Exploring Substances: Acidic, Basic and Neutral Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 2 Free PDF
Introduction
On 28 February, the school celebrated National Science Day with a science fair. At the entrance, Ashwin and Keerthi were given plain white sheets of paper. They were puzzled—why a blank sheet?
Soon, a volunteer sprayed a liquid on their sheets, and like magic, the words "Welcome to the Wonderful World of Science" appeared! This amazing trick made them very curious.
At the Colourful World of Substances stall, they saw many experiments where mixing things changed their colour. Excited to learn more, they decided to explore the science behind it.
Let’s join them on this fun journey!
Nature - Our Science Laboratory
We can determine if a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral by using special tools called indicators, which change color or smell when mixed with different substances.
1. Litmus as an Indicator
What is Litmus?
- Litmus is a natural material obtained from lichens, which are organisms formed by a fungus and an alga living together, often found on rocks and trees in rainy, clean areas.
- Forms of Litmus: It is available as blue and red litmus paper strips, used to test substances
- It is called as an acid-base indicator.
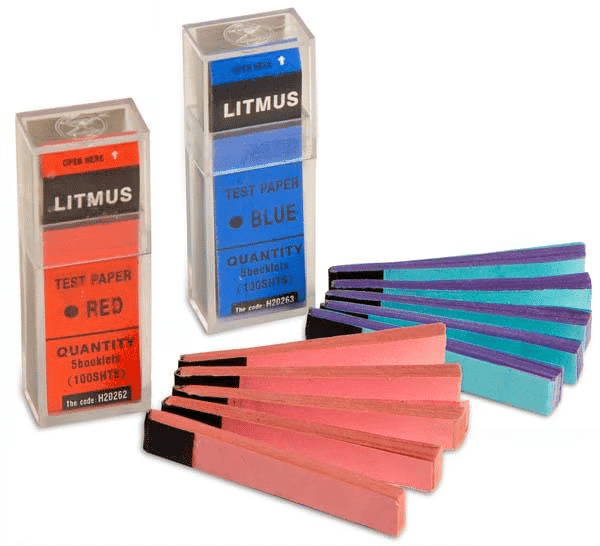

How Litmus Works:
- If a substance turns blue litmus paper red, it is acidic.
- If a substance turns red litmus paper blue, it is basic.
- If there’s no color change in either litmus paper, the substance is neutral.
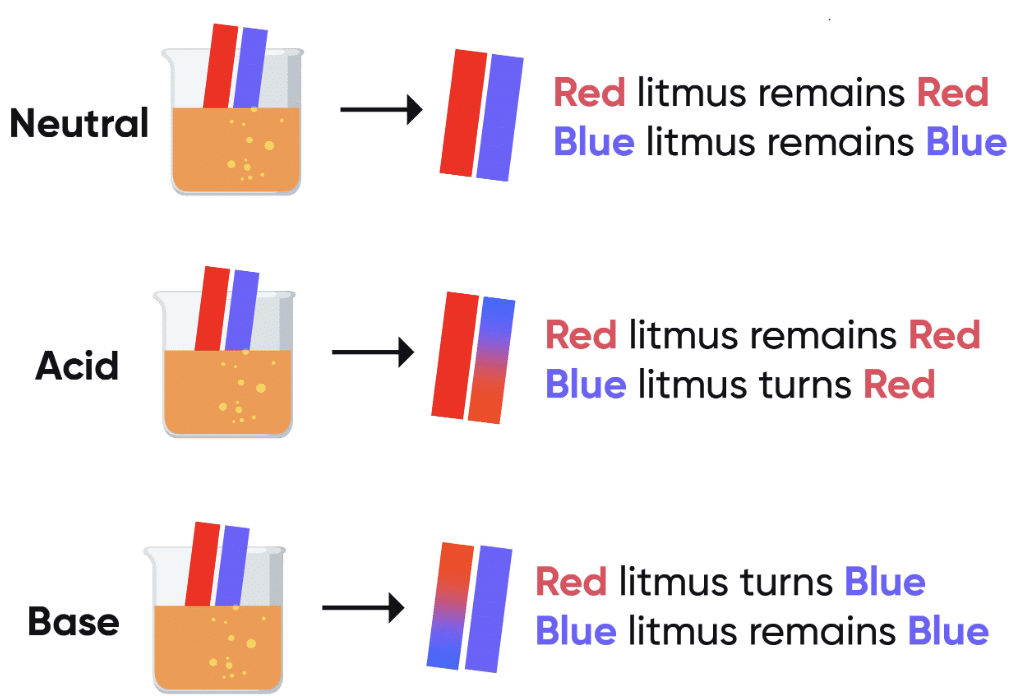
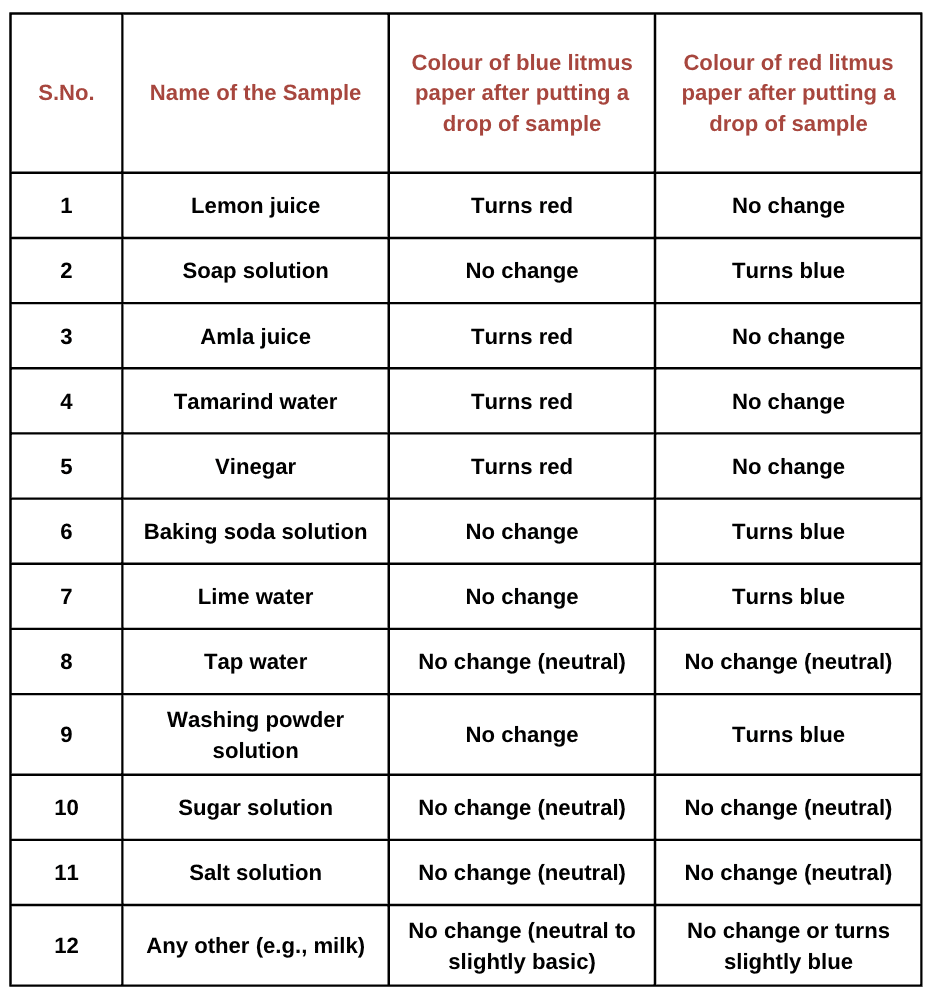
Here are the test results showing the nature of samples using blue and red litmus papers.
