Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Notes - Manufacturing Industries
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Importance of Manufacturing |

|
| Agro-Based Industries |

|
| Mineral-based Industries |

|
| Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation |

|
| Control of Environmental Degradation |

|
Introduction
Manufacturing is the process of producing goods in large quantities after processing raw materials into more valuable products.
- For Example: Paper is manufactured from wood, sugar from sugarcane, iron and steel from iron ore, and aluminium from bauxite.
 Sugar is produced from Sugarcane
Sugar is produced from Sugarcane
- Some types of clothes are manufactured from yarn, which itself is an industrial product.
- People employed in secondary activities are responsible for manufacturing primary materials into finished goods.
- Examples of workers in the secondary sector include those in steel factories, car, breweries, textile industries, and bakeries.
- A country's economic power is measured by the growth and advancement of its manufacturing industries.
Importance of Manufacturing
Economic Backbone: The manufacturing sector is crucial for overall and economic development.
1. Modernizing Agriculture:
- Helps modernize agriculture.
- Reduces dependence on agricultural income by creating jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
2. Eradication of Unemployment and Poverty:
- Essential for eliminating unemployment and poverty.
- Public and joint sector industries aim to reduce regional disparities by setting up industries in tribal and backward areas.
3. Trade and Foreign Exchange:
- Exporting manufactured goods boosts trade and commerce.
- Generates foreign exchange.
4. Prosperity through Value Addition:
- Prosperous countries transform raw materials into diverse, high-value finished goods.
- India’s growth depends on increasing and diversifying its manufacturing sector.
5. Synergy with Agriculture:
- Agro-industries enhance agricultural productivity.
- Provide essential products like irrigation pumps, fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery to farmers.
- Manufacturing industry supports and improves agricultural efficiency.
6. Global Competition:
- Efficiency and competitiveness are crucial in a globalized world.
- Indian manufactured goods must meet international quality standards to compete globally.

Classification of Industries
1. Based on source of raw materials used:
- Agro-based: cotton, woollen, jute, silk textile, rubber and sugar, tea, coffee, edible oil.

- Mineral-based: iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals.
2. According to their main role:
- Basic or key industries that supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods. Example: iron and steel and copper smelting, aluminium smelting.
- Consumer industries that produce goods for direct use by consumers. Example: sugar, toothpaste, paper, sewing machines, fans etc.
3. Based on capital investment:
- A small scale industry is described based on the maximum investment allowed on its assets, which currently stands at rupees one crore. If the investment exceeds this amount in any sector, it is classified as a large scale industry.
4. Based on ownership:
- Public sector, owned and operated by government agencies– BHEL, SAIL etc.
- Private sector industries owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals–Reliance, TATA, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries.
- Joint sector industries which are jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Oil India Ltd. (OIL) is jointly owned by public and private sector.
- Cooperative sector industries are those owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers, or both. They gather resources together and divide profits or losses accordingly, like the sugar industry in Maharashtra and the coir industry in Kerala. Examples include Amul and Lijjat Papad.
5. Based on the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods:
- Heavy industries such as iron and steel
- Light industries that use light raw materials and produce light goods such as electrical industries.
Agro-Based Industries
Cotton, jute, silk, woollen textiles, sugar and edible oil, etc. industries are based on agricultural raw materials.
I. Textile Industry
- The textile sector is unusual in the Indian economy because it contributes significantly to industrial production (14%).
- Employment in the textile sector involves 35 million people directly, second only to agriculture.
- Textiles contribute to foreign exchange profits at about 24.6 per cent.
- It is the country's sole industry that is self-sufficient and comprehensive throughout the value chain, from raw materials to the highest value-added products.
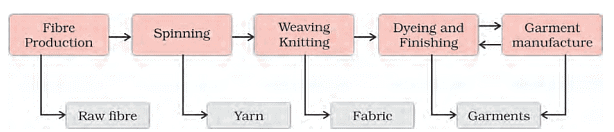 Value addition in the textile industry
Value addition in the textile industry
II. Cotton Textiles
- Cotton textiles were made in ancient India using hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques.
- Power looms were popular after the 18th century.
- During the colonial period, our traditional businesses experienced a setback since they couldn't compete with England's mill-made textiles.
 Cotton Industry in 18th Century
Cotton Industry in 18th Century
- The cotton textile industry initially developed in the cotton growing regions of Maharashtra and Gujarat due to factors such as the availability of raw cotton, suitable climate, accessible market and transport facilities, and labor.
- This industry is closely connected to agriculture and provides livelihoods to farmers, cotton boll pluckers, and workers involved in various stages of production such as ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring, and sewing.
- The industry's growth also supports other sectors like chemicals and dyes, packaging materials, and engineering works.
- While spinning is still concentrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, weaving is decentralized to incorporate traditional skills and designs in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc.
- India excels in spinning production but struggles to produce high-quality fabrics due to limitations in weaving technology and the inability to fully utilize the high-quality yarn produced in the country.
- Weaving is carried out through handloom, powerloom, and mills.
- The handspun khadi industry, which involves weaving in homes as a cottage industry, provides significant employment opportunities for weavers.
The first successful textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854. The two world wars were fought in Europe, India was a British colony. There was a demand for cloth in U.K. hence, they gave a boost to the development of the cotton textile industry.
III. Jute Textiles
- India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods.
- It is the second largest exporter of jute after Bangladesh.
 Jute Industry
Jute Industry
- Most of the jute mills are located in West Bengal, along the banks of the Hugli river.
- The proximity of jute producing areas is a factor responsible for their location in the Hugli basin.
- The availability of inexpensive water transport is another factor supporting their location.
- A good network of railways, roadways, and waterways facilitates the movement of raw material to the mills.
- The Hugli river provides abundant water for processing raw jute.
- Cheap labor from West Bengal and neighboring states such as Bihar, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh is available.
- Kolkata, being a large urban center, provides banking, insurance, and port facilities for the export of jute goods.
The first jute mill was set up near Kolkata in 1855 at Rishra.

