
The Authority of a Constitution

- The authority of a constitution comes from its status as the highest legal authority in a country. It sets the rules for how the government operates and protects individual rights and freedoms.
- In many nations, the 'Constitution' is a concise document that includes several articles detailing how the state is structured and the principles it follows.
- The constitution outlines who has the power to make decisions within a society, determining the structure of the government.
- However, many constitutions exist only as written documents and may not be effectively implemented. The key question is: how effective is a constitution? What factors contribute to its effectiveness? This depends on various elements.
Mode of promulgation
The mode of promulgation means to how a constitution comes into being and who crafted it.
- Constitutions may become ineffective if they are established by unpopular leaders who cannot connect with the public. The most effective constitutions, such as those of India, South Africa, and the United States, were developed following significant national movements.
- India’s Constitution was crafted by a Constituent Assembly between December 1946 and November 1949, influenced by the nationalist movement.
- The Constitution gained significant legitimacy because it was created by individuals who had strong public credibility and could negotiate well, earning respect from various segments of society. These framers assured the public that the constitution represented a national consensus rather than personal interests.
- Although the Indian Constitution was never put to a referendum, it still held great public authority, as it was supported by popular leaders. The people accepted it as their own by adhering to its provisions.
- Thus, the authority of those who establish the constitution plays a crucial role in determining its success.
 Debate over Constitution making in Nepal
Debate over Constitution making in Nepal
The substantive provisions of a constitution
- A successful constitution ensures that everyone in society has a reason to support it. If a constitution allows majorities to oppress minorities, those minorities will not want to follow it.
- A constitution that favors some members over others or strengthens the power of a small group will lose support. If any group feels their identity is being suppressed, they won’t abide by it.
- While no constitution achieves perfect justice on its own, it must convince people that it offers a basis for basic justice.
- Thought experiment: Think about what basic rules would make everyone willing to follow them. The more a constitution preserves freedom and equality for all its members, the more likely it is to succeed.
- The Indian Constitution generally provides a reason for everyone to follow its guidelines.
Balanced Institutional design
Constitutions are often undermined by small groups trying to increase their own power, rather than by the general public. Well-designed constitutions fragment power to prevent any single group from dominating.
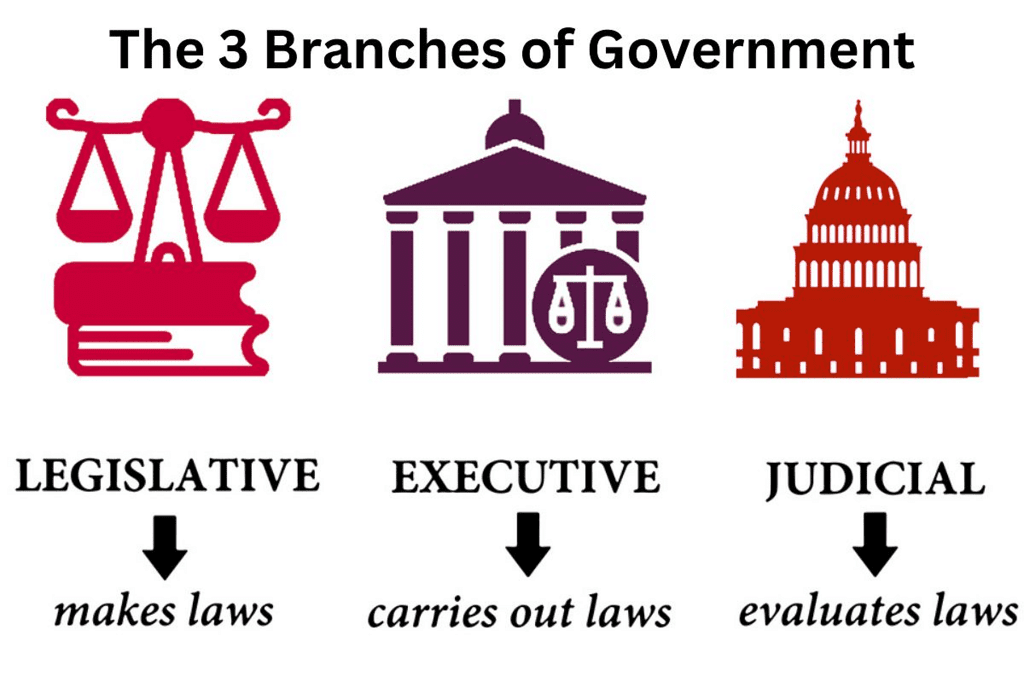
The Indian Constitution divides power among the Legislature, Executive, Judiciary, and bodies like the Election Commission, ensuring checks and balances.
