General Organic Chemistry
HOMOLYTIC BOND FISSION HOMOLYSIS
The bond cleavage in which each bonded atom gets their own contribution
Cleavage takes place due to
HELP (H = Heat, E = Electricity, L = light, P = Peroxide)
Favoured when E.N. difference is less or zero.
Cleavage favoured in non polar solvent.
Hetrolytic Bond fission
It is formed when the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is more
formation is favoured by polar solvent
ve charge of the solvent attracts the -ve pole of compound and the -ve pole of the solvent attracts ve pole of compound and the bond breaks.
Intermediates of organic compounds
Free Radical Carbocation Carbanion
(1) Lone pair 0 0 1
(2) Bond pair 3 3 3
(3) Unpaired e- 1 × ×
(4) Bond Angle 120º 120º 107º
(5) Hybridisation sp2 sp2 sp3
(6) Shape Trigonal planer Trigonal planer Pyramidal
(7) Magnetic property Paramagnetic Diamagnetic Diamagnetic
(8) Stability order 3º > 2º > 1º 3º > 2º > 1º 1º > 2º > 3º
(As per inductive effect)
(9) e- rich/deficient/poor ED(Deficient) ED ER(Rich)
(10) Reactivity order 1º > 2º > 3º 1º > 2º > 3º 3º > 2º > 1º
(11) +I/-I (stablized) +I +I -I
Electronic Displacement Effect
The displacement of electrons within the same molecule is known as electronic displacement. These effects affect the stability of a species or compound and it also affect the acidic & basic strength.
Electronic Displacement Effect is divided into two parts:-
(1) Permanent effect
(2) Temporary effect
(1) Permanent effect
(i) Inductive effect
(ii) Mesomeric (resonance) effect
(iii) Hyperconjugation
(2) Temporary effect:
(i) Electromeric effect
(ii) Inductomeric effect
(i) Inductive effect:
It is an effect in which permanent polarisation arises due to partial displacement of s-electrons along carbon chain or partial displacement of sigma-bonded electron toward more electronegative atom in carbon chain.
Magnitude of partial positive charge
d1 > d2 > d3 = d- (net charge remain constant in a molecule having inductive effect)
Inductive effect
It is a permanent effect
(-I effect of X)
if X i.e more electronegative
(After carbon No. 3 the effect disappears)
( I effect of Y)
* (- I effect order)
* O- < O < O (-I effect order)
It is a permanent effect
It is caused due to electronegative difference.
It operates via s bonded electron.
It is distance dependent effect.
As distance increases, its effect decreases.
It can be negalected after third carbon.
It is a destablising effect.
It is divided into 2 parts. (On the basis of electronegativity w.r.t. hydrogen atom)
(1) + I effect
(2) - I effect
If any atom or group having electronegativity greater than that of hydrogen. than it is considered as - I effect and vice-versa.
+I effect - I effect
(i) e- releasing group (i) e- accepting group
(ii) EN less than H (ii) EN greater than H
(iii) Those group which are (iii) Those group showing -I effect
showing I effect, disperses disperses ve charge on the C-chain
partial - ve charge on the C-chain
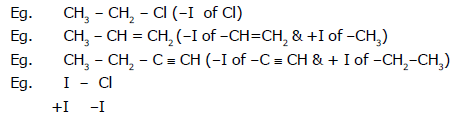
Eg. CH2 = CH (-I of -ph)
Order of -I effect showing group:
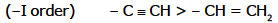
Order of I effect showing group
Bond Strength : CT3 > CD3 > CH3 (+I of T > D > H)
Q. Why carbon - hydrogen bond is longer than C - T bond
Ans. As the mass increases, vibration decreases as a result of which the heavier isotope will be more closer to the C-atom for a longer time. Therefore C - T bond is stronger C - T > C - D > C - H
Which implies that C - H bond has longest bond
Application of inductive effect
To compare the stability of intermediates.
Intermediates
These are real separable species having measurable stability formed during coversion of reactant to produ ct. (After bond cleavage and before bond formation).
