Genetic & Chromosomal Disorders | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Pedigree Analysis? |

|
| Mendelian Disorder |

|
| Hemophilia |

|
| Colour Blindness |

|
| What are Chromosomal Abnormalities (Disorders)? |

|
| Aneuploidy |

|
| Polyploidy |

|
Mendel’s works on the principle of inheritance in genetics remained a mystery for quite some time. Even though his works were not accepted during his era, later it was rediscovered and gained credibility. Currently, Mendel’s work is fundamental for studying inheritance pattern in living organisms. In addition, it helped to discover and predict how genetic disorders function. Let’s learn about pedigree analysis and how it helps in predicting genetic disorders.
What is a Pedigree Analysis?
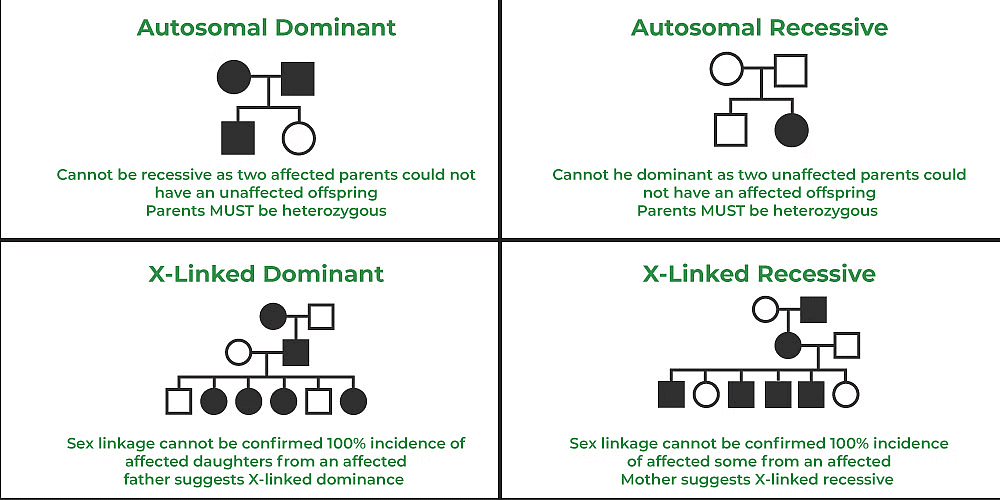
Pedigree analysis is a chart that represents a family tree, which displays the members of the family who are affected by a genetic trait.
Here, the rows represent the generations of a family, squares represent males and circles represent females. In many cases, including various plant and animal species, scientists use pedigree analysis to analyse the inheritance of phenotypes, or traits, using mating experiments called crosses.
Mendel’s experiments revealed that the ‘factors’, what we know as genes, are responsible for the inheritance of traits. They are also accountable for the disorders prevailing in living organisms. Genes are the hereditary unit of organisms, responsible for structural and functional changes in them. Besides this, it is the cause of variation in organisms which can either result in a good or bad trait.
- DNA sequences are made up of various, which, in turn, code for a particular protein. Any changes in this sequence, e.g. mistakes during DNA replication may lead to a change in the genetic codes or chromosomal aberrations.
- This can be transferred from parents to offspring. Inheritance of altered genes causes genetic disorders in offspring. The Mendelian disorders may arise due to change or alteration in one gene. Their genetic inheritance is governed by Mendelian genetics. Mendelian disorders mostly occur in families with a certain pattern reflecting the alteration in a single gene.
- Prediction of these disorders is based on family history and can be done with the help of a family tree. This process of analysis of a number of generations of a family is called the pedigree analysis.
- Pedigree analysis is a strong tool in human genetics which helps to predict the pattern of inheritance, even when data is limited.
A family tree can be represented by a pedigree chart with all the members of a family. They may be having a genetic disorder or maybe carrier of the disease. In the pedigree analysis, standard symbols are used to distinguish between different family.