A successful constitution balances core values with the ability to adapt to change, avoiding extremes of being too rigid or too flexible.
The Indian Constitution is a living document, allowing changes while maintaining respect and stability.
To evaluate a constitution's authority, consider the credibility of its framers, the organization of power, and whether it provides reasons for everyone to follow it.
 Authority of a Constitution
Authority of a Constitution
How was the Indian Constitution made?
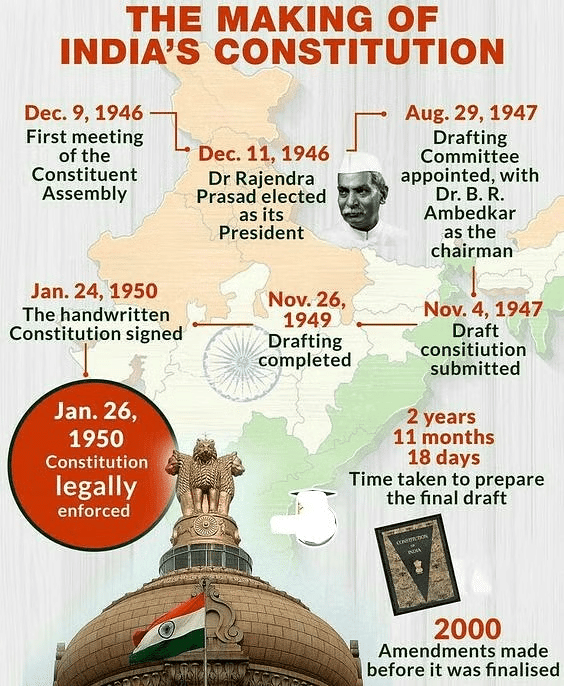
- The Constitution of India was created by a Constituent Assembly elected for undivided India, and was guided by the British Cabinet Mission (1946).
- Seats in the Assembly were allocated based on population, with a ratio of roughly 1 seat per 10 lakh (10,00,000) people.
- This resulted in 292 members from the provinces and a minimum of 93 seats for princely states.
- Seats within each province were divided among the main communities—Muslim, Sikh, and General—in proportion to their populations.
- The method for selecting representatives from princely states was decided through consultation.
Composition of the Constituent Assembly

- After the Partition on June 3, 1947, members elected from territories that became Pakistan were removed from the Constituent Assembly, reducing its number to 299.
- The Constitution was adopted on November 26, 1949, with 284 members signing it on January 24, 1950. It officially came into force on January 26, 1950.
- The Constitution was created amid the violence of Partition, but the framers managed to draft it under great pressure and learned from the chaos.
- It established a new idea of citizenship where minorities were protected, and religious identity did not affect citizenship rights.
- Although the Constituent Assembly was not elected by universal suffrage, efforts were made to ensure it was representative, with members from all religions and twenty-eight members from the Scheduled Castes.
- The Congress Party dominated the Assembly, holding eighty-two percent of the seats post-Partition, and was diverse enough to include a range of opinions.
The Principle of Deliberation
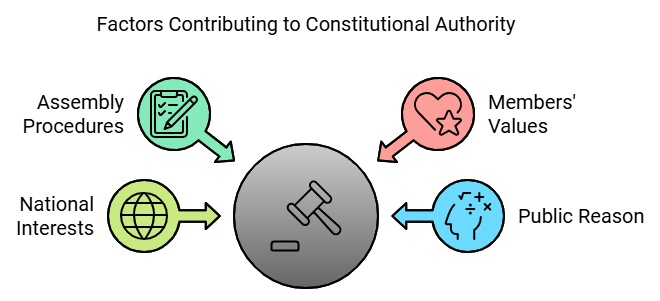
- The authority of the Constituent Assembly comes not just from its broad representation but from its procedures and the values of its members.