6 types of intermediates:
(i) Free radical (ii) Carbocation (iii) Carbanion
(iv) Carbene (v) Nitrene (vi) Benzyne
They are formed by homolytical and heterolytical cleavage.
Mesomeric Effect (Resonance effect)
Mesomeric effect is valid only for conjugated system.
Types
1 M effect ( R)
2 - M Effect (-R)
* Consider the following conjugated system
* Consider another conjugated system
Mesomeric effect in phenol ( M effect)
M effect in aniline
If the movement of e- is towards ring → ( M effect)
→ This effect increases the electron density over benzene ring.
* -M effect in Benzaldehyde
→
Ex.23 Idenfity the compound showing M or -M seperately
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. (a) (-M) (b) (-M) (c) +M
* M group increases electron density of ring while - M decreases the electron density of benzene ring.
* if NO2 is present on the ortho or para position then along with its -I effect, It will also show -M effect.
* Above compound have M of -OH and -M of NO2 group.
as we can easily see that -NO2 at meta position is not attracting e- density towards it self and that's why it will not show -M effect at m-position
Resonance
Delocalisation of p-electrons in conjugation is known as resonance.
(Actual Structure)
(resonating structures) (Resonance hybrid)
in this form
Condition for showing resonance
1. Molecule should be planer, nearly planer or a part of it is planar
Q.1 Which are planer
(A) (B)
*(C)
*(D)
Because all carbon atoms are sp2 hybridised.
2. Molecule should posses conjugated system.
Conjugated system :-
Continuous unhybridised p-orbital parallel to each-other.
Types of conjugated system:-
(1) p-bond alternate to p-bond
CH2 = CH - CH = CH2
(2) p-bond alternate to charge
CH2 = CH - CH2
Eg.
Eg.
Eg.
(4)
(5)
(6) CH2 = CH - BH2
(7)
1. Resonance takes place due to delocalization of p e-.
(a) Resonance (b)
Resonance absent
(c) Resonance (d)
Resonance
2. Position of the atoms remains the same, only delocalization of p e- takes place.
Note:- [They are not resonating structure rather they are tautomer]
3. Bond pair get converted into lone pair and l.p. get converted into b.p.
4. In Resonance No. of unpaired e- remains the same
CH2 = CH - CH = CH2
(They are not resonating structure)
Resonating structure :
(1) Hypothetical strtucture exist on paper
(2) The energy difference b/w different resonating structure is very small.
(3) All R. S. contribute twoards the formation of resonance hybrid (Their contribution may different)
(4) A single R. S. Can't explain each & every property of that particular compound
Draw the resonating structures : -
Q.1
Q.2 -m of NO2 group
Resonance hybrid : -
It is a real structure which explain all the properties of a compound, formed by the contribution of different R. S.. It has got maximum stability as compared R. S.
Resonance Energy : -
It is the diffrence b/w theoretical value of H.O.H & experimental value.
Or
It is the difference b/w more stable R.S. & R. H.
* More the resonance energy, more stable will be the molecule.
* Cyclohexane is thermodynamically more stable than benzene, even though resonance energy of benzene is more.
* Resoance energy is a absolute term.
Contribution of different R. S. towards resoance hybrid
(1) Non-polar R. S. contribute more than polar R. S.
(a) CH2 = CH - CH = CH2 (b) CH2-CH = CH - CH2y (c) yCH2 - CH = CH - CH2
a > b = c stability
(2) Polar R. S. with complete octet will contribute more as compared with the one with incomplete octet
CH3 - CH - OCH3 CH3 - CH = :O - CH3
Incomplete octet Complete octet
(3) In polar R. S. The -ve charge should be on more electro - ve atom & ve charge should be on more electro ve atom
(a) (more stable )
(b) (less stable )
(4) Compound with more covalent bond will contribute more
(5) Unlike charges should be closer to each other whereas like charges should be isotated.
(6) Extended conjugation contribute more than cross conjugation.
