Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Extra Question Answers - Manufacturing Industries
Short Answer Questions
Q1: ‘‘Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of economic development of a country.’’ Support the statement with examples.
Ans: Manufacturing sector is consider as the backbone:
- It helps in modernizing agriculture.
- Helps in providing jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Reduces unemployment and poverty.
- It brings down the regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
- The export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce.
Q2:How can agriculture and industry go hand in hand?
Ans:The agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its production. It produces equipments like tractors, harvesters, threshers, etc. On the other hand, industries are run on agricultural products like cotton, sugarcane, jute, edible oils, etc.
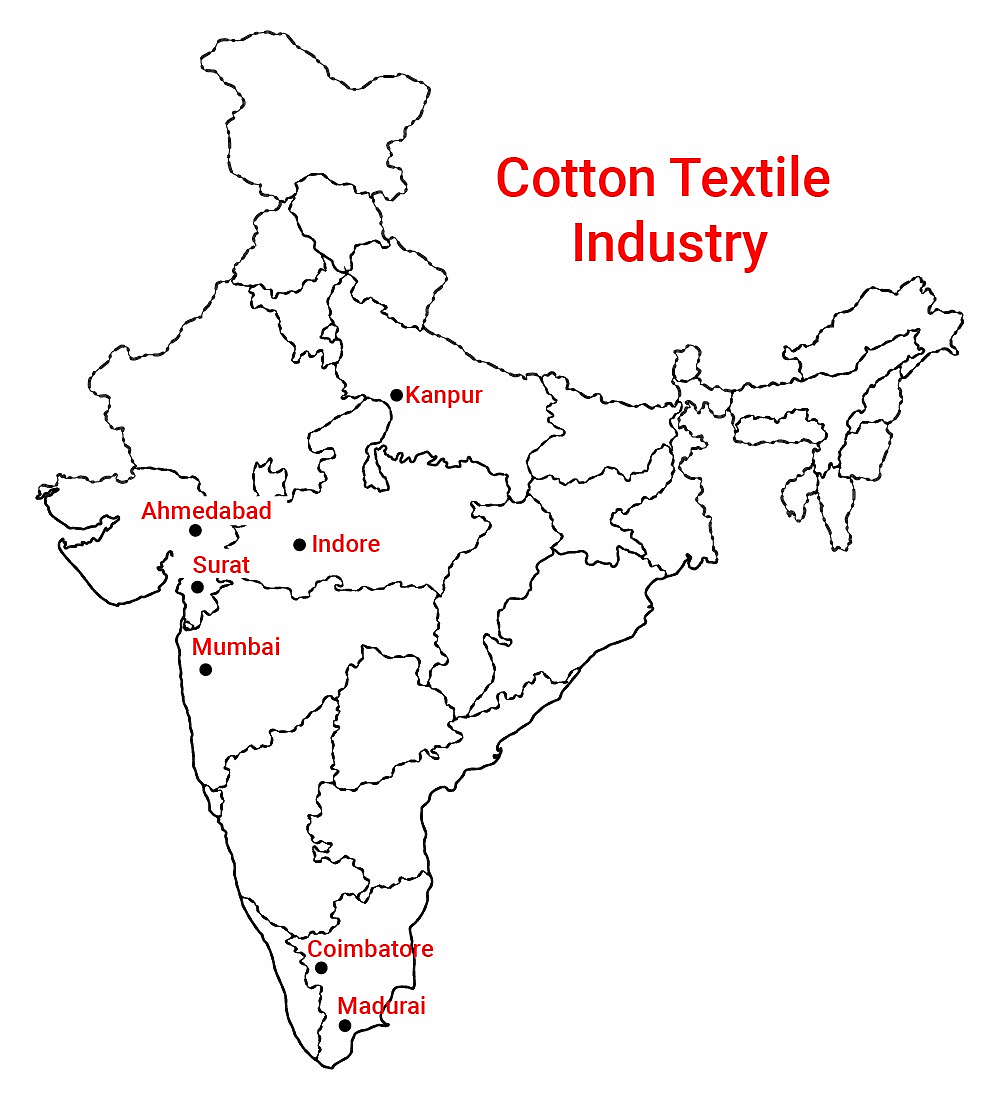
Q3:Which factors were responsible for the concentration of cotton textile industries in Maharashtra and Gujarat?
Ans:Factors responsible for the concentration of cotton textile industries in Maharashtra and Gujarat:
- Raw cotton is easily available in and around that area because of the black cotton soil.
- Transport including accessible port facilities for export of cotton goods.
- Cheap and skilled labour is available around that area.
- Favourable moist climate contribute towards its localisation.
Q4: What is the contribution of industry to the national economy of India? Compare it with the East-Asian countries. What is the desired growth and present position of industry in GDP?
Ans:Desired growth and present position of industry in GDP are as follows:
- The share of the manufacturing sector is 17% of the GDP out of a total of 27% for the industry. Out of this 10% is for the mining, quarrying, electricity and gas. As compared to East-Asian countries, it is very low where it is about 25% to 35%.
