Exponential & Logarithmic Functions | Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Exponential Function
In Mathematics, an exponential function is a function whose value is a constant which is raised to the power of an argument, especially with the constant “e”. The exponent function is often used in many real-life applications. In this article, let us discuss what is an exponential function formula, properties, derivatives with examples.
Exponential Function Formula
The exponential function is an important mathematical function which is of the form
f(x) = ax
Where a>0 and a is not equal to 1.
x is any real number.
If the variable is negative, the function is undefined for -1 < x < 1.
Here,
“x” is a variable
“a” is a constant, which is the base of the function.
But, mostly the base of the exponential function is encountered by the transcendental number “e”, which is approximately equal to 2.71828.
Exponential Function Graph
The following figure represents the graph of exponents of x. It can be seen that as the exponent increases, the curves get steeper and the rate of growth increases respectively. Thus for x > 1, the value of y = fn(x) increases for increasing values of (n).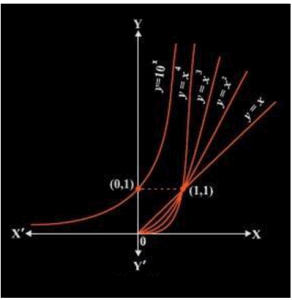 From the above discussion, it can be seen that the nature of polynomial functions is dependent on its degree. Higher the degree of any polynomial function, then higher is its growth. A function which grows faster than a polynomial function is y = f(x) = ax, where a>1. Thus, for any of the positive integers n the function f (x) is said to grow faster than that of fn(x).
From the above discussion, it can be seen that the nature of polynomial functions is dependent on its degree. Higher the degree of any polynomial function, then higher is its growth. A function which grows faster than a polynomial function is y = f(x) = ax, where a>1. Thus, for any of the positive integers n the function f (x) is said to grow faster than that of fn(x).
Thus, the exponential function having base greater than 1, i.e., a > 1 is defined as y = f(x) = ax. The domain of exponential function will be the set of entire real numbers R and the range are said to be the set of all the positive real numbers.
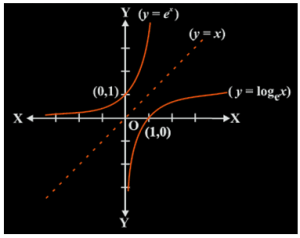
It must be noted that exponential function is increasing and the point (0, 1) always lies on the graph of an exponential function. Also, it is very close to zero if the value of x is largely negative.
Exponential function having base 10 is known as a common exponential function. Consider the following series: 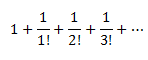
The value of this series lies between 2 &3. it is represented by e. Keeping e as base the function, we get y = ex, which is a very important function in mathematics known as a natural exponential function.
For a > 1, the logarithm of b to base a is x if ax = b. Thus, loga b = x if ax = b. This function is known as logarithmic function. 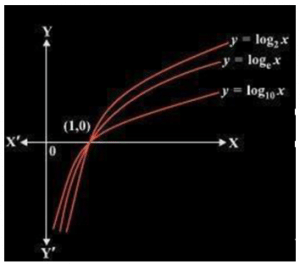
For base a = 10, this function is known as common logarithm and for base a = e, it is known as natural logarithm denoted by ln x. Following are some of the important observations regarding logarithmic functions which has base a>1.
- The domain of log function consists of positive real numbers only, as we cannot interpret the meaning of log functions for negative values.
- For the log function, though the domain is only the set of positive real numbers, the range is set of all real values, I.e. R
- When we plot the graph of log functions and move from left to right, the functions show increasing behaviour.
- The graph of log function never cuts x-axis or y-axis, though it seems to tend towards them.
- Logap = α, logbp = β and logba = µ, then aα = p, bβ = p and bµ = a
- Logbpq = Logbp + Logbq
- Logbpy = ylogbp
- Logb (p/q) = logbp – logbq
Exponential Function Derivative
Let us now focus on the derivative of exponential functions.
The derivative of ex with respect to x is ex, I.e. d(ex)/dx = ex
It is noted that the exponential function f(x) =ex has a special property. It means that the derivative of the function is the function itself.
(i.e) = f ‘(x) = ex = f(x)
Exponential Function Properties
The following are the properties of the exponential functions: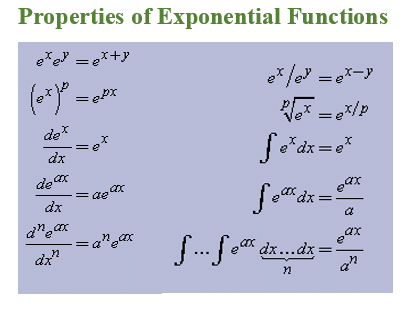
Exponential Function Example
Example 1: Solve 4x = 43
Solution: Since the bases are the same (i.e. 5), equate the values of powers.
So, the value of x is 3.
Example 2: Solve 61-x = 64
Solution: From the given equation, it is noted that the bases are the same (i.e. 6), equate the values of powers.
It means that
1-x = 4
Now, simplify this equation, we get
-x = 4 - 1
-x = 3
x = -3
Therefore, the value of x is -3.
|
146 videos|222 docs|220 tests
|
FAQs on Exponential & Logarithmic Functions - Mathematics for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is an exponential function? |  |
| 2. How are exponential functions different from linear functions? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of exponential functions? |  |
| 4. How are logarithmic functions related to exponential functions? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of exponential functions? |  |
















