|
Card: 1 / 46 |
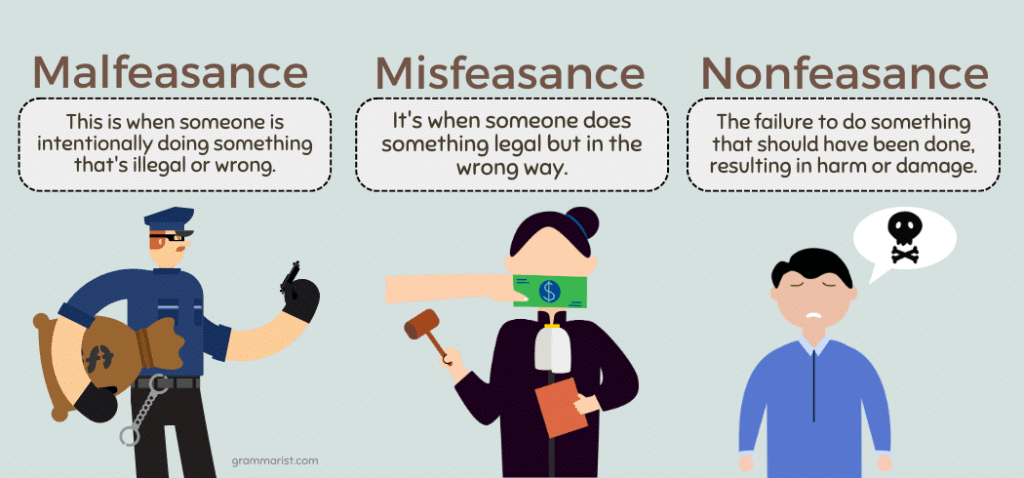
Tort law is based on the principle 'Ubi jus ibi remedium', which means ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 3 / 46 |
Injuria sine damnum refers to a situation where ___ occurs without any actual harm to the plaintiff. |
|
Card: 5 / 46 |
True or False: In the case of Bhim Singh v. State of J&K, the plaintiff was awarded damages due to wrongful detention despite no physical harm. |
|
Card: 7 / 46 |
Damno sine injuria signifies that loss without a violation of a legal right results in ___ for the plaintiff. |
|
Card: 9 / 46 |
Fill in the blank: In the Gloucester Grammar School Case, competition caused loss but there was ___ of legal right. |
|
Card: 11 / 46 |
What legal principle was upheld in Chesmore vs. Richards regarding the use of underground water? |
|
Card: 12 / 46 |
Defendants were not liable as they lawfully used underground water affecting the plaintiff’s mill. |
|
Card: 13 / 46 |
True or False: The demolition of an illegally constructed building can be deemed lawful even if done with malicious intent. |
|
Card: 15 / 46 |
Torts are classified into three main categories based on the mental element; name these categories. |
|
Card: 17 / 46 |
The defense of volenti non fit injuria cannot be invoked if the defendant breaches a duty imposed by ___ . |
|
Card: 19 / 46 |
The legal principle 'Ex turpi causa non oritur action' means that ___ cannot arise from an immoral or illegal cause. |
|
Card: 21 / 46 |
True or False: A plaintiff who is a wrongdoer is automatically prevented from recovering damages in tort. |
|
Card: 22 / 46 |
False; a plaintiff may recover if their unlawful conduct is not directly connected to the harm suffered. |
|
Card: 24 / 46 |
An event that is unintended and beyond the foreseeability or prevention by reasonable precautions, often used as a defense in negligence claims. |
|
Card: 25 / 46 |
True or False: The principle of Vis Major refers to human actions that cause accidents. |
|
Card: 26 / 46 |
False; Vis Major refers to natural events or 'Acts of God' that are unforeseeable. |
|
Card: 29 / 46 |
What distinguishes the necessity defense from an inevitable accident in tort law? |
|
Card: 30 / 46 |
In necessity, harm is intentionally caused to prevent greater harm, while in inevitable accidents, harm occurs despite efforts to prevent it. |
|
Card: 31 / 46 |
Statutory authority provides a complete defense in tort cases if the act is authorized by law, either absolutely or conditionally. True or False? |
|
Card: 33 / 46 |
An act performed under absolute authority is actionable if it results in injurious consequences. True or False? |
|
Card: 34 / 46 |
False - An act performed under absolute authority is not actionable as a tort, providing a complete defense. |
|
Card: 35 / 46 |
Conditional authority allows for acts that may lead to liability if performed with malice or negligence. Fill in the blank: Conditional authority permits acts but does not ___ them. |
|
Card: 37 / 46 |
In cases of statutory authority, what is the primary limitation on remedies available to the injured party? |
|
Card: 38 / 46 |
The injured party can seek compensation only as outlined in the statute, with no additional remedies. |
|
Card: 39 / 46 |
What type of statutory authority is described as mandated by statute despite injurious consequences? |
|
Card: 43 / 46 |
True or False: The subjective theory of negligence views negligence as a breach of the duty to take reasonable care. |
|
Card: 46 / 46 |
It established negligence as a separate tort and defined the duty of care for manufacturers towards end consumers. |