- Over the last decade, the growth rate in manufacturing has been 7% per annum.
- The desired growth rate is 12% for the next decade. It has increased to 9% to 10% per annum since 2003.
- It is expected that due to the inclusion of policy by the government and efforts by the industry to increase production, economists predicted that such measures might increase manufacturing over the next decade.
- To fulfil this aspect, the National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) has been set up.
Q5: Mention any two challenges faced by the jute industry in India. State any one step taken by the government to stimulate its demand.
Ans:The two important challenges faced by the jute industry in India are as follows:
- Stiff competition in the International market from synthetic substitutes and
- To face the challenges of competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil, Phillippines, Egypt, and Thailand.
- The government policy of mandatory use of jute packaging is one step on this line.
Q6: Mention any two factors that have contributed to the healthy growth of the automobile industry in India. Name two centres where this industry is located.
Ans: Two factors that have contributed to the healthy growth of the automobile industry in India are as follows:
- The introduction of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the industry with global developments.
- The two centres of the automobile industry:
(i) Jamshedpur and
(ii) Gurgaon.
Q7: What are the three main reasons for shifting the sugar mills to Maharashtra in recent years?
Ans:Three main reasons are as follows:
- The cane produced has a higher sucrose content.
- The cooler climate ensures a longer crushing season.
- The cooperatives are more successful in these state.
 Sugar Mill
Sugar Mill
Q8: What is natural gas? What are its advantages? Name one region of India where its reserves are found.
Ans:Natural gas is an important clean energy resource found in association with or without petroleum.
- It is used as a source of energy as well as industrial raw materials in the petrochemical industry.
- Large reserves of Natural gas have been discovered in the Krishna-Godavari basin of Andhra Pradesh.
Q9: What are software technology parks? State any two points of significance of the Information Technology industry in India?
Ans:Software technology parks provide single window services and high data communication facilities to software experts.
The two significant points of IT industries are as follows:
- It generates huge employment. Up to March 31, 2005, it employed over one million persons, 30 per cent of which are women.
- The industry has been a major foreign exchange earner through growing Business processes outsourcing (BPO) sources.
Q10:Why do you feel that there are plans to shift sugar mills to South India?
Ans: Reasons to shift sugar mills:
- Sugarcane produced in these states have higher sugar content.
- The cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
- The cooperatives are more successful in these states.
- If sugarcane is transported from South to North India, due to delays in trains, sugarcane loses its sugar content as it is a perishable good.
Q11: Mention any six factors responsible for the location of jute mills in the Hugli basin.
Ans:Six factors responsible for the location of jute mills in the Hugli basin as follows:
- Proximity of the jute-producing areas.
- Cheap water transport facilities.
- Good network of railways, roadways and waterways to facilitate movement of raw materials to the mills.
- Abundant water for processing raw jute.
- Cheap labour from West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh.
- Bank, insurance and port facilities for the export of jute goods.
Q12: Why is there a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states in India? Explain any three reasons.
Ans: Three main reasons are as follows:
- The cane produced has a higher sucrose content.
- The cooler climate ensures a longer crushing season.
- The cooperatives are more successful in these states.
Q13: Distinguish between an integrated steel plant and a mini steel plants stating three points of distinction.
Ans:Distinguishing between the two as follows:
- An Integrated steel plant is larger than Mini Steel Plant.
- Mini steel plant use steel scrap and sponge iron while Integrated steel plant use basic raw materials ie iron ore for making steel.
- Mini steel plant produces mild and alloy steel while integrated steel plant produces only steel.
Q14: Explain any three problems faced by cotton textile industries in India.
Ans:Three problems faced by cotton textile industries in India are as follows:
- The power supply is erratic and the machinery is backdated.
- Output of labour is low.
- Facing stiff competition with the synthetic fibre industry.
 Cotton Industry
Cotton Industry
Q15: Distinguish between agro-based and mineral-based industries. Also, give two examples of each.
Ans:Distinguishing between the two as follows: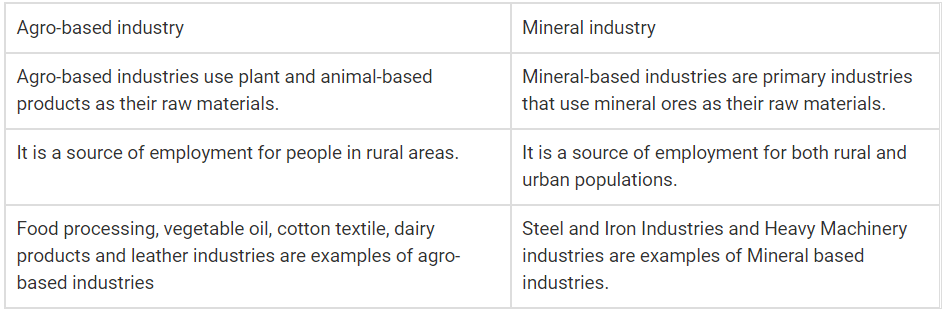
Q16: Why is the iron and steel industry called the basic and heavy industry?