IV. Sugar Industry
- India is the second-largest producer of sugar in the world, but it holds the first position in the production of gur and khandsari.
- The raw material used in this industry is bulky, and its sucrose content reduces during transportation.
 Sugar Mill
Sugar Mill
- The sugar mills are located in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Sixty percent of the mills are in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- The seasonal nature of the industry makes it suitable for the cooperative sector.
- In recent years, there has been a shift and concentration of mills in the southern and western states, particularly in Maharashtra.
- This is because the cane produced in these states has a higher sucrose content and the cooler climate allows for a longer crushing season.
- The cooperatives are more successful in these states.
Mineral-based Industries
I. Iron and Steel Industry
 India: Iron and Steel Plants
India: Iron and Steel Plants
- The steel industry is considered to be the backbone of other industries as they rely on it for machinery.
- Steel is necessary for the production of various engineering goods, construction materials, defense equipment, medical devices, telephonic equipment, scientific equipment, and consumer goods.
- The production and consumption of steel are often seen as indicators of a country's development.
- Iron and steel is classified as a heavy industry because both the raw materials (iron ore, coking coal, limestone) and finished products are heavy and bulky, leading to high transportation costs.
- The raw materials are needed in the ratio of approximately 4:2:1, with manganese also required to harden the steel.
- The ideal location for steel plants should have an efficient transport network for distribution to markets.
- The Chhotanagpur plateau region is the most suitable location for iron and steel industries due to its advantages, such as low-cost iron ore, high-grade raw materials in close proximity, cheap labor, and a large domestic market with growth potential.
 Process and Manufacture of Steel
Process and Manufacture of Steel
II. Aluminium Smelting
- Aluminium smelting is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
- It is known for its light weight, resistance to corrosion, good heat conductivity, malleability, and strength when mixed with other metals.
- It is commonly used in the manufacturing of aircraft, utensils, and wires.
- It has gained popularity as a substitute for steel, copper, zinc, and lead in various industries.
- Aluminium smelting plants are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
- Bauxite, a bulky dark reddish colored rock, is the raw material used in the smelting process.
- The availability of regular electricity supply and affordable raw materials are key factors for the location of aluminium smelting plants.
 Manufacturing in Aluminium Industry
Manufacturing in Aluminium Industry
III. Chemical Industries
- The chemical industry in India is experiencing rapid growth and diversification.
- It consists of both large and small scale manufacturing units.
- Significant growth has been observed in both the inorganic and organic sectors.
- Inorganic chemicals such as sulphuric acid, nitric acid, soda ash, and caustic soda are widely produced and used in various industries including fertilizers, synthetic fibers, plastics, adhesives, paints, dyes, glass, soaps, detergents, and paper.
- These industries are spread across the country.
- Organic chemicals, particularly petrochemicals, are used in the manufacturing of synthetic fibers, rubber, plastics, dyes, drugs, and pharmaceuticals.
- Organic chemical plants are usually located near oil refineries or petrochemical plants.
- The chemical industry is a major consumer of its own products.
- Basic chemicals are processed to produce other chemicals that are used in industrial applications, agriculture, or directly for consumer markets.
IV. Fertilizer Industry
 Fertiliser Industry
Fertiliser Industry
- The fertilizer industry in India primarily focuses on producing nitrogenous fertilizers, phosphatic fertilizers, ammonium phosphate (DAP), and complex fertilizers.
- Nitrogenous fertilizers, particularly urea, are the main products of the industry.
- Complex fertilizers contain a combination of nitrogen (N), phosphate (P), and potash (K).
- Potash, or potassium, is entirely imported as India does not have any commercially usable reserves of potash or potassium compounds.
- The industry expanded to various parts of the country after the Green Revolution.
- Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Kerala contribute to half of the fertilizer production in India.
- Other significant fertilizer producers include Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka.
V. Cement Industry
 Cement Industry
Cement Industry- Cement is necessary for various construction activities, including building houses, factories, bridges, roads, airports, dams, and commercial establishments.
- The cement industry requires large and heavy raw materials such as limestone, silica, and gypsum.
- It also relies on coal and electric power, as well as rail transportation.
- Plants have been strategically located in Gujarat, India, to have convenient access to the Gulf countries' market.
VI. Automobile Industry
- Automobiles in India are used for quick transportation of goods and passengers.
- Various types of vehicles such as trucks, buses, cars, motorcycles, scooters, three-wheelers, and utility vehicles are manufactured in India.
- The liberalization of the economy led to the introduction of new and modern vehicle models, which increased the demand for vehicles in the market.
- This resulted in a healthy growth of the automobile industry, including the production of passenger cars, two-wheelers, and three-wheelers.
- The automobile industry is mainly located around major cities like Delhi, Gurugram, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur, and Bengaluru.