Mendelian Disorder
“Mendelian disorders are the genetic disorders caused at a single genetic locus.”
What are Mendelian Disorders?
Mendelian disorder is a type of genetic disorder primarily resulting due to alterations in one gene or as a result of abnormalities in the genome. Such a condition can be seen since birth and be deduced on the basis of family history using the family tree. The analysis hence carried out is known as pedigree analysis.
These genetic disorders are quite rare and may affect one person in every thousand or a million. Genetic disorders may or may not be inherited. Inheritable genetic disorders usually occur in the germline cells, whereas in non-inheritable genetic disorders the defects are generally caused by new mutations or due to some changes in the DNA. For instance, cancer may either be caused by an inherited genetic condition, or by a new mutation caused by the environmental causes or otherwise.
Types of Mendelian Genetic Disorders
According to Mendel’s’ laws of inheritance, the different types of Mendelian disorders include:
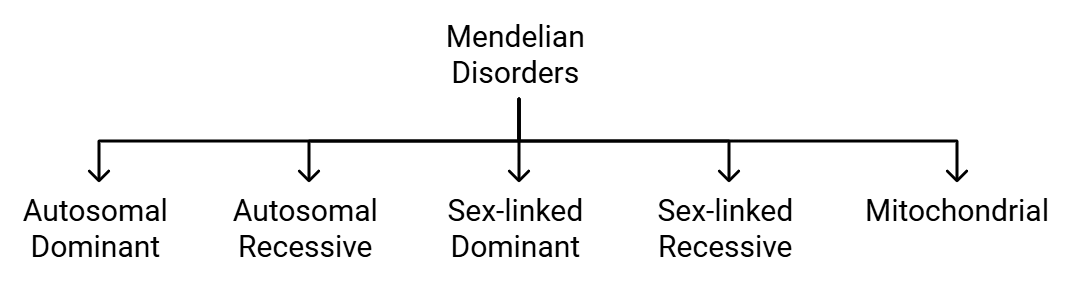 Mendelian Genetic Disorders
Mendelian Genetic Disorders
The various types of Mendelian disorders can be identified easily from the pedigree analysis.
Examples of Mendelian Disorders
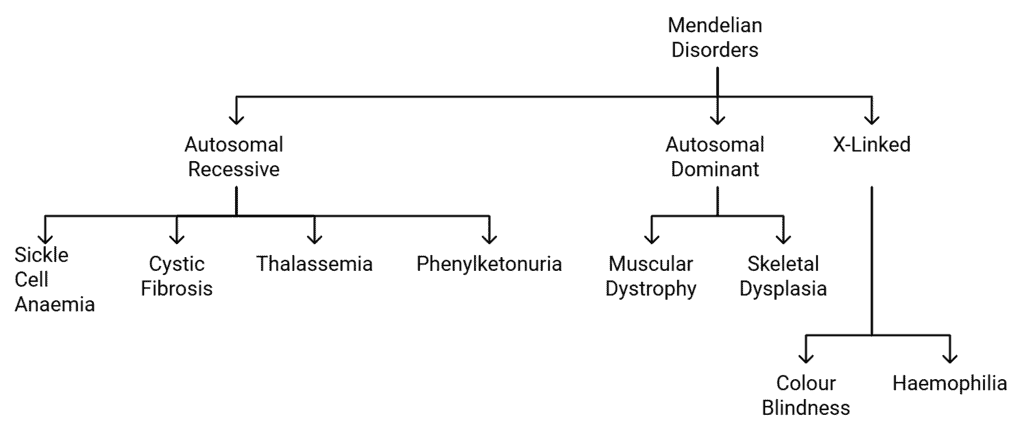 Examples of Mendelian Disorders
Examples of Mendelian Disorders
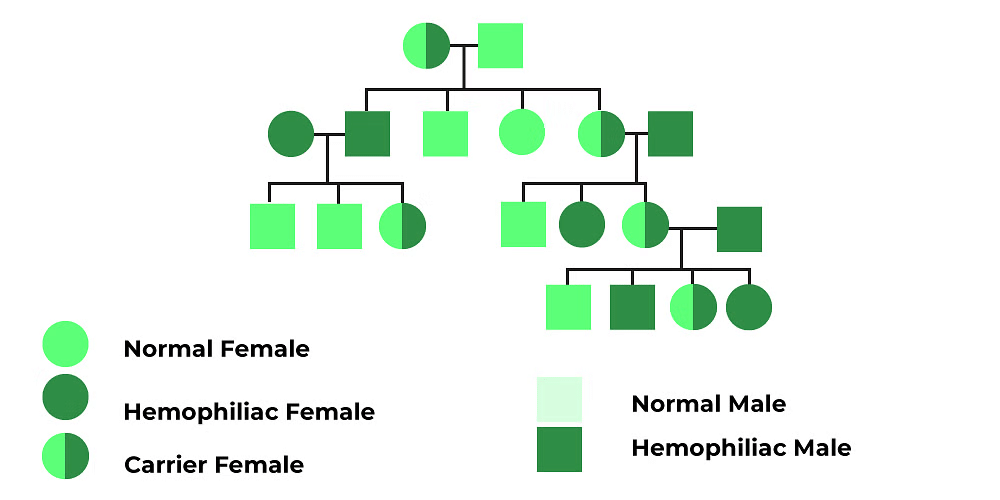
Haemophilia
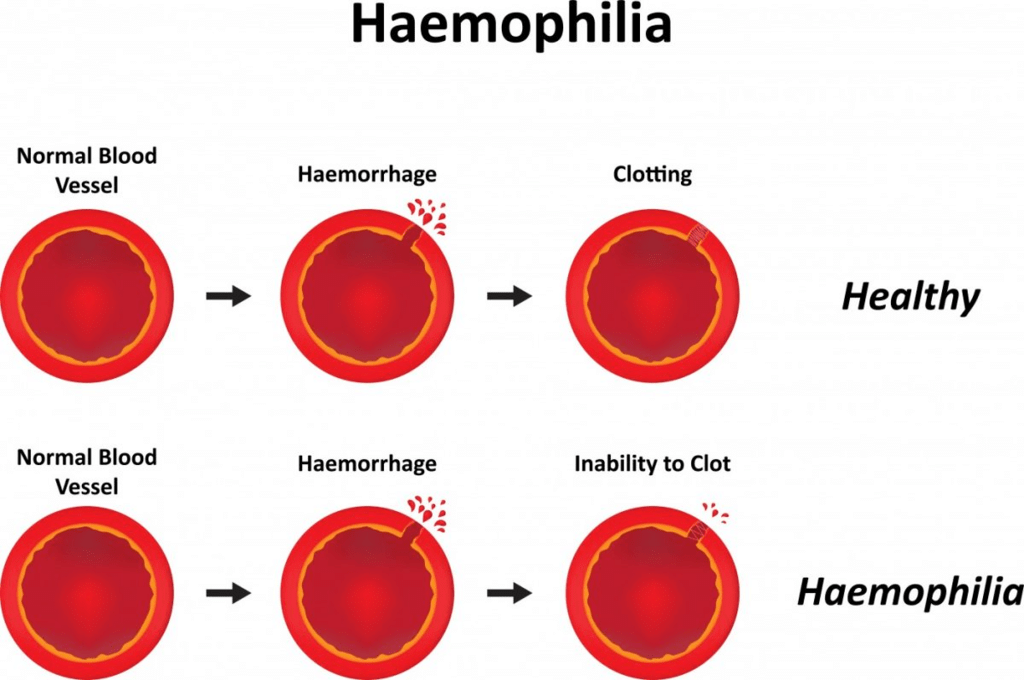
- This is a type of sex-linked recessive disorders. According to the genetic inheritance pattern, the unaffected carrier mother passes on the haemophilic genes to sons.