<
Cross conjugation < Extended conjugation
Fries Rule :-
Compound with more benzenoid structure are more stable as their Resonance energy is greater than those in which lesser no. of benzenoid structure are present.
R. E. is <
* If double bond is participating in resonance then it will aquire partial single bond character as a result of which bond length increase & bond strength decreases.
If a single bond is involved in resonance then it will aquire partial doulbe bond character. As a result of which bond length decreases & bond strength increase.
Q.1
a = e > b = d > c
Q.2 (a) (b)
(c) (incomplete) (d)
(incomplete)
a > b > c > d
Q.3
Stability <
(back bonding)
Q.4 (a) (b) yCH2 - CH = F a > b (stability)
*
Note:-When lone pair as well as double bond is present in some atom. Then only p bond will participating resonance. Where as lone pair remains sp2 hybridised orbital.
When an atom has two or more then two lone pair then only one lone pair will participate in resonance and the other one remains in sp2 hybridised orbital.
Hyper conjugation
Permanent polarisation caused by displacement of s-electrons into p-molecular orbital is known as hyperconjugation
Hyper conjugation is called No bond Resonance
* More a C - H bond, more will be the no bond resonating structure (Hyper conjugation)
More a (C - H) bond, more will be the stability of free radical.
Properties of Free Radical
1. It is a neutral species.
2. It has one upaired electron that's why paramagnetic in nature.
Structure :
→ methyl free Radical
→ ethyl free radical
3. its hydridisation is sp2 and triangular planer shape.
Note : unpaired electron is not counted while calculating the hybridisation state.
(unpaired electron stay perpendicular to the plane)
Stability of free Radical :
Its stability can be determined with the help of hyperconjugation as well as Resonance effect
Allylic Free Radical
(Free Radical is on next carbon to doubly bonded carbon atoms)
Effect of Resonance > Hyper conjugation
Benzylic Free Radical
* More Resonating structure, more will be the stability of the free Radical.
(di-benzylic free Radical)
No. of Resonating structure = 7
(Tri-benzylic free Radical)
No. of Resonating structure = 10
Stability Order :
Ex.1 Compare the stability of the following free Radical.
(a) (b) (c)
Sol. (a) will be most stable due to hyper conjugation.
Between and
→ more s-character
→ more electronegative
→ e- density maximum
→ more repulsion
→ less stable
Ans. a > b > c
* More repulsion, less stability
Ex.2 Compare the stability of the following free Radicals
(a)
(b)
(c)
(Therefore this resonating structure is not possible)
Sol. b > a > c
Ex.3 (a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Compare the bond energy of the above compounds.
Sol. After forming free radical from the compound
(3°) (2°) (1°) methyl free radical
(a) (b) (c) (d)

*
*
Ex.4 Compare the potential energy of the following compounds (above compounds)
Sol. If compound after being in free Radical form is very stable (i.e., less energy) it mean it would have possessed more energy initially i.e. it potential energy will be most
a < b < c < d
* Potential energy ≈ stability of free Radical
Ex.5 Compare the bond energies of C - H bond
(at a, b, c, d, e and f position)
e > b > a > f > c = d
Stability order of free Radical that might be formed after removal of H (Homolytically) from the given carbon.
→ e < b < a < f < c = d
(C - H bond energies)
In the above compound while comparing 2° benzylic allylic stability at two given position
while drawing the resonating structure of the
(Here inspite of Resonace three a(C - H) bond are available for no bond Resonance.
→ Therefore extra stable than which have only two a (C - H) bond for Hyper conjugation.
Therefore 2° benzylic allylic corresponding to structure (a) is more stable than that of structure (b)
Ex.6 Compare the stability of the following free Radical
Sol.
