Cyber Ethics: Short Answer Type Questions | Computer Application: Class 10 PDF Download
Q.1. What is software license? (2 Marks)
Ans: A software license is a legal document that describes the legal rights pertaining to the authorized use or redistribution of software. It defines the responsibilities of the parties entering into the license agreement and may impose restrictions on how the software can be used.
Q.2. Write a short note on DRM. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a systematic approach to copyright protection for digital media. The purpose of DRM is to prevent unauthorized redistribution of digital media and restrict the ways consumers can copy content they’ve purchased.
- Digital rights refers to the relationship between copyrighted digital works (such as film, music and art) and user permissions and rights related to computers, networks and electronic devices.
- Digital rights also refers to the access and control of digital information. The definition of digital rights and responsibilities is having the right and freedom to use all types of digital technology while using the technology in an acceptable and appropriate manner. As a user of digital technology, you also have the right to privacy and the freedom of personal expression.
Q.3. What is open source software? (2 Marks)
Ans: Open source software is a software that any programmer can download from the internet free and modify with suggested improvements. The changes must be made available to all. Any programmer can make improvements, which can result in better quality software
Example: Firefox web browser, Linux OS etc.
Q.4. Can we use open source software (OSS) for all organisations? (2 Marks)
OR
What are the disadvantages of open source software? (2 Marks)
Ans: The open source software:
- May not provide long term support
- May not be secure enough
- May not be scalable
So, they cannot be recommended for all organizations. Though, OSS software suite (LAMP – Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP) can be used even for military organisations as they have community-development groups, security and scalability.
Q.5. What is proprietary software? (2 Marks)
Ans: Proprietary softwares are commercial or packaged softwares, It is copyrighted software that prohibits the redistribution or modification of its program.
Example: Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop etc.
Q.6. Kuhu has just learnt how to do online banking. Name any two precautions that she should take to prevent online fraud. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Do not share user id and password with anyone.
- Avoid doing transactions from cyber cafe and other public places.
Detailed Answer:
- Use bigger and strong password.
- Do not use predictable passwords like mobile number, date of birth.
Q.7. What is freedom of information? (2 Marks)
Ans: Freedom of information refers to a citizen’s right to access information that is held by the government. The right to information is a fundamental right. It helps in creating a more open and democratic society, challenging corruption and enhancing transparency.
Q.8. What is free open source software movement? (2 Marks)
Ans: Free/open-source software movement (FOSSM) or free/libre open-source software movement (FLOSSM) is a social movement with the goal of obtaining and guaranteeing certain freedoms for software users, namely the freedom to run the software, to study and change the software, and to redistribute copies with or without changes. Richard Stallman formally founded the movement in 1983 by launching the GNU Project. Stallman, later established the Free Software Foundation in 1985 to support the movement.
Q.9. What are digital property rights? (2 Marks)
Ans: Digital property rights includes data, internet accounts and other rights in the digital world. Intellectual property rights can also exist in digital property such as pictures, music, movies, literary works, web pages, computer code. It refers to access and control of digital information.
Q.10. What do you mean by e-Commerce? How has it benefitted the customer? (2 Marks)
Ans: e-Commerce is the ability to do business online via internet. Consumers no longer need to travel to shops or stores to get their daily needs. All they have to do in browse through the Internet and purchase the product needed using their computer connected to the Internet and save their time and energy.
Q.11. What is online fraud? (2 Marks)
Ans: Fraud committed using the Internet is called online fraud.
Online fraud may occur in many forms such as:
- Non-delivered goods
- Stealing information
- Fraudulent payments
- Non-existent companies
Q.12. Why is privacy important in e-Commerce? (2 Marks)
Ans: Privacy is the protection of personal information given online. The privacy of the users must be respected by ensuring that data collected is not sold to irresponsible parties. The merchant should also say clearly in terms and conditions about how the data will be used.
Q.13. What is secure data transmission? (2 Marks)
Ans: Secure data transmission means applying enough technical safeguards so that the data travels safely to its target, without being compromised or eavesdropped.
Some techniques are:
(i) SSL secure data transmission
(ii) Data encryption
(iii) Using safe protocols e.g. SFTP
Q.14. What is digital signature? (2 Marks)
Ans: A digital signature is a digital code that can be authenticated through encryption and password attached to an electronically transmitted message to uniquely identify the sender. Digital signatures enable the recipient of the information to verify the authenticity of the information’s origin, and also verify that the information is intact.
Q.15. Define Plagiarism? (2 Marks)
Ans: Plagiarism is the wrongful appropriation and stealing the publication of another author’s language, thoughts, ideas as one’s own original work. It is considered as an academic dishonesty and a breach of journalistic ethics. It is an act of fraud.
Q.16. What is cryptography? (2 Marks)
Ans: Cryptography is a technology which keeps the messages secret from unauthorized access. Sender of the information encrypts the data using a secret code and only the specified receiver can decrypt the data using the same or a different secret code.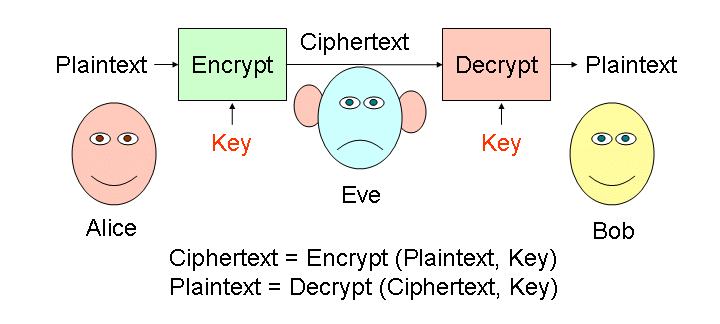 To encrypt a message, the message is passed to an algorithm that transforms the message using a key into a meaningless script called cryptogram or ciphertext. The ciphertext can be sent to the intended recipient. The recipient has a key to decrypt the ciphertext back to the original message.
To encrypt a message, the message is passed to an algorithm that transforms the message using a key into a meaningless script called cryptogram or ciphertext. The ciphertext can be sent to the intended recipient. The recipient has a key to decrypt the ciphertext back to the original message.
|
11 videos|49 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Cyber Ethics: Short Answer Type Questions - Computer Application: Class 10
| 1. What is cyber ethics? |  |
| 2. Why is cyber ethics important? |  |
| 3. What are some common cyber ethics violations? |  |
| 4. How can individuals practice cyber ethics? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of not following cyber ethics? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