- It is a very rare type of disease among females because for a female to get the disease, the mother should either be hemophilic or a carrier but the father should be haemophilic.
- This is a disorder in which blood doesn’t clot normally as the protein which helps in clotting of blood is affected. Therefore, a person suffering from this disease usually has symptoms of unexplained and excessive bleeding from cuts or injuries.
- This type of genetic disorder is caused when the affected gene is located on the X chromosomes. Therefore, males are more frequently affected.
Sickle-Cell Anaemia
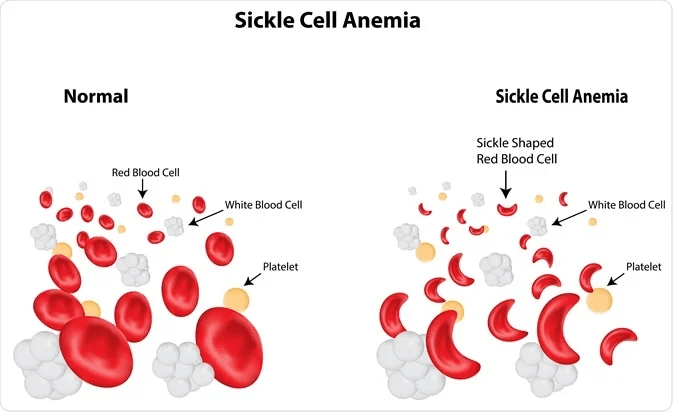
- This is a type of autosomal recessive genetic disorder.
- According to Mendelian genetics, its inheritance pattern follows inheritance from two carrying parents.
- It is caused when the glutamic acid in the sixth position of the beta-globin chain of haemoglobin molecule is replaced by valine. The mutant haemoglobin molecule undergoes a physical change which changes the biconcave shape into the sickle shape.
- This reduces the oxygen-binding capacity of the haemoglobin molecule.
Phenylketonuria
- This genetic disorder is autosomal recessive in nature.
- It is an inborn error caused due to the decreased metabolism level of the amino acid phenylalanine.
- In this disorder, the affected person does not have the enzyme that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. As a result, phenylalanine accumulation takes place in the body and is converted into many derivatives which result in mental retardation.
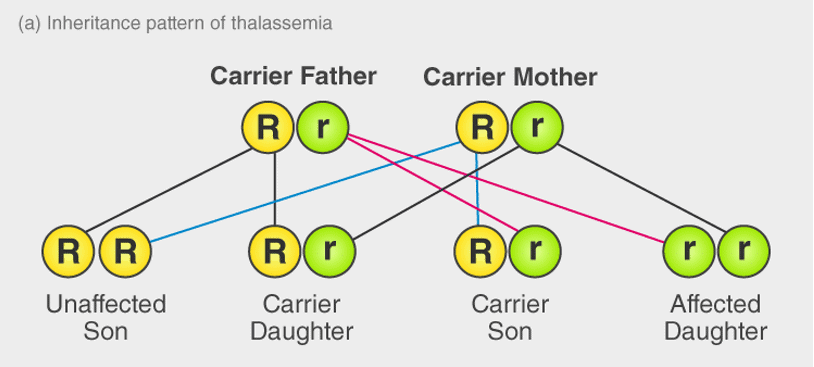
Thalassemia
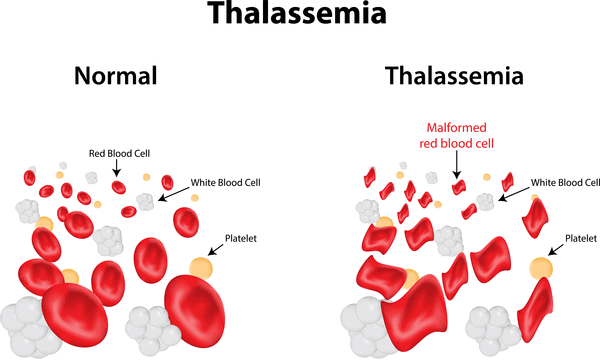
- This is a type of disorder in which the body makes an abnormal amount of hemoglobin. As a result, a large number of red blood cells are destroyed which leads to anemia.