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids:
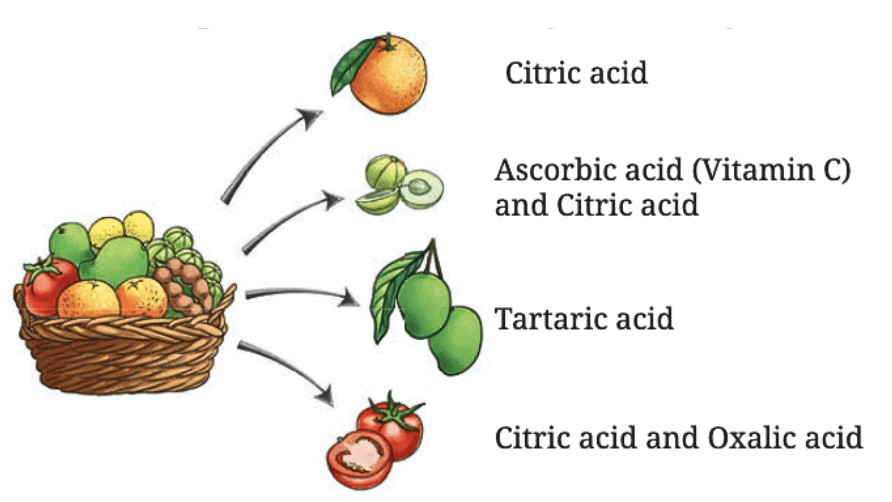
- Taste sour, like lemon juice, tamarind, or vinegar.
- Contain specific acids, e.g., citric acid in lemon, lactic acid in curd, tartaric acid in tamarind, and acetic acid in vinegar.
- Turn blue litmus red and red rose extract red.
Bases:
- Feel slippery or soapy when rubbed, like baking soda solution or soap.
- Often taste bitter, but not all bitter things are bases (e.g., bitter gourd is not basic).
- Turn red litmus blue, red rose extract green, and turmeric paper red.
Neutral Substances:
- Do not have a strong taste or slippery feel.
- Do not change the color of indicators like litmus, red rose extract, or turmeric.
2. Red Rose as an Indicator

Preparation of Red Rose Extract
- Red rose extract is prepared by collecting fresh rose petals and washing them properly.
- The petals are then crushed and soaked in hot water.
- After some time, the mixture is filtered to get a red-colored liquid known as red rose extract.
How It Works:
- In acidic substances, the extract changes to a shade of red.
- In basic substances, it changes to a shade of green.
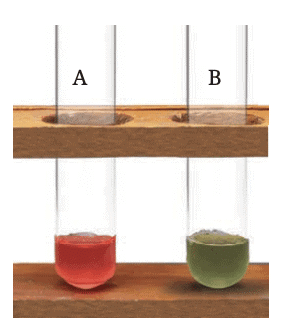 The changes in colour of the red rose extract on adding lemon juice (A) and soap solution (B)
The changes in colour of the red rose extract on adding lemon juice (A) and soap solution (B) - In neutral substances, the extract’s color remains unchanged.
- Red rose extract is an acid-base indicator because it shows different colors for acidic and basic substances, similar to litmus.
Some examples:
- Lemon juice (acidic) turns the extract red.
- Soap solution (basic) turns it green.
- Neutral substances like sugar solution don’t affect the color.
3. Turmeric as an Indicator
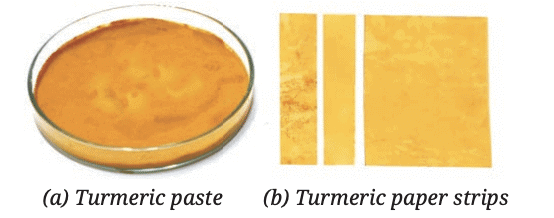
Preparation
Turmeric powder is mixed with water to make a paste, spread on filter paper, and dried to create yellow turmeric paper strips.
 How It Works:
How It Works:
- Basic substances turn turmeric paper red.
- Acidic and neutral substances do not change the yellow color of turmeric paper.
- A turmeric stain on a shirt changes color when soap (basic) is applied, showing its indicator property.
- Turmeric paper can only identify basic substances, not distinguish between acidic and neutral ones.
