Crashing of Networks | Construction Materials & Management - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Crashing an activity (Crashing the network)
Reducing the time required to complete an activity (in hopes that this will reduce the completion time of the entire project) by assigning additional resources to that activity but reducing the duration time of the activities on the critical path may change the critical path.
- Normal time (NT): the expected time to complete an activity
- Normal cost (NC): the cost to complete the activity in its normal time
- Crash time (CT): the shortest possible time in which the activity can be completed
- Crash cost (CC): the cost to complete the activity in the shortest possible time (i.e., the cost to complete the activity in its crash time)
- Crash cost per time period = (CC - NC) / (NT - CT)
Approaches to crashing a project network
1. Minimum-time schedule" method
- use the normal times for each activity to determine the critical path.
- Crash every activity from its normal time to its crash time (minimum duration time) - this gives the minimum-time schedule.
If you must make the minimum time but want to reduce the cost, you can un-crash activities that aren't critical, beginning with the most expensive ones.
2. "Minimum cost schedule" method
- use the normal times for each activity to determine the critical path
- crash the activity on the critical path that has the lowest cost to crash per unit time, until the activity duration time cannot be reduced any further; or another path becomes critical; or the additional costs of crashing outweigh savings from crashing
- repeat step 2 until the cost of continuing to crash the project is greater than the savings from crashing
- when there is more than one critical path, it may be necessary to crash an activity on each path simultaneously. If so, select the activities that give the lowest total cost per unit time.
Example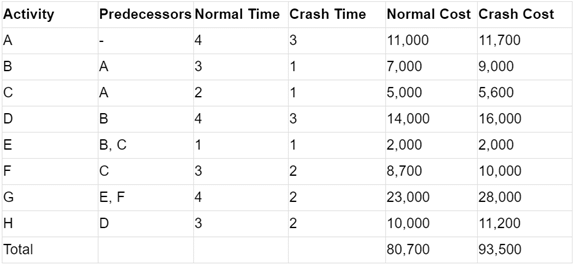
Project Planning with Uncertain Activity Time
Generally, the distribution of the activity times is unknown and must be estimated. A typical method of dealing with the situation is to estimate three activity duration times for each activity, optimistic, most likely and pessimistic. Use these estimates to estimate a normally distributed activity time:
Most optimistic time (a): the probability of completing the activity in less than a is about 1%
Most likely time (m): the estimated average time required to complete the activity.
Most pessimistic time (b): the probability of taking longer than b is about 1%
The activity time is assumed to be normally distributed with mean, te, and variance as follows:
Expected time: te = ( a + 4m + b ) / 6
Variance: var[te] = [ ( b - a) / 6 ]2
Assumptions
- Duration of activities along the critical path determine project completion time
- Duration time of one activity is independent of duration times of all other activities. Using the Central Limit Theorem, the project completion time is assumed to be normally distributed with the mean equal to the sum of the activity times on the critical path. The variance is equal to the sum of the variances of the activities on the critical path.
Once the mean and standard deviation of the critical path is known, it is possible to calculate the probability of completing the project in a certain time.
If a project has two critical paths, the critical path with the largest variance should be used to calculate the probability that the project will be completed within a certain time.
Note: Only considering the critical path makes a very strong assumption. In real situations, you should be aware of the other paths which may become critical. If an activity not on the critical path has a large variance of a duration time, that activity can become a critical path activity simply through random occurrences.
Cost Model Analysis
In the whole of the CPM Cost Model, we will be assuming that project duration is reduced by deploying more resources on critical activities.
1. Project Cost
Total Project cost is the sum of two separate costs the direct cost for accomplishing the work, and the indirect cost related to the control or direction of that work, financial overhead, lost production, and the hike.
The components of the total cost are depicted in figure
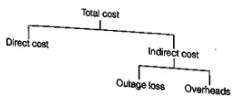
2. Components of Project cost
- Indirect Project Cost: Indirect costs on a project are those expenditures that cannot be apportioned or clearly allocated to the individual activities of a project but are assessed as a whole.
