Direction Sense Test | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
The direction and distance reasoning questions, as the name implies, includes two types of questions i.e.:
- Direction Sense Test
- Distance Related questions
The details of both these question types are discussed below in detail to help the candidates prepare this topic easily and solve the related questions effectively.
Direction Sense Reasoning:
The questions based on directions require the candidates to identifying the direction of an individual or shadow from a set of statements. Some important points are given which can help to understand and solve the related question easily.
- Know about the Directions Thoroughly
In general, there are four main directions i.e. North, South, East and West. Apart from these four, there are four additional directions derived from the main ones. They are called North-East, North-West, South-East and South-West. A chart is given below for reference.
Direction Chart: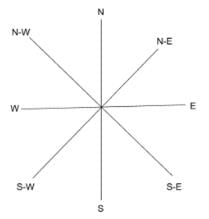
Direction Questions:
Example :
A is standing on the east of B who is standing in the north of C. In which direction is D with respect to A if D is standing in the south of C?
Solution: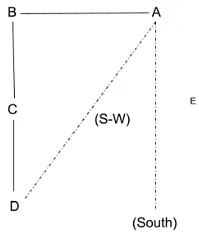
From the above statement, a direction diagram can be made as follows.
From the diagram, it is clear that D is standing in the south-west direction of A.
- Get Acquainted with the casting of Shadows
Often the questions are asked when the candidates need to identify the direction where one’s shadow is cast. Some of the important points are given below which can help the candidates to solve the questions related to shadows effectively.
- If a man faces a rising sun, his shadow will always be in the west.
- During sunset, one’s shadow will always be casted in the east.
- Similarly, if a man faces north, his shadow will be on his right during sunrise and on his left during sunset.
- In mid-noon, no shadows are seen as the sun’s rays are vertically downwards.
Direction Questions:
Example:
Mr. X and Mr. Y are facing each other and are enjoying the sunrise. If Mr. X’s shadow falls on his left side, then which direction is Mr. Y facing?
Solution:
As it is sunrise, any shadow has to fall in the west direction. As it is given that Mr. X’s shadow falls on his left side, it can easily be interpreted that Mr. X is facing North (since his left side is facing west). Now as Mr. X and Mr. Y are facing each other, Mr.Y has to face South.
- Get well-versed with the rotations
Often some statements are given where the subject rotates either to the left or to the right. It should always be remembered that rotating right implies clockwise rotation while rotating left implies rotating anti-clockwise.
Direction Questions:
Example:
Mr. R moves North and then turns to his right and keep walking. After that, he again turns left and walks 1 km distance and then finally walks to the left. In which direction is he walking now?
Solution:
The problem becomes simple if a diagram is constructed according to the given statements.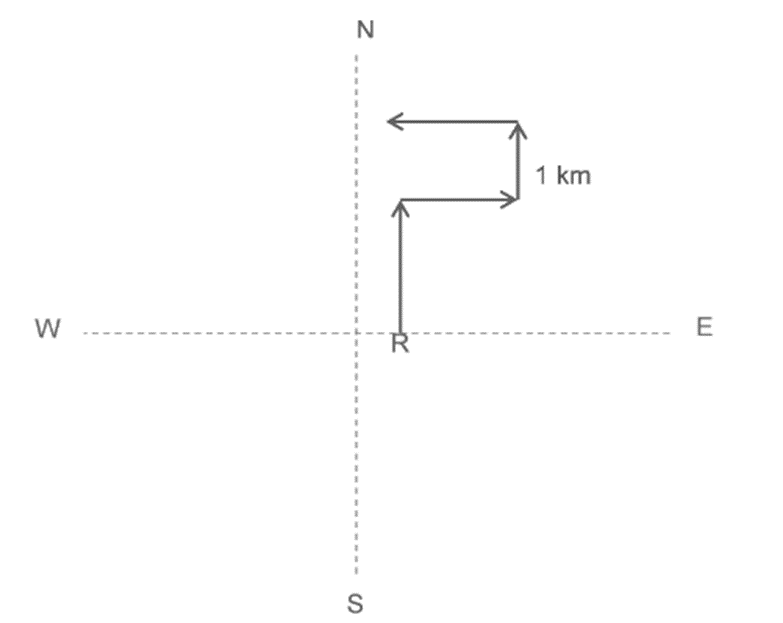
From the diagram, it can be easily interpreted that Mr. A is now walking towards the West.
Distance Related Questions
In most of the direction and distance questions, the candidates are required to calculate a certain parameter from the question statement. The questions can be related to the total distance walked, shortest path, the distance between two entities, etc.
While solving the distance related question, one must be thorough with the Pythagorean Theorem to be able to solve most of the questions. The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate the shortest path traveled, the minimum distance between two points, etc. A couple of examples are given below to illustrate the direction and distance questions better.
Direction And Distance Reasoning Questions:
Example:
Mr. P walked 3 km towards east. After that, he moved clockwise and walked 4 Kms. What would have been the distance if he took the shortest path from his initial position to his final position?
Solution:
At first, one must construct the diagram of his movement. The movement route of Mr. P is given below.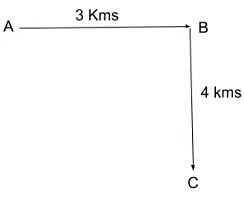
In this diagram, the positions of Mr. P are marked as A, B and C where A is the initial position and C is the final position. From the diagram, the shortest path from his initial position to the final position will be AC.
AC= √(AB²+ BC²)
So, AC= 5.
Therefore, the shortest path from the initial distance to the final distance will be 5 Kms.
Direction And Distance Reasoning Questions:
Example:
Mr. M walked 20m towards the west and turned left and again walked 15m. Then he moved anti-clockwise and walked 20m. At last, he moved clockwise and walked another 10m. How far is Mr. M now from his initial position?
Solution:
First, a diagram should be constructed taking all his movements into consideration. The diagram will come up as:
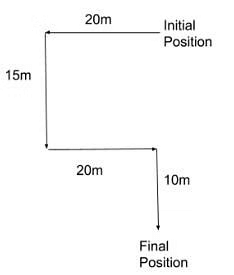
From this diagram, the distance between initial and final position can be easily calculated which will be: 15m + 10m = 25m.
|
205 videos|265 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Direction Sense Test - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. ডিরেকশন সেন্স টেস্ট কি ও এটা কি ধরণের পরীক্ষা? |  |
| 2. ডিরেকশন সেন্স টেস্টের ধরণ কি কি? |  |
| 3. ডিরেকশন সেন্স টেস্টে কোন ধরণের প্রশ্ন থাকতে পারে? |  |
| 4. ডিরেকশন সেন্স টেস্ট কেন গুরুত্বপূর্ণ? |  |
| 5. ডিরেকশন সেন্স টেস্ট কিভাবে প্রস্তুতি করতে পারি? |  |






