Here are the test results showing the nature of samples using turmeric paper: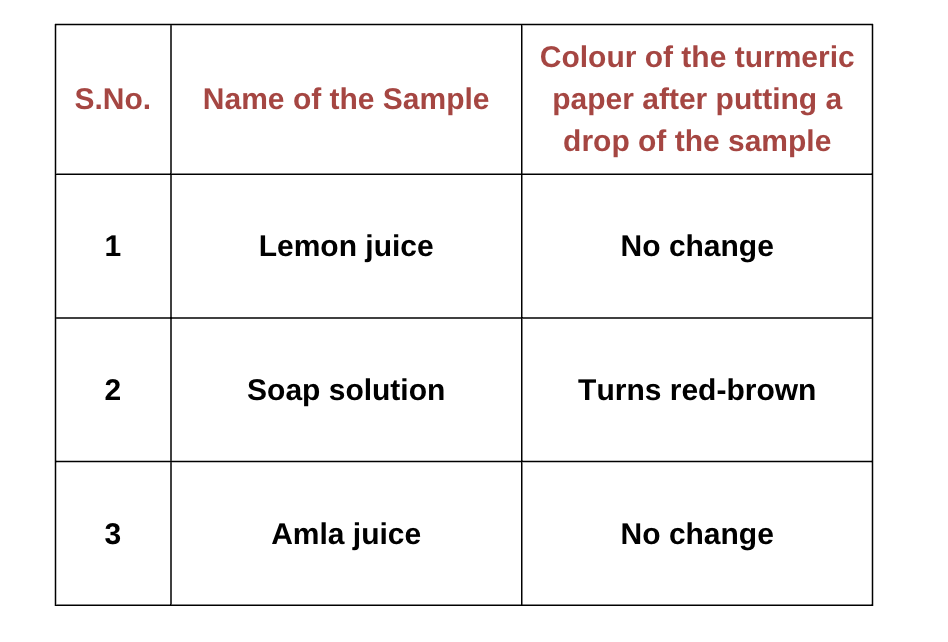
Fascinating Facts: Why is Turmeric Called the ‘Golden’ Spice?
Turmeric, also known as Haldi, is a bright yellow spice that belongs to the ginger family. Grown widely in India and other countries, it’s a common ingredient in everyday cooking. But turmeric is much more than just a flavouring agent!
In the Ayurvedic system of medicine, turmeric is believed to offer several health benefits. That’s why it plays a key role in many traditional home remedies. Its rich golden color and healing properties have earned it the name ‘Golden Spice’.
Researchers today are also studying turmeric for its potential benefits beyond taste and color—making this age-old spice even more special!
4. Olfactory Indicators
- Olfactory indicators are special substances whose smell changes when they come in contact with acidic or basic substances.
- For example, a cloth soaked in onion juice loses its smell when mixed with tamarind water (which is acidic) or baking soda solution (which is basic).
- These indicators are useful because they help us identify whether a substance is acidic or basic just by observing changes in smell.

5. Other Natural Indicators
Substances like beetroot, purple cabbage, red hibiscus (gudhal), and Indian blackberry (jamun) can also act as acid-base indicators, changing colors in acidic or basic solutions.
Did You Know ?
Hydrangea plants in the Himalayas or North-eastern states produce blue flowers in acidic soil and pink or red flowers in basic soil, showing how soil nature affects plants.
Know a Scientist: Acharya Prafulla Chandra Ray
Acharya Prafulla Chandra Ray is known as the Father of Modern Indian Chemistry. He earned his chemistry doctorate in the UK and later returned to India. In 1901, he started India’s first pharmaceutical company.
He wrote about the history of Indian science to show the world the achievements of ancient Indian scientists. A true reformer, he also supported teaching in the mother tongue to make education easier and more meaningful.
Let's Revise
Q: How does turmeric act as a natural indicator?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Turmeric turns red when it comes in contact with basic substances, but it stays yellow with acidic or neutral substances.
Q: What are olfactory indicators and how do they work?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Olfactory indicators change their smell when mixed with acids or bases—for example, onion juice loses its smell when mixed with acidic or basic solutions.
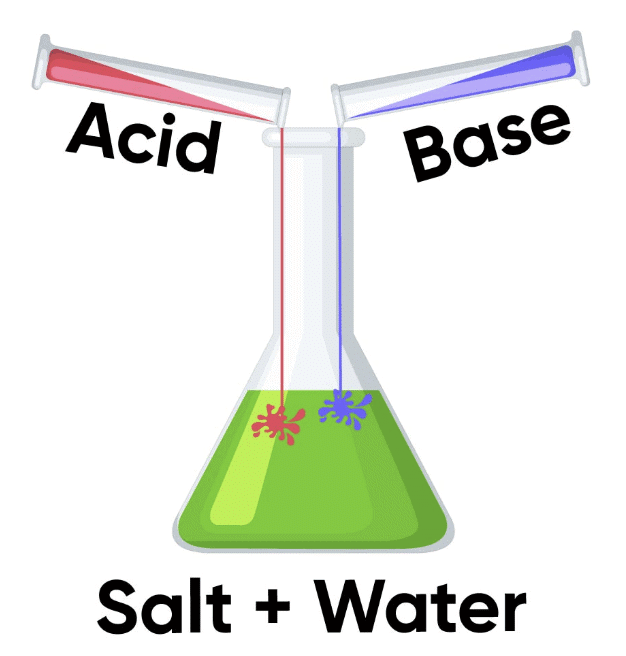
What Happens When Acidic Substances Mix with Basic Substances?