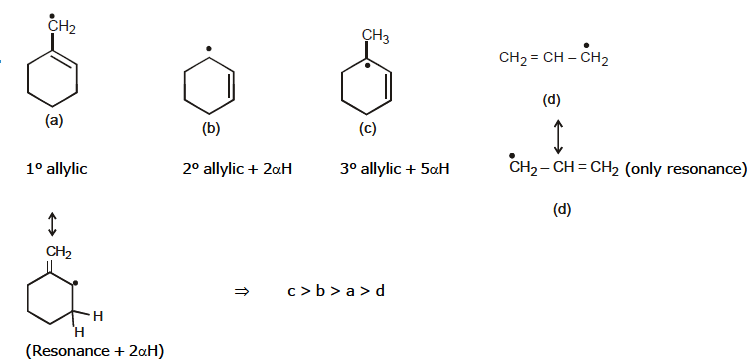
Ex.7 Compare the potential energy of CH3 - CH3, CH2 = CH2, 
Sol. After making free Radical of the above compounds
,
a > b > c
Carbocation
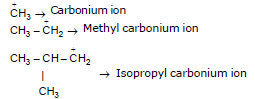
Properties of Carbocation :
1. it is positivly charged species
2. it has sixtet of electrons i.e. diamanetic
3. it is formed by heterolysis
4. it is generally formed due to polar solvent
Structure :
(sp2) Triangular planer
Stability :
Its stability can be determined with the help of Inductive effect, Hyper conjugation and Resonance effect.
Stability of Carbocation :
<
Stability of carbocation can also be determined by Hyper conjugation (no bond Resonance)
9 α C - H bond 6αC - H bond 3α C - H bond
Allylic Carbocation
Benzylic Carbocation
Ex.8 Compare the stability of th following carbocation
(a) (b)
(c)
→ more s charactor
→ more electronegativity
→ ve charge on more electronegative element is symbol of unstability.
a > b > c
Ex.9 Compare the stability of the following compounds
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. d > c > b > a
F being most electron attracting group decreases the e- density from positively charged C-atom and decreases the charge density and makes the carbocation less stable.
Ex.10 Compare the stability of the following carbocation :
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. due to greater size of Iodine, its L.P. will not be available for coordinate bond. Therefore L.P. would not stabilize corbocation.
In case of F due to its small size its lone pair can be easily coordinated to making it most stable
a > b > c > d (Stability)
* By coordination the carbocation completes its octet and structure having complete octet of its atom is supposed to be most stable.
(Each atom has its full octet)
*
Note : In Rasonating Structure of , at least one C gets sixtet of e- and hence less stable than coordinated compound.
Ex.11 Compare the stabilities of the following corbocation
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. N, O, F belongs to same period
→ In period Electronegativity of the atom is deciding factor
→ F being most electronegative, holds its e- pair very firmly.
→ Its L.P. will not be easily available for coordination.
→ Stability by it will be minimum.
a > b > c
Ex.12 Compare the following corbocation in order of their stability.
(a) (b)
Sol. If periods of atoms which have to donate their electrons for coordination (for stability) is different then atomic size will be deciding factor. The atom whose size is greater will be unable to make its e- pair available for coordination.
b > a
Ex.13 Compare the stability of the following compounds
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol → more s-character
→ more e.n.