- It is an autosomal recessive disease.
- Facial bone deformities, abdominal swelling, and dark urine are some of the symptoms of thalassemia.
- It is an inherited disease which is mainly caused due to abnormal hemoglobin synthesis. It is transferred by one of the parents who is a carrier of this disease due to either deletion of particular key gene fragments or a genetic mutation.
- There are two types of thalassemia:
- Alpha-thalassemia – A disorder in which one of the genes of alpha-globin has a mutation or abnormality.
- Beta-thalassemia – The genes of beta-globin are abnormal.
It develops when there is some abnormality in any one of the genes that are involved in the production of hemoglobin and this defect is inherited from the parents. If any of the parents have thalassemia, the baby is more likely to develop this disease so-called thalassemia minor. If both the parents suffer from this disease, you are more likely to get the disease.
There are no symptoms at an early stage but are likely to be a disease carrier. It is the most common disease in people of Asia, Africa, the Middle East, Turkey, and Greece.
Cystic Fibrosis
- This is an autosomal recessive disorder.
- This disease affects the lungs and the digestive system and the body produces thick and sticky mucus that blocks the lungs and pancreas.
- People suffering from this disorder have a very short life-span.
Hemophilia
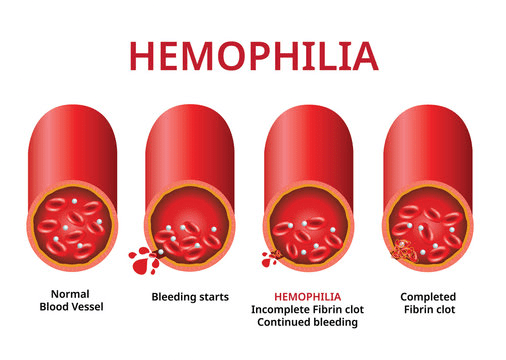 This disorder is characterized by uncontrolled bleeding and the inability of the blood to clot properly. Even a small cut or a minor injury can result in severe bleeding. Haemophilia is one among the many X-linked recessive inherited genetic disorders, where the gene causing the disorder or dysfunction is located on the X-chromosome. It results in massive internal bleeding (known as haemorrhaging) in the joints such as the knees, elbows, ankles, and also in the tissues and muscles. This can lead to considerable consequences, such as swelling and pain in the affected areas. It can even cause permanent damage to the affected body parts. When bleeding happens in a vital organ, especially in the brain, it has the potential to turn fatal.
This disorder is characterized by uncontrolled bleeding and the inability of the blood to clot properly. Even a small cut or a minor injury can result in severe bleeding. Haemophilia is one among the many X-linked recessive inherited genetic disorders, where the gene causing the disorder or dysfunction is located on the X-chromosome. It results in massive internal bleeding (known as haemorrhaging) in the joints such as the knees, elbows, ankles, and also in the tissues and muscles. This can lead to considerable consequences, such as swelling and pain in the affected areas. It can even cause permanent damage to the affected body parts. When bleeding happens in a vital organ, especially in the brain, it has the potential to turn fatal.
Types of Hemophilia
Haemophilia exists in two forms:
- Hemophilia A: It is caused specifically by a mutation in the Factor VIII gene on the X chromosome.
- Hemophilia B: This is caused by a mutation in the Factor IX gene on the X chromosome.
Hemophilia Prevention
Since haemophilia is a hereditary condition, it cannot be prevented; but it can be diagnosed and help the mother understand the risks of having a baby with haemophilia. The female members of the family are the only carriers of this syndrome. If there is a history of haemophilia in a family, it is better to consult a physician and have a blood test to examine the clotting factors and to perform a molecular genetic test to examine the carriers in their genes.