1. Neutralization Process
- When an acid (e.g., lemon juice) is mixed with a base (e.g., lime water) in the right amount, they react to form a solution that is neither acidic nor basic.
- This reaction is called neutralization.
- Neutralization shows how acids and bases balance each other, creating a neutral substance that doesn’t affect indicators.
- This process is key to understanding how substances interact chemically.
Activity
Let’s see how acids and bases react using litmus solution:
First, add lemon juice (which is acidic) to a blue litmus solution. It turns red, showing the presence of an acid.
Now, slowly add lime water (a base) to the same solution. As more base is added, the red color starts changing back to blue, showing the solution is becoming neutral or basic.
This happens because the base cancels the effect of the acid, resulting in a neutral solution.
2. Products of Neutralization
- The reaction produces salt, water, and releases heat.
- Acid + Base → Salt + Water + Heat.
Neutralization in Daily Life
Situation 1: Ant Bite
- When a red ant bites, it injects formic acid into the skin, causing redness and stinging pain.
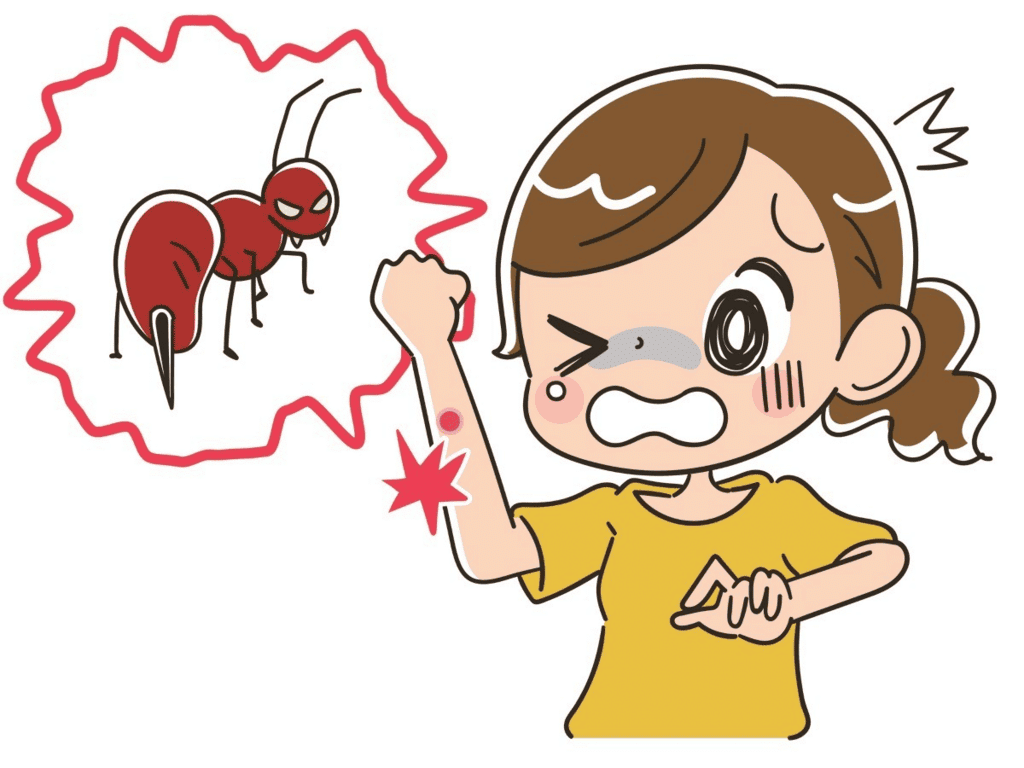
- Applying moist baking soda, which is a base, neutralizes the formic acid, relieving the pain and reducing swelling.
- Different regions may use other basic remedies, like lime water, for ant bites.