- While diverse representation is important, members also considered the nation's overall interests rather than just their own communities.
- The Assembly faced disagreements on key issues like centralization versus decentralization, state and central relations, judicial powers, and property rights. However, most debates were not about personal interests but about principles.
- The only provision passed with minimal debate was universal suffrage, which granted voting rights to all citizens regardless of religion, caste, gender, or income.
- The Constitution gained authority from the Assembly's commitment to public reason. Members focused on discussion and reasoned argument, offering principled reasons rather than personal interests.
- The extensive debates in the Assembly, scrutinizing every clause, are a testament to public reason and are considered as significant as the French and American revolutions in the history of constitution making.
Procedures
- The importance of public reason was evident in the procedures of the Assembly.
- The Constituent Assembly had eight major committees chaired by figures like Jawaharlal Nehru, Rajendra Prasad, Sardar Patel, and B.R. Ambedkar. Despite their differences—Ambedkar's criticism of the Congress and Gandhi, and Patel and Nehru's disagreements—they worked together effectively.
- Each committee drafted specific Constitution provisions, which were then debated by the entire Assembly.
- The aim was to reach a consensus to ensure that the provisions would not harm any particular interests.
- Some provisions were put to a vote, but every argument or concern was addressed carefully and in writing.
- The Assembly met for 166 days over nearly three years, with sessions open to the press and the public.
Inheritance of the Nationalist Movement

- No constitution is merely the result of the Assembly that drafts it.
- The Constituent Assembly of India could not have functioned effectively without a background consensus on the core principles the Constitution should embody.
- These principles were shaped during the long struggle for freedom.
- The Assembly was essentially giving concrete shape to the principles inherited from the nationalist movement.
- For decades before the Constitution was enacted, the nationalist movement debated crucial questions about the form of government, values, and inequalities that needed addressing. The answers developed from these debates were finalized in the Constitution.
- The Objective Resolution of 1946, moved by Jawaharlal Nehru, best summarizes the principles brought to the Assembly.
- This resolution reflected the aspirations and values behind the Constitution and inspired its substantive provisions.
- The Constitution institutionalized fundamental commitments such as equality, liberty, democracy, sovereignty, and a cosmopolitan identity.
- Thus, it represents not just a set of rules but a moral commitment to establish a government that fulfills the promises made by the nationalist movement.
Institutional arrangements
- The third factor in ensuring the effectiveness of a constitution is a balanced arrangement of government institutions.
- A key principle is that the government must be democratic and focused on the welfare of the people.
- The Constituent Assembly carefully balanced the roles of the executive, legislature, and judiciary, leading to the adoption of a parliamentary system and a federal structure.
- This setup distributes powers between the States and the central government, as well as between the legislature and the executive.
- In creating this balance, the framers of the Constitution learned from the experiences of other countries.
- They borrowed provisions from various constitutional traditions, but these ideas were adapted to suit Indian needs and aspirations.
- Rather than simply imitating, the Assembly thoughtfully integrated the best practices from around the world, ensuring that each provision was relevant to India's unique context.
Conclusion
The authority and effectiveness of a constitution come from its ability to balance power, adapt to change, and embody the core values and aspirations of society. The Indian Constitution, crafted with public credibility and broad consensus, provides a robust framework for justice, equality, and governance, demonstrating why a well-structured constitution is vital for any nation.
|
43 videos|278 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Constitution: Why and How? Class 11 Political Science
| 1. Why is a constitution necessary for a country? |  |
| 2. How was the Indian Constitution created? |  |
| 3. What was the role of the Nationalist Movement in shaping the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How did the principle of deliberation influence the making of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. What are the institutional arrangements outlined in the Indian Constitution? |  |

