As per the studies conducted on this inherited genetic disorder, the genes from the mother can be transmitted to both her children. Among them, there are 50% chances that her son will have haemophilia A or B and 50% chances that her daughter will be a carrier of this gene.
Symptoms of Hemophilia
The signs and symptoms of haemophilia vary based on the levels of clotting factors present. These clotting factors are substances in the blood affect the process of blood coagulation. If the clotting factors are slightly reduced, then the bleeding is observed only after the surgeries. If the clotting factors are completely reduced, then spontaneous bleeding is observed.
Symptoms of spontaneous bleeding include
- Many large or deep bruises.
- Joint pain and swelling (caused by bleeding)
- Unexplained bruises or bleeding.
- Blood in urine or in stools.
- More bleeding for a normal cut or injury.
- Nosebleeds for no apparent reason.
- Excessive bleeding in tooth gums.
- Unusual bleeding after vaccinations.
Colour Blindness
Introduction
Colour blindness can be simply defined as trouble in seeing or identifying colours like blue, green and red. There are some rare cases where a person cannot see and identify any colours at all. A person with this syndrome also finds difficulties in differentiating the colours with shades. This syndrome is also called a colour vision problem or colour vision deficiency.
Colour blindness was discovered by an English chemist named John Dalton in the year 1798. During the discovery, he was also suffering from colour blindness. He wrote his first article about colour blindness, which was based on his own experience. Colour blindness is also called as Daltonism, which is named after its discoverer – John Dalton.
What are Chromosomal Abnormalities (Disorders)?
Chromosomal abnormalities are the type of genetic disorders caused due to the change in one or many chromosomes or the abnormal arrangement of the chromosomes. There are different types of chromosomal abnormalities as follows:
1. Aneuploidy – It is a condition in which there is a loss or gain of chromosomes due to abnormal segregation of genes during cell division.
2. Polyploidy – It is a condition in which the count of the entire set of chromosomes increases due to the failure of cytokinesis in cell division. It is mostly observed in plants.
In humans, when there is an extra copy of a chromosome in one of the pairs, it is called trisomy and when one of the chromosome from the pair is lacking, it is called monosomy.
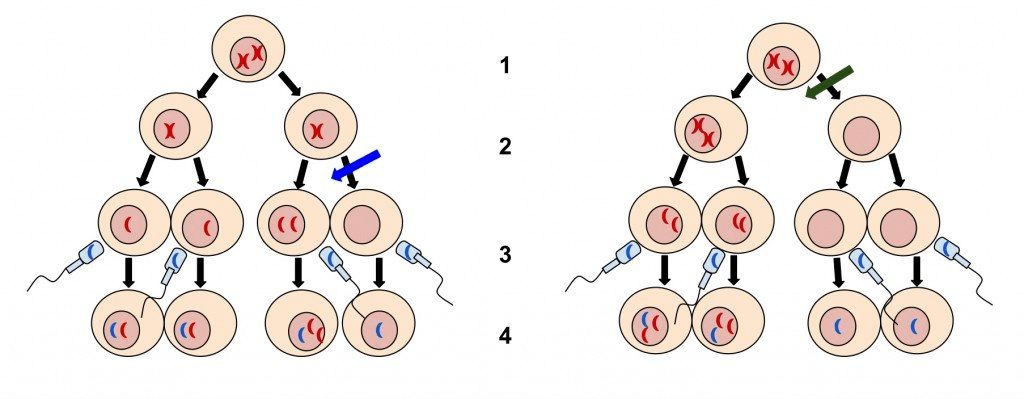 Aneuploidy v/s Polyploidy
Aneuploidy v/s Polyploidy
Aneuploidy
Normal human beings have forty six chromosomes arranged in twenty three pairs. However, even a slight variation from this pattern causes abnormalities. Chromosomal disorders are caused either due to changes in chromosomal number or changes in chromosomal structure. Changes in chromosomal number occur due to non-disjunction of chromosomes which is the failure of chromatids to dis-join during cell division leading to either aneuploidy or euploidy. Aneuploidy is a condition where one or more chromosomes are either gained or lost. Aneuploidy is of two types – trisomy and monosomy. A normal diploid individual has 2n number of chromosomes. However, when an extra chromosome is added, the condition is known as trisomy. On the other hand, when a chromosome is lost or absent, the condition is known as monosomy.