Situation 2: Soil Treatment
- Farmers may notice poor plant growth if the soil becomes too acidic due to excessive use of chemical fertilizers.
- Adding lime (a base, like calcium oxide) neutralizes the acidic soil, making it suitable for plant growth.

- If the soil is too basic, organic matter like manure or composted leaves is added, which releases acids to neutralize the basic soil.
- Neutral soil may still need nutrients if plants are unhealthy, showing that soil health involves more than just acidity or basicity.
Situation 3: Factory Waste
- Acidic waste from factories can pollute lakes, harming fish and other aquatic life.
- Before releasing waste into lakes, basic substances are added to neutralize the acidity, making the water safe for fish.
Q: What is a neutralization reaction and what are its products?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid and a base react to form salt, water, and heat.
Q: How does baking soda help relieve pain from an ant bite?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Baking soda, being a base, neutralizes the formic acid injected by the ant, reducing pain and swelling.
Points to Remember
- Substance Classification: Substances are grouped into acidic, basic, or neutral based on how they interact with indicators.
- Litmus: From lichens, comes as blue and red paper: acids turn blue litmus red, and bases turn red litmus blue, while neutral substances cause no change.
- Red-Rose Extract: Made from crushed petals, it turns red in acidic solutions and green in basic solutions, acting as an acid–base indicator.
- Turmeric Paper: Prepared from turmeric paste, it turns red in basic solutions but remains yellow in acidic or neutral solutions, making it useful only for detecting bases.
- Olfactory Indicators: Like onion-soaked cloth, they change smell when mixed with acidic or basic substances, helping identify their nature.
- Other Natural Indicators: Beetroot, purple cabbage, red hibiscus, and Indian blackberry also show color changes in acidic or basic solutions.
- Acid Properties: Acids taste sour (e.g., lemon juice contains citric acid; vinegar contains acetic acid) and turn blue litmus red.
- Base Properties: Bases feel slippery, often taste bitter, and turn red litmus blue, red-rose extract green, and turmeric paper red.
- Neutral Substances: Like tap water or sugar solution, they don’t change the color or smell of indicators.
- Neutralization: The reaction between an acid and a base forms salt, water, and releases heat, resulting in a neutral solution.
Neutralization in Daily Life:
Relieve ant bites by applying baking-soda paste to neutralize formic acid.
Treat acidic soil with lime or basic soil with organic matter to help plants grow.
Neutralize acidic factory waste to protect aquatic life in lakes.
Hydrangea flowers change color based on soil pH: blue in acidic soil, pink/red in basic soil—nature’s own acid–base indicator.
Creative uses, like writing messages with basic solutions on turmeric paper, show how indicators can be applied in art or communication.
Difficult Words and Their Meanings
- Acidic: A substance that tastes sour, turns blue litmus paper red, and red rose extract red, like lemon juice or vinegar.
- Basic: A substance that feels slippery turns red litmus paper blue, red rose extract green, and turmeric paper red, like soap or baking soda.
- Neutral: A substance that doesn’t affect indicators’ color or smell and is neither acidic nor basic, like sugar solution or tap water.
- Indicator: A tool that changes color or smell to show if a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral, such as litmus, red rose extract, or turmeric.
- Litmus: A natural substance from lichens, used as blue or red paper strips to test if a substance is acidic (turns blue litmus red) or basic (turns red litmus blue).
- Lichens: Organisms made of a fungus and an alga living together, found on rocks and trees, used to make litmus.
- Neutralization: A chemical reaction where an acid and base mix to form salt, water, and heat, creating a neutral solution.
- Olfactory: Related to the sense of smell, used for indicators like onion that change odor in acidic or basic substances.
- Extract: A liquid obtained by crushing and soaking a substance (like red rose petals) in water and filtering it, used as an indicator.
- Formic Acid: An acidic substance injected by ants during a bite, causing pain and redness, which can be neutralized by a base like baking soda.
FAQs on Exploring Substances: Acidic, Basic and Neutral Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 2 Free PDF
| 1. What are the main characteristics of acidic, basic, and neutral substances? |  |
| 2. How can we identify acidic and basic substances at home? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acidic, basic, and neutral substances? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to understand the properties of acids and bases? |  |
| 5. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |




