The indirect cost rises with increased duration.
The total indirect cost curve will thus be curved.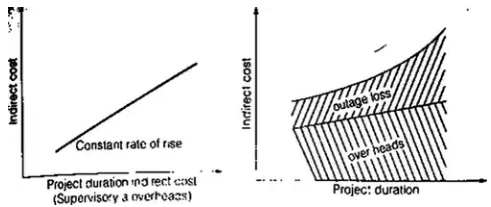
- Direct Project Cost: These include labour cost, material cost, equipment cost etc.
(i) Normal time (in): Normal time is the standard time that an estimator would usually allow for an activity.
(ii) Crash time (tc): Crash time is the minimum possible time to complete an activity by employing extra resources. Crash Time is that time beyond which any amount of increase in resources cannot shorten the activity.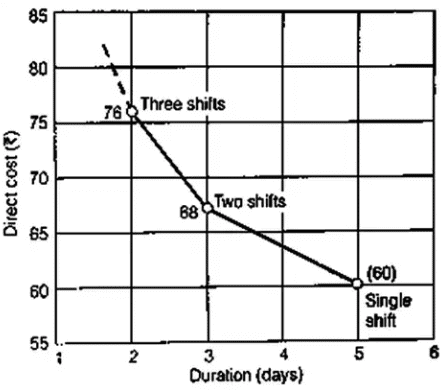
- Normal cost (Cn): This is the direct cost required to complete the activity in normal time duration.
- Crash cost (Cc): This is the direct cost corresponding to the completion of the activity within crash time.
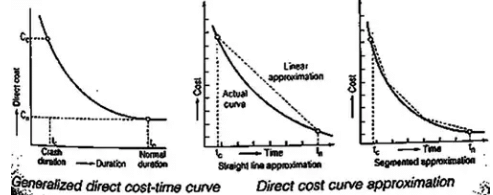 The straight line or segmented approximation of the direct cost curve is helpful in carrying out the project cost analysis. In such analysis, the cost slope is used.
The straight line or segmented approximation of the direct cost curve is helpful in carrying out the project cost analysis. In such analysis, the cost slope is used. - Cost Slope: The cost slope is the slope of the direct cost curve, approximated as a straight line. It is defined as follows:
- Cost Slope = Crash Cost - Normal Cost/Normal Time - Crash Time
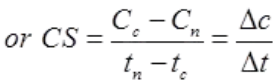
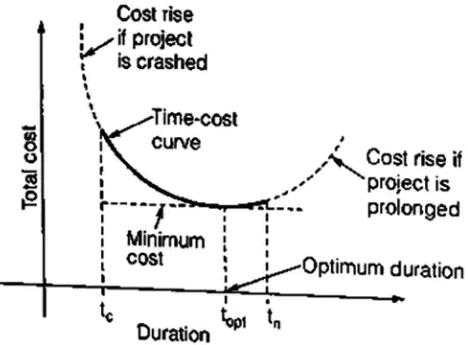
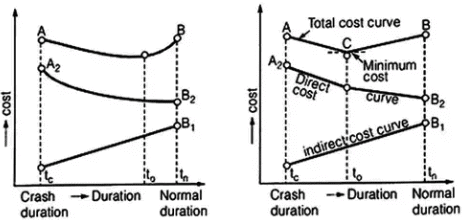
- Total Project Cost and Optimum Duration: The total project cost is the sum of the direct cost and indirect costs.
We find that the minimum total cost is obtained at some duration known as the optimum duration. The corresponding cost is known as the minimum cost. If the project duration is increased, the total cost will increase, while if project duration is decreased to the crash value, the project cost will be the highest.
|
5 videos|29 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Crashing of Networks - Construction Materials & Management - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is network crashing in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How does network crashing affect project completion time? |  |
| 3. What are the potential risks associated with network crashing in civil engineering projects? |  |
| 4. How can civil engineers determine which activities to crash in a network? |  |
| 5. What are the common techniques used for network crashing in civil engineering? |  |
