→ attracts e-
→ reduces, stability
b > a > c
Carbanion
1. it is a -ve charged species 2. it has octet of electrons. 3. diamagnetic
Strucutre :
* if -ve charge is in Resonance then the hybridisation of carbanion is sp2(Triangular planer shape)
* If -ve charge is not in Resonance then the hybridisation of carbanion is sp3(pyramidal)
Stability :
Its stability can be determined with the help of
(1) Inductive effect
(2) Resonance effect
Ex.14
a > b (stability)
* Stability of the carbanion is as follows
Ex.15 Compare the stability of the following carbacation
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. c > a > b
Ex.16 Compare the stability of the following carbanion
(a) (b)
(c)
→ become more stable
Sol. b > a > c
Ex.17 Compare the stability of the following carbanion
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. a > b > c
Ex.18 Arrange the following anion order of their stability
(a) Cl-, (b) Br- (c) F- (d) I- (maximum size)
→ maximum dispersion of -ve charge
→ max stability
Sol. d > b > a > c
Ex.19 Compare the stability of the following
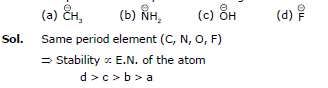
Ex.20 Compare the acidic strength
(a) HCl (b) HF (C) HBr (D) HI
Sol. Acidic strength ≈ stability of the anion formed (conjugate base)
as we know I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
→ H I > HBr > HCl > HF
Ex.21 Compare the Acidic strength of the following
(a) NH3 (b) pH3 (c) AsH3 (d) SbH3 (e) BiH3
Sol. Anion formed from there acids are
→ acidic strength e > d > c > b > a
Ex.22 Compare the acidic strength of the following comounds
CH4, NH3, H2O, HF
Sol. The conjugate base of the given acid is as follows
we have already proved that
>
>
>
(Stability)
→ HF > H2O > NH3 > CH4 (acidic strength)
Ex.24 Compare the stability of the following carbanion.
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. d > c > b > a
* M or -M is not distance dependent
Ex.25 compare the stability of the following carbocation
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. a > b > c > d
Ex.26 Compare the stability of the following carbocation.
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. M (OH) > M (OCH3)
b > c > d > a
Ex.27 Compare the stability of the following carbocation
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. c > a > b
Ex.28 Compare order of dehydration of the following alcohols :
(a) (b)
(c) C - C - C - OH
Sol. After formation of carbocation
,
Since 3° carbocation is most stable therefore it will show greatest tendency to lose water as after lose of water it comes in stable form.
Types of Reagent
1. Electrophilic reagent : All electron deficient atom or group of atoms is known as Electrophilic reagent, the electrophile attacks at the electron rich centre.
(a) all positively charged species are electrophile
H , NO2 , Br , Cl , etc.
(b) The compound in which the octet of central atom is not complete
BF3, AlCl3, ZnCl2, etc.
(c) all the compound in which the central atom can expand its octet
SnCl4, SiCl4, etc.
(d) all polarising functional group are electrophile as well as nuelophile
Nucleophile :
All electron rich compounds are nucleophile and attack at the electron deficient centre.
(a) all negatively charqed species
H-, Cl-, NO2-, Br-, CH3- etc.
(b) the compound in which the central atom has lone pair of electron.
NH3, H2O, ,
etc.
(c) all organometallic compounds are nucleophile
R - Mgx, RLi, R2Cd
(d) The compound having p e- density, CH2 = CH2, etc.
Nucleophilicity :
The power of nucleophile is known as nucleophilicity .
→ The nucleophilicity of negative charge is greater than the nucleophilicity of lone pair
→ If lone pair or -ve charge is present on the different atom then less electronegativity, more will be the nucleophilicity.
,
,
,
Nucleophilicity
→ NH3 < PH3 < AsH3 < SbH3 < BiH3 (Nucleophilicity)
→ If -ve charge or lone pair of electron is present on the same atom then the less stable -ve charge will be the better nucleophile
(nucleophilicity)
Activator & deactivator
The groups in benzene which show M effect or I effect Increases the electron density on benzene it means they activate the ring towards electrophile and known as activator.
,
, -CH3, -OR, -NHMe,
,
The groups which shows -M or -I effect (resultant) decreases the e- density from benzene ring. It means they deactivate the ring towards electrophile
,
,
,
,
,
,
etc.
Ortho, Para & meta director
The groups which shows +I (resultant) or +M effect then negative charge is developed at the ortho & para position. Therefore electrophile attack at the ortho & para position and the groups are known as OP director.
The groups which shows -M effect or - I effect (resultant) then ve charge is developed at the ortho & para position this means electron density is minimum at the ortho & para positions and electronphile will attack at the meta position the groups are known as meta director.
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
Heat of hydrogenation(H.O.H)
It is the amount of energy realeased when one mole of H2 is added to any unsaturated system.
