JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Physics for JEE Main & Advanced > Electric Potential of a Dipole & a System of Charges
Electric Potential of a Dipole & a System of Charges | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Potential due to an Electric Dipole
- The electric dipole is an arrangement that consists of two equal and opposite charges +q and -q separated by a small distance 2a.
- Electric dipole moment is represented by a vector p of magnitude 2qa and this vector points in the direction from -q to +q.
- To find electric potential due to a dipole consider charge -q is placed at point P and charge +q is placed at point Q as shown below in the figure.
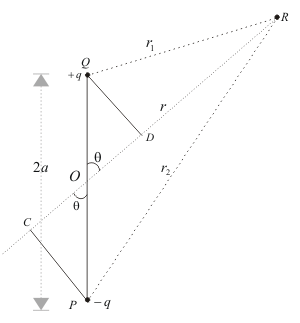 A Dipole
A Dipole - Since electric potential obeys the superposition principle so potential due to electric dipole as a whole would be sum of potential due to both the charges +q and -q. Thus
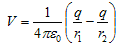
where r1 and r2 respectively are distance of charge +q and -q from point R. - Now draw line PC perpandicular to RO and line QD perpandicular to RO as shown in figure.
- From triangle POC
cosθ = OC/OP = OC/a
therefore OC=acosθ similarly OD=acosθ
Now ,
r1 = QR≅RD = OR-OD = r-acosθ
r2 = PR≅RC = OR+OC = r+acosθ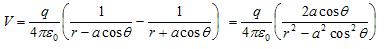
- Since magnitude of dipole is |p| = 2qa
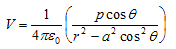
- If we consider the case where r>>a then
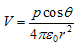
again since pcosθ= p·rˆ where, rˆ is the unit vector along the vector OR then electric potential of dipole is: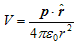
for r>>a - From above equation we can see that potential due to electric dipole is inversly proportional to r2 not ad 1/r which is the case for potential due to single charge.
Potential due to electric dipole does not only depends on r but also depends on angle between position vector r and dipole moment p.
Potential Due To A System Of Charges
- Consider a system of charges q1, q2,…, qn with position vectors r1, r2,…, r n relative to some origin. The potential V1 at P due to the charge q1 is:
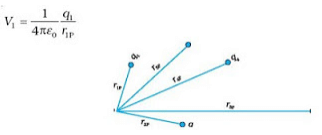 where r1P is the distance between q1 and P.
where r1P is the distance between q1 and P. - Similarly, the potential V2 at P due to q2 and due to q are given by
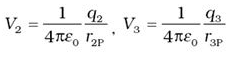 where r2P and r3P are the distances of P from charges q2 and q3, respectively; and so on for the potential due to other charges.
where r2P and r3P are the distances of P from charges q2 and q3, respectively; and so on for the potential due to other charges. - By the superposition principle, the potential V at P due to the total charge configuration is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to the individual charges
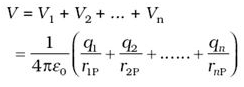
- The electric field outside the shell is as if the entire charge is concentrated at the centre. Thus, the potential outside the shell is given by:
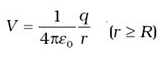 where q is the total charge on the shell and R its radius.
where q is the total charge on the shell and R its radius. - The electric field inside the shell is zero. This implies that potential is constant inside the shell (as no work is done in moving a charge inside the shell), and, therefore, equals its value at the surface, which is
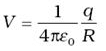
The document Electric Potential of a Dipole & a System of Charges | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Physics for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
268 videos|809 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Electric Potential of a Dipole & a System of Charges - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the electric potential of a dipole? |  |
Ans. The electric potential of a dipole is the potential energy per unit charge at a given point in the electric field created by the dipole. It is a scalar quantity and is given by the formula V = k * p * cosθ / r^2, where V is the electric potential, k is the electrostatic constant, p is the magnitude of the dipole moment, θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the position vector, and r is the distance from the dipole.
| 2. How is the electric potential of a system of charges calculated? |  |
Ans. The electric potential of a system of charges is calculated by summing up the electric potentials due to each individual charge in the system. The electric potential at a point is given by the formula V = k * q / r, where V is the electric potential, k is the electrostatic constant, q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge to the point.
| 3. Can the electric potential of a dipole be zero? |  |
Ans. Yes, the electric potential of a dipole can be zero at certain points in space. This occurs when the distance from the dipole is either very large or when the angle between the dipole moment and the position vector is 90 degrees. In these cases, the cosθ term in the formula for electric potential becomes zero, resulting in a zero potential.
| 4. How does the electric potential of a dipole change with distance? |  |
Ans. The electric potential of a dipole decreases with increasing distance from the dipole. This is because the potential is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, according to the formula V = k * p * cosθ / r^2. As the distance increases, the denominator in the formula increases, leading to a decrease in the electric potential.
| 5. Are the electric potentials of a dipole and a system of charges additive? |  |
Ans. Yes, the electric potentials of a dipole and a system of charges are additive. This means that the total electric potential at a point due to both the dipole and the charges in the system can be obtained by summing up the individual potentials. The resultant potential is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to the dipole and the charges.
Related Searches
















