Detailed Notes: Internet (Part - 2) | Computer - Class 5 PDF Download
To surf on the Net, perform the following steps:
1. Enter the name/address of the website on the address bar. http://www.silverzone.org
2. Click on Go B or press enter. You will get the Homepage of the website on the screen.
Now you can click on other links (hyperlinks, underlined links) or use scrollbars or arrow keys to move to other pages or other places within the same page.
Some basic Inter terminology:
WWW | I World Wide Web |
ISP | Internet Service Provider |
URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
Server | A computer that provides a service to another computer. |
Search engine | Find web pages with specific content. |
Cookie | A file left on your computer by a website's browser containing your login, password, user preferences and other personalized information. |
Browser | Software used to "browse" the internet. Most common examples are Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome. |
Domain name | The unique name that identifies on Internet site. |
HTML | Hyper Text Markup Language - computer code used to create documents on the www. |
HTTP | Hyper Text transfer Protocol - protocol for moving hypertext files across the Internet. |
Downloading | Copying a file from a remote computer to your computer. |
Uploading | Copying a file from your computer to a remote computer. |
Bookmark | Function used to save a webpage location for future reference. |
ASCII | American Standard Code For Information Interchange. |
Home page | Page your computer will go to when you initially log onto the Internet. |
Link hyperlink | Text found on a web page which when clicked, will take you to another web location. |
Back | Moves to pervious page on website. |
Forward | Moves to next page on website. |
Refresh | Starts the process of opening a web page again. |
History | Shows a list of pages visited recently. |
Mail: | Opens a drop-down menu with different options for sending or receiving e-mail. |
E-mail (Electronic mail)
E-mail is short for electronic mail. An email is a letter that is send over a computer network instead of being sent through the post. You can attach documents and photos to e-mails, just like you can include a photo or a document with a letter.
You can also attach computer files such as programs and spreadsheets.
Steps for setting up an E-mail account with Gmail:
Go to www.gmail.com in your web browser. This takes you to the Gmail login page. 
We don't have an account yet, so it's time to create one. Left-click on the create an Account button.
After clicking on it the Google Account sign-up page will appear. 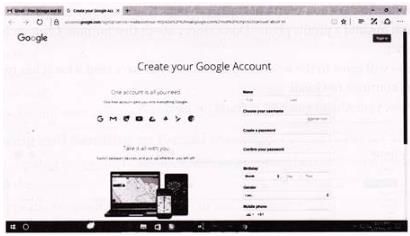
Now, in the appropriate fields, you need enter the required detail:
- Your First Name
- Your Last Name
A user name for your email address.
username@gmail.com where user name is the name you enter into the field.
- A password (which you have to retype to confirm it) your password could be anything but try to make it strong as the combination of alphabet or numbers.
Note: Type in a password and write it down in a safe place. This password must have at least 8 letters or numbers in it. - Retype your password in the next box and google will double check it for accuracy.
- Your birthday
- Your gender
- Your current email address
- Your location
- Now, you will have to solve the captcha (that's the box with the hard to read words in it) by typing in the words you see in the box into the field just below it
- You will also have to check the box that says:
I agree to the google terms of service and privacy policy.
Note: Sometime choosing a user name is often difficult, since so many of the common onces are already taken. Unless you have a highly unusual name, it's likely that your name is already taken. If username is already taken, google will immediately let you know it and suggest alternatives (which as usually whatever you entered with a string of number at the end).
- When you are done, left-click on next step.
- You can add a profile photo. Don't worry about that for now. Click on Next step again.
- You will come to the welcome page. When you have read what it has to say click on continue to Gmail.
Now, your Gmail email-id is ready for used. 
Now, you can log into email at any time by going to www.gmail.com. Instead of clicking on create new account, however you now type your user name and password into the login fields.
On the left are your navigation items:
- Inbox
- Starred
- Important
- Sent mail
- Drafts and with a big red compose button about them.
Composing and Sending an E-mail Message
- To create a new e-mail click the red "Compose mail button (on the left hand side of the screen).
- Type the recipient's email address in the "To" box.
- To send a message to more than one person, you may enter multiple address by placing a comma and space between each address.
- E.g. abc@gmail.com, xyz@example.com, pqr@example.com
- Ensure that you correctly enter the email address or the message will be send either to a different person or returned back to you with a note that it was undeliverable -just like the postal service.
- Type the subject of the message in the "Subject" box. Keep the subject to a word or pharse summarizing the content of your message. (E.g.: subject: Daily Report).
- Use your mouse and click inside the message box (the large box under "Plain text" in the picture below - it is where you will write your email letter) and move the cursor to that space.
- Type the body of your message.
- When you are finished typing your message and ready to send it, click the blue "send" button
Reading an email message
To read an email, click on the subject of the email.
Note: Unread message in your inbox will be bolded.
Replying to a message
- Open the message that you replaying to.
- Click the "Reply button" which looks like an arrow pointing to the left. The program will present you with a message already addressed to the sender. The subject line will state "Re:" and then the old message's subject. You will probably not change the subject like so the receiver knows that you are replying to a previously an email that was previously sent.
- Click in the box above the text to which you are replying.
- Begin typing your reply.
- Click "Sent" when you are finished typing your message and are ready to send it.
Note: The different between "Reply" and "Reply All". Clicking the "Reply" button will send your reply only to the original sender of the message. Clicking the "Reply All" button will send your reply to everyone who received the original message.
Forwarding a message
- Open the message you wish to forward to another person.
- Click the down arrow next to the reply arrow.
- Click on "forward".
- Type the recipient's address in the "To:" box.
- Type a note above the forwarded message (optional).
- Click Send.
Some E-mail related terms
- Attachment: A text file or image, such as photography sent as part of an email message
- BCC: A "Blind Carbon Copy" a feature where if you "BCC" it means, the original receiver of the message will not know that copy of the message will be received by the individual who is "BCC".
- CC: A Carbon Copy, a feature which will send an copy of your email to the "CC person.
|
33 videos|30 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Detailed Notes: Internet (Part - 2) - Computer - Class 5
| 1. What is the difference between the internet and the World Wide Web? |  |
| 2. How does the internet work? |  |
| 3. What are some common internet protocols? |  |
| 4. How secure is the internet? |  |
| 5. What is the future of the internet? |  |






