Polyploidy
Euploidy is a polyploidic condition, where more than two haploid sets of chromosomes are formed due to the failure of cytokinesis. Depending on the number of chromosomal sets added, euploidy can be triploidy, tetraploidy, pentaploid and so on.
Other common examples of chromosomal abnormalities are down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Turner syndrome.
1. Down’s Syndrome
It is caused due to the presence of an extra copy of the twenty first chromosome.The symptoms are a swollen face, bulging and slanting eyes, a small mouth and a protruding and furrowed tongue.
2. Klinefelter’s Syndrome
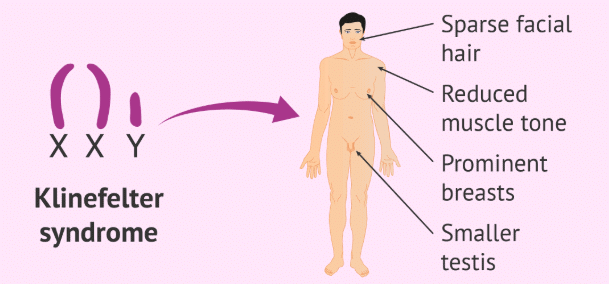 Klinefelter’s Syndrome is a condition where males have an additional X-chromosome, which results in a karyotype of forty seven, that is, XXY. It is one of the most common sex chromosome disorders in males and shows symptoms such as poor beard growth, narrow shoulders, gynaecomastia or breast development and under-developed testis. Moreover, such males are sterile.
Klinefelter’s Syndrome is a condition where males have an additional X-chromosome, which results in a karyotype of forty seven, that is, XXY. It is one of the most common sex chromosome disorders in males and shows symptoms such as poor beard growth, narrow shoulders, gynaecomastia or breast development and under-developed testis. Moreover, such males are sterile.
3. Turner’s Syndrome
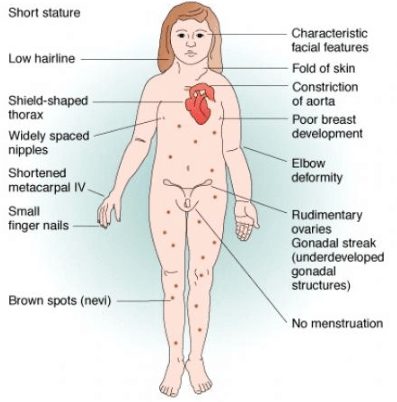 Turner’s Syndrome
Turner’s Syndrome
Turner’s Syndrome where one of the X-chromosomes is absent in females. Chromosomes in these females will be forty five with XO. Females with this syndrome show symptoms like a webbed neck, constriction of the aorta, poor breast development, under-developed ovaries and short stature.
Changes in chromosomal structure can take several forms. Some of these changes include a portion of a chromosome getting deleted, duplicated or transferred to another chromosome. While some of these structural changes in a chromosome are inherited others take place accidentally when reproductive cells are being formed or during early foetal development. Jacobsen Syndrome and Cri-du Chat Syndrome are some disorders caused due to changes in chromosomal structure. Therefore, chromosomes hold the genetic keys to all the functions of our body and any change in the number or structure of a chromosome can lead to chromosomal disorders.
|
65 videos|386 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Genetic & Chromosomal Disorders - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is a Pedigree Analysis? |  |
| 2. What is a Mendelian Disorder? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of Mendelian Disorders? |  |
| 4. What are Chromosomal Abnormalities (Disorders)? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a Mendelian Disorder and a Chromosomal Abnormality? |  |





















