D/A and A/D Convertors | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
D/A converters change digital signals into analog signals.
Digital Data:
- Values that are evenly spaced and distinct.
- Happen at specific times and have specific amounts.
Analog Data (Natural Events):
- A wide range of continuous values.
- Continuously happening over time, with no breaks.
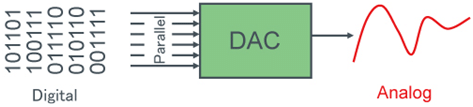
Basic Operation of a D/A Converter
- A D/A converter takes a specific number (usually a fixed-point binary number) and changes it into something physical, like voltage or pressure. We use D/A converters when we want to turn data that's in fixed steps into a smooth, continuous signal.
- An ideal D/A converter takes numbers from a series of impulses and fills in the gaps between them using a method called interpolation. In simpler terms, a regular D/A converter turns these numbers into a series of blocks, almost like building a signal with Legos, and this is often represented by what's called a zero-order hold.
- The job of a D/A converter is to rebuild the original signal with a certain level of accuracy. When we turn something into digital data (like when we take a photo), there can be tiny errors in the process. These errors create a type of quiet background noise in the final reconstructed signal. The smallest amount of change that can happen in the digital signal is called the Least Significant Bit (LSB). The difference between the original signal and the digital version is called quantization error.
Applications of D/A Converters
D/A converters are used in:
- Digital Audio: CDs, MiniDiscs, 1-bit audio
- Digital Video: DVDs, Digital Cameras
- Communication Gear: Smartphones, fax machines, ADSL devices (internet connection gear)
- Computers: Audio cards, video cards
- Instruments: Devices that control power, among others.
Analog to Digital Converters (A/D Converters)
An A/D converter changes analog signals (usually voltage) from things in the world into digital signals.
This process has different steps, like sampling (taking regular measurements), quantization (assigning digital values to measurements), and coding (putting the digital values into a form that a computer can understand).
Basic Operation of an A/D Converter
The A/D converter takes the analog signal and chops it up into pieces at specific moments. These pieces are then turned into digital values. The "resolution" of an A/D converter tells us how many different values it can make from a range of analog ones, usually shown by the number of bits. For example, in a 3-bit A/D converter, the highest value (b2) is called the Most Significant Bit (MSB) and the lowest (b0) is the Least Significant Bit (LSB).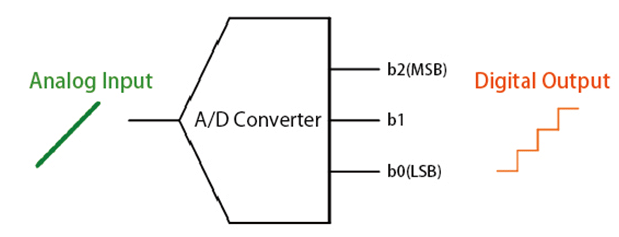
The graph below shows how the analog input relates to the digital output.
The first change in the digital signal (from 000 to 001) below 0.5 LSB is called the zero scale, while the last change (from 110 to 111) is called the full scale. The space between zero and full scale is the full scale range.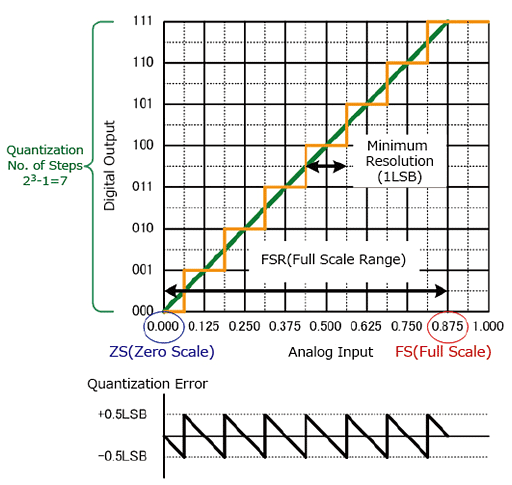
How We Turn Analog to Digital
Sampling:
- Sampling means taking the values of the analog signal at specific times (sampling period Ts).
- [Sampling Period Ts = 1/Fs (Sampling Frequency)]
- We use a Sample and Hold (S&H) circuit to do this.
Quantization:
- Quantization gives each sampled value a number from a range of possible values covering the whole range of the signal (based on the number of bits).
- [Quantization error: Sampled Value - Quantized Value]
Coding:
Once we have the numbers, we turn them into binary using an Encoder.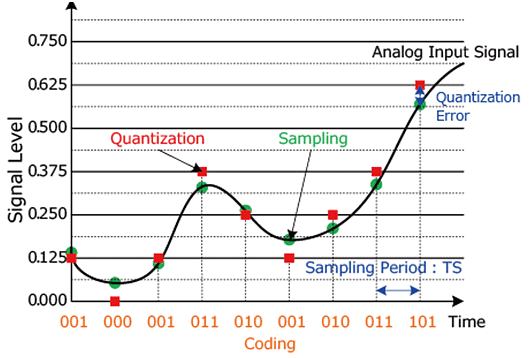
Applications of A/D Converters
A/D converters are used in:
- Digital Audio: Recording music, making digital music, pulse-code modulation (a way to change analog audio into digital)
- Digital Signal Processing: TV cards, small computers (microcontrollers), digital oscilloscopes (tools to measure electronic signals)
- Scientific Tools: Cameras, radar systems, temperature sensors
Requirements for A/D and D/A Converters
- Modern computers and digital signal processors (CPUs and DSPs) handle the electrical work needed for A/D and D/A conversion.
- Here's how it works: first, natural events are turned into digital signals using an A/D converter. Then, they can be processed digitally. Finally, if we need them as analog signals again, we use a D/A converter to change them back.
- Advances in Making Tiny Circuits→Using Signals Digitally →We need A/D and D/A converters.

|
135 videos|181 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on D/A and A/D Convertors - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. How does a D/A converter work? |  |
| 2. What are some common applications of D/A converters? |  |
| 3. What is the basic operation of an A/D converter? |  |
| 4. How do we turn analog signals into digital signals? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of A/D converters? |  |
















