Distance and Displacement - Motion, Class 9, Science PDF Download
Introduction
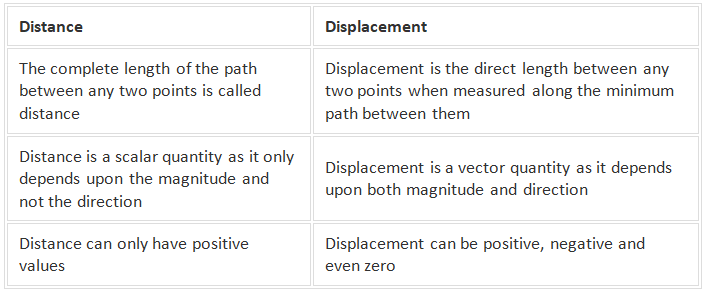
Distance and displacement are two quantities that seem to mean the same but are distinctly different with different meanings and definitions. Distance is the measure of “how much ground an object has covered during its motion” while displacement refers to the measure of “how far out of place is an object.”
Distance
Distance is the total movement of an object without any regard to direction. We can define distance as to how much ground an object has covered despite its starting or ending point.
Distance = Length of the path I (ACB)
Distance is a scalar quantity.
Unit In SI system: metre (m)
In CGS system: centimeter (cm)
Large unit Kilometre (km)
Distance Formula: 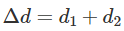
Displacement
Displacement is defined as the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity and has a direction and magnitude. It is represented as an arrow that points from the starting position to the final position.
For example: If an object moves from A position to B, then the object’s position changes. This change in position of an object is known as Displacement.
Displacement of an object = Final position – Initial position of the object.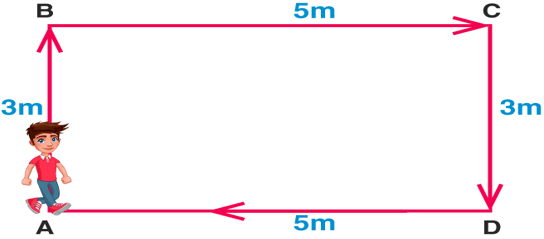 Displacement at point A = 0
Displacement at point A = 0
Distance travelled at point A = 0
Displacement = Δx = xf − x0
xf = Final Position
x0 = Initial Position
Δx = Displacement
Examples of Distance and Displacement
Q.1. John travels 250 miles to North but then back-tracks to South for 105 miles to pick up a friend. What is John’s total displacement?
Ans: John’s starting position Xi= 0.
Her final position Xf is the distance travelled N minus the distance South.
Calculating displacement, i.e.D.
D = ΔX = (Xf – Xi)
D = (250 mi N – 105 mi S) – 0
D = 145 mi N
Q.2. An object moves along the grid through points A, B, C, D, E, and F as shown below. The side of square tiles measures 0.5 km.
(a) Calculate the distance covered by the moving object.
(b) Find the magnitude of the displacement of the object.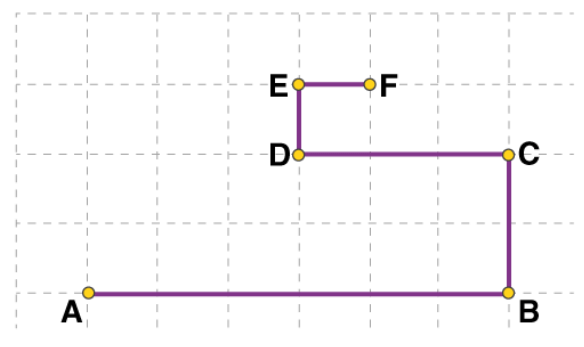 Ans: (a) The distance covered by the moving object is calculated as follows:
Ans: (a) The distance covered by the moving object is calculated as follows:
AB + BC + CD + DE + EF
3 + 1 + 1.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 = 6.5 km
The distance covered by the moving object is 6.5 km.
(b) The initial point is A and the final point is F, hence the magnitude of the displacement is equal to the distance AF which is calculated by applying Pythagoras’s theorem to the triangle AHF as shown in the figure below: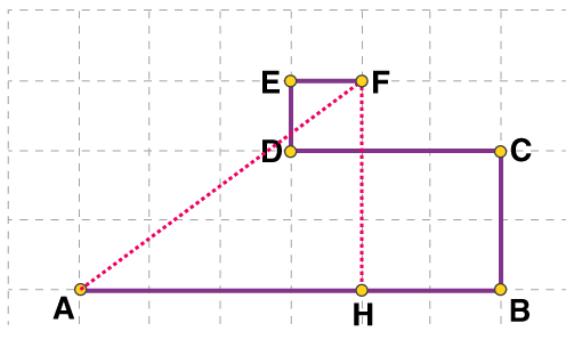 Applying the Pythagorean formula, we get
Applying the Pythagorean formula, we get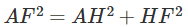
Substituting the formula, we get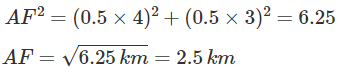
The magnitude of displacement is 2.5 km.
Distance vs Displacement
Go through Short Notes of the chapter Motion from here.
Go through NCERT solutions of the chapter Motion from here.
FAQs on Distance and Displacement - Motion, Class 9, Science
| 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate displacement? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |
| 4. Can the displacement be greater than the distance? |  |
| 5. How can you determine the direction of velocity? |  |