VII. Information Technology and Electronics Industry
- The electronics industry in India encompasses a wide range of products such as transistor sets, televisions, telephones, cellular telecom, telephone exchanges, radars, and computers.
- Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India, but other important centers for electronic goods include Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Coimbatore.
- The major industry concentration is found in Bengaluru, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Pune.
- One of the significant impacts of this industry is the generation of employment opportunities.
- The growth in both hardware and software sectors is crucial for the success of the IT industry in India.

Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Although industries contribute significantly to India’s economic growth and development, the increase in pollution of land, water, air, noise and the resulting degradation of environment that they have caused, cannot be overlooked.Industries are responsible for four types of pollution:
(a) Air
(b) Water
(c) Land
(d) Noise
The polluting industries also include thermal power plants.
 I. Air pollution
I. Air pollution - Causes: High levels of sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide; particulate matter from smoke and industrial activities.
- Sources: Factories, chemical plants, and fossil fuel burning.
- Effects: Harm to health, animals, plants, buildings, and contributes to climate change.
II. Water pollution
- Causes: Discharge of industrial wastes, including dyes, detergents, heavy metals, and pesticides.
- Sources: Textile, chemical, petroleum refineries, and tanneries.
- Effects: Thermal pollution affects aquatic life; nuclear waste causes severe health issues; soil contamination impacts groundwater.
III. Thermal pollution
- Cause: Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
- Effect: Disrupts aquatic life by altering water temperature.
IV. Nuclear Pollution:
- Cause: Waste from nuclear power plants and weapon production.
- Effects: Causes cancers, birth defects, and miscarriages.
V. Soil and Water Pollution:
- Cause: Dumping of wastes specially glass, harmful chemicals, industrial effluents, packaging, salts and garbage renders the soil useless.
- Effect: Contaminates soil and groundwater; rainwater carries pollutants into the soil.
VI. Noise pollution
- Causes: Industrial activities, machinery, and construction work. Industrial and construction activities, machinery, factory equipment, generators, saws and pneumatic and electric drills also make a lot of noise.
- Effects: Hearing impairment, increased heart rate, blood pressure, and stress.
Control of Environmental Degradation

To reduce industrial pollution and manage environmental impact, consider the following measures:
I. Reduction of Freshwater Pollution:
- Minimize Water Use: Reuse and recycle water in multiple stages.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collect and use rainwater for various needs.
- Effluent Treatment: Treat hot water and effluents before releasing into water bodies.
II. Industrial Effluent Treatment:
- Primary Treatment: Mechanical processes such as screening, grinding, flocculation, and sedimentation.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes to further clean the water.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced biological, chemical, and physical processes for recycling wastewater.
Groundwater Management:
- Regulate Withdrawal: Legally control excessive groundwater extraction to protect resources.
Air Pollution Control:
- Reduce Particulate Matter: Install electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and inertial separators in smoke stacks.
- Switch Fuel: Use oil or gas instead of coal to lower smoke emissions.
- Noise Reduction: Equip machinery with silencers, use noise-absorbing materials, and redesign machinery for efficiency.
Sustainable Development: Integrate economic development with environmental concerns to achieve long-term sustainability.
NTPC Shows the Way
NTPC's Environmental Initiatives
NTPC, a major power corporation in India, is committed to environmental management with ISO 14001 certification. It focuses on:
- Optimizing Equipment: Using advanced techniques and upgrading machinery.
- Minimizing Waste: Enhancing ash utilization.
- Maintaining Green Belts: Supporting ecological balance and afforestation.
- Reducing Pollution: Managing ash ponds, recycling ash water, and handling liquid waste.
- Monitoring: Conducting ecological reviews and managing data for power stations.
|
63 videos|445 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Notes - Manufacturing Industries
| 1. What is the importance of manufacturing industries? |  |
| 2. What are agro-based industries? |  |
| 3. How do mineral-based industries contribute to the economy? |  |
| 4. What are the impacts of industrial pollution on the environment? |  |
| 5. How can environmental degradation from industrial activities be controlled? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