CH2 = CH2 + H2 → CH3 - CH3 energy
HOH is exothermic process DH = - ve
*HOH ≈ No. of p-bonds in compound
If no. of p-bonds is same then
*HOH ≈
In case of alkene
**
Ex. a
b
c
b > c > a
Energy
Some examples of Arromatic(A), Non-arromatic(NA) and Anti-arromatic(AA)
(1) (A) (2)
(AA) (3)
(AA)
(4) (NA) (5)
(AA) (6)
(A)
(7) (A) (8)
(A)
(9) (A) (2pe) (10)
(A) (6pe) (11)
(NA)
(12) (NA) (13)
(AA) (4pe) (14)
(A)
(15) (NA) (16)
(A) (17)
(A)
(18) (AA) (19)
(A)
(20) (AA) (21)
(AA)
(22) (AA) (23)
(A) (24)
(A)
(25) (A) (26)
(A) (27)
(NA)
Acidity & Basicity
HA
Acid Conjugate base
Note : More stable the conjugate base (i.e., ), more will be the forward reaction which results more acidic nature of HA.
Ex.1 Compare the acidic strength of the following acids.
(a) C - C - C - COOH (b) C = C - C - COOH (c) 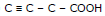
Sol. The acid whose conjugate base is most stable will be more acidic.
After forming conjugate base from the above acids.
(a) (b)
(c)
It is clear that sp hybridised carbon being most electronegative will decrease e-density from O most effectively making the conjugate base most stable.
c > b > a (acidic strength)
Ex.2 Which is more acidic between the two
(a) CHF3 (b) CHCl3
Sol. CHF3 > CHCl3
If we consider the -I effect of F and Cl But this effect will not be considered here
After the removal of proton
(a) (b)
(vacant d-orbital available where C will coordinate its electron) (pπ - dπ bonding)
→ a < b (acidic strength)
Ex.3 Compare the acidic strength of the following
(a) CHF3 (b) CHCl3
(c) CHBr3 (pπ - dπ bonding in Br is not as much as effective as in Cl due to large size of Br)
Sol. CHCl3 > CHBr3 > CHF3
Ex.4 Compare the acidic strength of the following
(a) CH (CN)3 (b) CH (NO2)3 (c) CHCl3
Sol. After removing H
(Resonance) In its resonating structure, -ve charge will be on N)
(Resonance) (- In its resonating structure -ve charge will reside on O
→ more effective Resonance
(pp - dp)
b > a > c
* -ve charge on O is more
stable than -ve charge on N as O is more electronegative than N.
* Pπ - dπ Resonance < Actual Resonance
Ex.5 Compare the acidic strength of the following
(a) 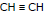 (b) CH2 = CH2 (c) CH3 - CH3
(b) CH2 = CH2 (c) CH3 - CH3
Sol.
(Stability of the conjugate base)
→ a > b > c (acidic strength)
Ex.6 Compare the acidic strength of the following :
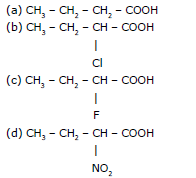
Sol. d > c > b > a
Ex.7 Compare the acidic strength of the following :
(a) H2O (b) H2S (c) H2Se (d) H2Te
Sol. Conjugate base is in an stability order
→ H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te (acidic strength)
Ex.8 Compare the acidic strength of the following compound
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. After forming conjugate base of the above
c > d > b > a
Ex.9 Compare the reactivity of the following compounds with 1 mole of AgNO3
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. After removing Cl-
( ve charge is not on resonance least stable)
(most stable as L.P. of Cl will be coordinated to ve charge completing the octet of each atom and making the corbocation most stable)
extent of ve charge decreases stability increases
Ex.10 Compare the acidic strength
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. After making conjugate base
c > b > a > d
BASIC STRENGTH
Basic strength directly depends on the availibility of lone pair for H
Ex.11 Compare the basic strength of following
Sol.
Ex.12 Compare the basic strength of the following
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. ,
,
,
CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF
(acidic strength)
* Strong Acids have weak conjugate base.
