Exercises: Chemical & Chemical Changes | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests PDF Download
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
Q.1. ____ (Mixture/Compound) is formed by chemical combination of two or more elements.
Compound is formed by chemical combination of two or more elements.
A mixture, on the other hand, is formed by the physical combination of two or more substances which retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means.
Q.2. ____ (Hydrogen/Water) is an element and ____ (water/hydrogen) is a compound.
Hydrogen is an element and water is a compound.
Water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, represented by the chemical formula H2O.
Q.3. Chemical ____ (symbols/formulae) are the abbreviations used to represent elements.
Chemical symbols are the abbreviations used to represent elements.
Each element is represented by a unique symbol, such as H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, and Na for sodium.
Q.4. Chemical ____ (abbreviation/formula) is the representation of a molecule of a compound using chemical symbols of its constituent elements.
Chemical formula is the representation of a molecule of a compound using chemical symbols of its constituent elements.
For example, the chemical formula for water is H2O, indicating that it is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Q.5. ____ (Atomicity/Valency) is the combining capacity of an element.
Valency is the combining capacity of an element.
It refers to the number of electrons that an atom of an element can gain, lose or share in order to form chemical bonds with other atoms. Atomicity, on the other hand, refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule of an element or compound.
Q.6. ____ (N/Ni) is the chemical symbol of Nickel.
Ni is the chemical symbol of Nickel. Chemical symbols are used to represent elements in the periodic table and in chemical formulas.
B. Choose the correct option.
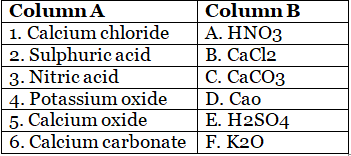
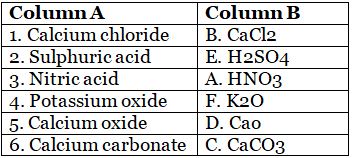
C. Match the following.
1. Calcium chloride is a compound made of calcium and chlorine ions. Its chemical formula is CaCl2. It is commonly used as a de-icer on roads and as a drying agent in laboratories.
2. Sulphuric acid, also known as oil of vitriol, is a highly corrosive strong acid with the chemical formula H2SO4. It is used in the manufacturing of fertilizers, detergents, and other chemical products.
3. Nitric acid is a strong acid with the chemical formula HNO3. It is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes.
4. Potassium oxide is a compound made of potassium and oxygen ions with the chemical formula K2O. It is used in the manufacturing of glass and ceramics.
5. Calcium oxide, also known as quicklime, is a white powder with the chemical formula CaO. It is used in the manufacturing of cement, paper, and chemicals.
6. Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks and is the main component of shells of marine organisms, snails, and eggs. It is also used as a dietary supplement and antacid.
II. Very short answer type questions
Write the chemical symbol/formula for the following.
Q.1. Sulphur
S
Q.2. Phosphorous
P
Q.3. Hydrochloric acid
HCl
Q.4. Aluminium
Al
Q.5. Zinc oxide
ZnO
III. Short Answer type Questions
Q.1. Differentiate between an element, a compound and a mixture. Give one relevant example for each.
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, while a compound is a pure substance made up of two or more different types of atoms chemically combined in a fixed ratio. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Example: Element - Oxygen, Compound - Water, Mixture - Saltwater.
Q.2. What is atomicity? Give one example each for monoatomic, diatomic and tetra atomic elements.
Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule. Monoatomic elements consist of only one atom, such as Helium (He). Diatomic elements consist of two atoms, such as Oxygen (O2) and Nitrogen (N2). Tetra atomic elements consist of four atoms, such as Phosphorus (P4).
Q.3. Name all the elements present in the following compounds: SO2, PbCl2, Ba(OH)2, LIF
Elements present in the compounds are: SO2 - Sulfur and Oxygen, PbCl2 - Lead and Chlorine, Ba(OH)2 - Barium, Oxygen, and Hydrogen, LIF - Lithium and Fluorine.
Q.4. Why do the cut surfaces of fruits and vegetables turn brown?
The cut surfaces of fruits and vegetables turn brown due to a process called oxidation. When the cells of fruits and vegetables are cut or damaged, they release an enzyme called polyphenol oxidase. This enzyme reacts with oxygen in the air, causing the cut surfaces to turn brown.
Q.5. Write a short note on crystallization.
Crystallization is a process in which a solid substance forms a crystal structure. This process occurs when a solid substance is dissolved in a liquid, and the liquid is then slowly evaporated or cooled. As the liquid evaporates or cools, the solute particles come together and form a repeating pattern, creating a crystal. Crystallization is used in many industries, such as the production of salt, sugar, and pharmaceuticals.
IV. Long answer type Questions
Q.1. Explain the process used for removing impurities from common salt.
The process used for removing impurities from common salt is called 'crystallization'. In this process, impure salt is dissolved in water to form a salt solution. The solution is then filtered to remove any insoluble impurities. Next, the solution is heated to evaporate the water and form salt crystals. The impurities are left behind in the solution and the pure salt crystals are collected.
Q.2. Represent the following using chemical symbols/formulae.
(a) Two atoms of the element neon
(b) A molecule of the element nitrogen
(c) A molecule of the compound carbon dioxide
(d) Three molecules of the compound water
(e) Four molecules of the compound magnesium oxide
(a) Ne
(b) N2
(c) CO2
(d) 3H2O
(e) 4MgO
Q.3. Balance the following equations.
(a) H2 + O2 → H2O
(b) N2 + H2 → NH3
(c) KClO3→ KCl + O2
(d) HCl + Mg(OH)2 → MgCl2 + H2O
(e) K + H2O → KOH + H2
(a)2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
(b) N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
(c) 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
(d) 2HCl + Mg(OH)2 → MgCl2 + 2H2O
(e) 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
Q.4. Complete the following word equations. Give their balanced chemical equations also.
(a) Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide (2Mg + O2 → 2MgO)
(b) Iron + Oxygen + Water → Iron oxide hydroxide (2Fe + 3O2 + 3H2O → Fe2O3.H2O)
(c) Vinegar + Baking soda → Carbon dioxide + Water + Sodium acetate (CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CO2 + H2O + CH3COONa)
(d) Carbon dioxide + Lime water → Calcium carbonate + Water (CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O)
(e) Copper sulphate + Iron → Iron sulphate + Copper (CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu)
|
139 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|