Equilibrium of a Rigid Body | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
6. Body is in equilibrium : -
We can say rigid body is in equillibrium when it is in
(a) Translational equilibrium
Fnet x = 0 and Fnet y = 0 and
(b) Rotational equilibrium
Note :
(i) If net force on the body is zero then net torque of the forces may or may not be zero.
example.
A pair of forces each of same magnitude and acting in opposite direction on the rod.
(2) If net force on the body is zero then torque of the forces about each and every point is same
t about B
t about C
Ex.18 Determine the point of application of third force for which body is in equillibrium when forces of 20 N & 30 N are acting on the rod as shown in figure
Sol. Let the magnitude of third force is F, is applied in upward direction then the body is in the equilibrium when
(i) (Translational Equillibrium)
⇒ 20 + F = 30 ⇒ F = 10 N
So the body is in translational equilibrium when 10 N force act on it in upward direction.
(ii)
Let us assume that this 10 N force act. Then keep the body in rotational equilibrium So Tor que about C = 0
30 x 20 = 10 x
x = 60 cm
so 10 N force is applied at 70 cm from point A to keep the body in equilibrium.
Ex.19 Determine the point of application of force, when forces are acting on the rod as shown in figure.
Sol. Since the body is in equillibrium so we conclude and torque about any point is zero i.e.,
Let us assume that we apply F force downward at A angle q from the horizontal, at x distance from B
⇒ Fnet x = 0 which gives
F2 = 8 N
From Fnet y = 0 ⇒ 5 + 6 = F1 + 3
⇒ F1 = 8 N
If body is in equilibrium then torque about point B is zero,
⇒ 3 x 5 + F1 x - 5 x 10 = 0
⇒ 15 + 8x - 50 = 0
Ex.20 A uniform rod length l, mass m is hung from two strings of equal length from a ceiling as shown in figure. Determine the tensions in the strings ?
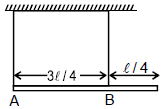
Sol. Let us assume that tension in left and right string is TA and TB respectively. Then
Rod is in equilibrium then
From
mg = TA + TB ...(1)
Ladder Problems :
Ex.21 A stationary uniform rod of mass `m', length `l' leans against a smooth vertical wall making an angle q with rough horizontal floor. Find the normal force & frictional force that is exerted by the floor on the rod?
Sol. As the rod is stationary so the linear acceleration and angular acceleration of rod is zero.
|
291 videos|648 docs|183 tests
|
FAQs on Equilibrium of a Rigid Body - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the concept of equilibrium in a rigid body? |  |
| 2. How can we determine if a rigid body is in equilibrium? |  |
| 3. What are the types of equilibrium in a rigid body? |  |
| 4. How can we calculate the sum of forces and torques in a rigid body? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of equilibrium in everyday life? |  |


