* For the same period
less electronegativity, more nucleophilicity as more electronegative element has less tendencey to give its electron pair.
Ex.13 Which is more basic or
?
Sol. >
Which is more basic NH3 or
forming conjugate acid
Comparison of Basicity of Ammonia and Alkyl Amines :
Ex.14 Compare the basic strength of the following NH3, CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N
Factors which affect the basicity of Amines
(1) steric effects (2) Inductive effect (3) solvation effect.
The base whose conjugate acid is more stable will be more acidic
forming conjugate acid of the given base
, , ,
Stability order of conjugate acid
(due to I effect)
Therefore basic strength
(CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > NH3
(vapor phase or gaseous is phase or in Non polar solvent)
In Aqueous solution or in polar solvent
(CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
In aqueous solution, the conjugate acids form H-bonds (intermolecular) with water molecules and stabilise them selves conjugat acid of 1° amine which has largest no. of H-atoms form maximum H-bond with water and is most stable. Consequently 1° amine is most basic.
Due to steric effect 1° amine is considered more basic as compared to 3° amine as lone pair is hindered by three alkyl group and less available for H .
Considering the combined effect of the three (Inductive, solvation and steric effect) we can conclude that
2° > 1° > 3° > NH3
Aromatic amines are least basic as their lone pair is in conjugation and less avaibable for protonation.
Ex.15 Compare the basic strength of the following
(a)
(b)
(c)
(if L.P. will be participate in Resonance, then molecule becomes aromatic)
Hence L.P. will have a greater tendency to take part in Resonance and will be less available for H
This compound will be least basic.
Ex.16 Compare the basic strength of the following
Sol. sp hybridised carbon being most electronegative will attract e- density from nitrogen and will make it less available for H . Hence basicity decreases.
c > b > a
Ex.17 Compare the basic strength
(a) (b)
a < b
Ex.18 Compare the basicity of the following compounds
(a) CH3 - CH2 - CH = CH - (b)
(c) (d)
Sol. In part (a) the lone pair of nitrogen in Resonance therefore will be less available for H making it least basic among all followed by sp, sp2, sp3 hybridised carbon atoms.
b > c > d > a
Ex.19 Compare the basicity of the numbered nitrogen atoms.
Sol. The planerity of ring will be destroyed if L.P. will take part in Resonance.
Basicity order of Nitrogen follows the order
N(sp3) > N(sp2) > N(sp)
(In this sp2, l.p. is in Resonance
with ring hence will be less
available for H therefore it will
be least basic)
Ex.20 Compare the basic strength of the following
(a) (b)
(c)
Sol. In part (a) NO2 is at p-position Hence will attract e- density by both -M and -I
In part (b) NO2 is at m-position hence will attract e- density by -I only
There is no such effect in part (c)
→ Availibity of L.P. on nitrogen in part (a) is minimum followed by b and then c.
c > b > a
Ortho effect :
The ortho substituted aniline are less basic than aniline and ortho substituted benzoic acids are more acidic than benzoic acid.
Ortho effect is valid only for benzoic acid and aniline.
e.g. Also
Ex.21 Compare the basic strength of the following :
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. a > b > d > c
* Due to ortho effect d > c
if c is less basic than d then it will be certainly less basic than b as b is more basic than d.
Ex.22 Compare the basic strength of the following :
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Sol. Do your selves
S.I.P → Steric inhibition of Protonation (ortho effect)
after protonation, repulsion increases therefore ortho substituted aniline is less basic than aniline
S.I.R → Steric inhibition of resonance
(a) (b)
FAQs on General Organic Chemistry, Class 11, Chemistry Detailed Chapter Notes - JEE
| 1. What is the difference between general chemistry and organic chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the principles of organic chemistry? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of organic chemistry in daily life? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of organic compounds? |  |
| 5. What is the role of organic chemistry in the pharmaceutical industry? |  |