Ans:Iron and steel industry is called basic heavy industry because its:
- Large scale of operation both input and output.
- It's output ie, steel is used for making machinery, construction, defence etc purposes as basic raw materials. Therefore it is called basic industry.
Q17: Why is the cotton textile industry the largest industry in India today? Give any three reasons.
Ans:Cotton textile industry the largest industry in India today:
- The cotton textile industry contributes 14 per cent of the total industrial production.
- It provides employment to 35 million persons directly – the second largest after agriculture.
- It earns foreign exchange of about 24.6 per cent (4 per cent of GDP).
Q18: How does industrial pollution degrade the environment? Explain with three examples.
Ans:The three types of pollution caused by industries are air pollution, water pollution and Noise pollution.
- Air pollution through the spewing of smoke from industry pollutes the air with sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Industrial wastes and effluents discharged through industries into rivers and ponds cause water pollution
- Besides, industrial and construction activities generate noise pollution.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain any two main challenges faced by the jute industry in India. Explain any three objectives of National Jute Policy.
Ans: Challenges faced by the jute industry:
- Stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes.
- To stimulate the demand of the products need to be diversified.
- Stiff competition from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil etc.
Objective of National Jute policy:
- Increasing productivity
- Improving quality
- Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers.
- Enhancing the yield per hectare.
Q2: What is India’s status in chemical production?
Ans:India's chemical industry stands as a pivotal contributor to the nation's economic framework, constituting approximately three percent of the GDP.
- Ranked as the third-largest in Asiaand twelfth globally, this industry exhibits a diverse landscape encompassing both large and small-scale manufacturing units, fostering adaptability and dynamism.
- The recent surge in growth within both the inorganic and organic sectors is propelled by factors like burgeoning domestic and global demand, supportive government policies, and a skilled workforce.
- This expansion has not only facilitated job creationbut has also opened up new avenues for exports, establishing India as a significant player in the worldwide chemical market.
- The sector's broad product spectrum, combined with strategic initiatives like "Make in India," reinforces its integral role in the nation's economic development, contributing to industrial resilience and global competitiveness.
 Chemical Industry
Chemical Industry
Q3: What is the status of the cement industry in India?
Ans: The cement industry in India has a rich history, with the establishment of thefirst plant in Chennai in 1904.Post-Independence, the sector witnessed significant expansion, and key policy reforms in 1989, including the decontrol of price and distribution, and accelerated progress in capacity, technology, and production processes.
Currently, India hosts 128 large and 332 mini cement plants, highlighting the industry's substantial role in driving infrastructure development. This diversification allows for the production of various cement types, catering to both domestic and international demands.
The industry's adaptability to modern processes is a noteworthy aspect that positions India competitively in the global cement market. This flexibility not only supports domestic construction requirements but also establishes India as a significant exporter, contributing significantly to international construction needs.
Q4: What is the current position of the automobile industry in India?
Ans: The current position of the automobile industry in India as follows:
- The automobile industry provides vehicles for quick transport of goods and passengers. Trucks, buses, cars, motorcycles, scooters, three-wheelers and multi-utility vehicles are manufactured in India at various centres.
- After the liberalisation, the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market, which led to the healthy growth of the industry including passenger cars, two and three-wheelers.
- The industry had experienced a quantum jump in less than 15 years. Foreign Direct Investment brought in new technology and aligned the industry with global developments.
Q5: Why are sugar mills concentrated in sugarcane-producing areas? Explain any three problems faced by the sugar industry in India.
Ans:Sugar industries are concentrated in the sugarcane-producing areas:
- Sugarcane is a perishable good, it loses its sucrose content if delays in transportation occur, so it needs to be in a nearby place.
- Sugarcane is bulky and perishable, so transportation cost reduces.
- Near it is to the production area, its production automatically increases.
- The raw material used in the sugar mills, sugarcane is bulky.
- In haulage, its sucrose content reduces.
Challenges:
- Seasonal natureof the industry.
- Old and inefficient methods of production.
- Transport delays in reaching cane to the mills.
- Need to maximise the use of bagasse.
Q6: Analyse the role of chemical industries in the Indian economy.
Ans:Role of chemical industries in the Indian Economy:
- It contributes approximately 3 % of the GDP.
- It is the 3rd largest in Asia and occupies the 12th place in the world.
- It compromises both large and small-scale manufacturing units.
- Rapid growth has been recorded in both inorganic and organic sector.
- Organic chemicals include petrochemicals which are used for manufacturing of synthetic fibers, rubber, plastics, and dye stuffs.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Extra Question Answers - Manufacturing Industries
| 1. What are the main types of manufacturing industries? |  |
| 2. What role do manufacturing industries play in the economy? |  |
| 3. How does the manufacturing process affect the environment? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by manufacturing industries today? |  |
| 5. How can manufacturing industries improve efficiency? |  |

















